| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 242 seats in the United States House of Representatives 122 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
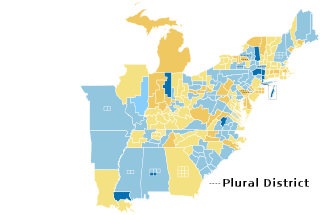 Results: Democratic hold Democratic gain Whig hold Whig gain Independent gain Independent Democrat gain | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 1840–41 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 6, 1840, and November 2, 1841. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives, before or after the first session of the 27th United States Congress convened on May 31, 1841. Elections were held for all 242 seats, representing 26 states.
In a Whig wave, voters gave the Whig Party a House majority for the first time. Most Americans experienced the Panic of 1837 as a severe economic downturn. Its perceived mishandling by Democratic President Martin Van Buren fueled new support for alternative economic policies favored by Whigs of which voters had previously been skeptical. Collapse of the Anti-Masonic Party in the late 1830s also drove some third-party incumbents into the Whig Party. Newly elected members included Robert M. T. Hunter, Independent of Virginia,[1][2][3] and Zadok Casey, Independent Democrat of Illinois.[4][5]
Election summaries
| 98 | 2 | 142 |
| Democratic | [b] | Whig |
| State | Type | Date | Total seats |
Democratic | Whig | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seats | Change | Seats | Change | ||||
| Louisiana | Districts | July 6–8, 1840 | 3 | 1 | 2 | ||
| Missouri | At-large | August 3, 1840 | 2 | 2 | 0 | ||
| Illinois | Districts | August 7, 1840 | 3 | 2[c] | 1 | ||
| Vermont | Districts | September 4, 1840 | 5 | 0 | 5 | ||
| Maine | Districts | September 14, 1840 | 8 | 4 | 4 | ||
| Arkansas | At-large | October 5, 1840 | 1 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Georgia | At-large | October 6, 1840 | 9 | 0 | 9 | ||
| South Carolina | Districts | October 12–13, 1840 | 9 | 8 | 1 | ||
| Ohio | Districts | October 13, 1840 | 19 | 7 | 12 | ||
| Pennsylvania | District (25[d]) | October 13, 1840 | 28 | 15 | 13 | ||
| New York | District (33[e]) | November 2–4, 1840 | 40 | 21 | 19 | ||
| Connecticut | Districts | November 3, 1840 | 6 | 0 | 6 | ||
| Michigan | At-large | November 3, 1840 | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| New Jersey | At-large | November 3, 1840 | 6 | 0 | 6 | ||
| Massachusetts | Districts | November 9, 1840 | 12 | 1 | 11 | ||
| Delaware | At-large | November 10, 1840 | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| 1841 elections | |||||||
| New Hampshire | At-large | March 9, 1841 | 5 | 5 | 0 | ||
| Rhode Island | At-large | April 21, 1841 | 2 | 0 | 2 | ||
| Virginia[f] | Districts | April 23, 1841 | 21[f] | 10 | 10 | ||
| Kentucky | Districts | April 26, 1841 | 13 | 2 | 11 | ||
| Indiana | Districts | May 3, 1841 | 7 | 1 | 6 | ||
| Tennessee | Districts | May 6, 1841 | 13 | 5 | 8 | ||
| North Carolina | Districts | May 13, 1841 | 13 | 5 | 8 | ||
| Maryland | District (7[g]) | May 17, 1841 | 8 | 2 | 6 | ||
| Alabama | At-large[h] | May 20, 1841 | 5 | 5 | 0 | ||
| Mississippi | At-large | November 1–2, 1841 | 2 | 2 | 0 | ||
| Total | 242 | 99[c] 40.9% |
142 59.5% |
||||
The previous election had two minor parties, the Anti-Masonic Party with 6 seats and the Conservative Party (of Virginia) with 2 seats, both of which disappeared in this election.
The 1st session of the 27th Congress began May 31, 1841, before Mississippi had elected Representatives, leaving that State unrepresented until the 2nd session.
Special elections
26th Congress
- Connecticut's 2nd congressional district: 1840
- ▌Georgia's at-large congressional district: January 1841 (one of the at-large seat)
- Indiana's 7th congressional district: 1840
- Massachusetts's 6th congressional district: 1840
- Ohio's 4th congressional district: 1840
- Pennsylvania's 22nd congressional district: 1840
- Pennsylvania's 13th congressional district: 1840
27th Congress
- Maine's 4th congressional district: 1841
- Massachusetts's 5th congressional district: 1841
- Pennsylvania's 2nd congressional district: 1841
- Pennsylvania's 13th congressional district: 1841
- Pennsylvania's 18th congressional district: 1841
- ▌Pennsylvania's 18th congressional district (again): 1841
- Pennsylvania's 20th congressional district: 1841
| District | Incumbent | This race | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Member | Party | First elected | Results | Candidates | |
| New York 26 | Francis Granger | Whig | 1838 | Incumbent resigned March 5, 1841 to become U.S. Postmaster General. New member elected May 13, 1841. Whig hold. Successor seated May 21, 1841. |
|
| New York 26 | John Greig | Whig | 1841 (Special) | Incumbent resigned September 25, 1841. New member elected November 3, 1841. Whig hold. Successor seated November 27, 1841. |
|
| Georgia at-large (Three of the at-large seats) |
William C. Dawson | Whig | 1836 (Special) | Incumbent resigned November 13, 1841 to run for Governor of Georgia. New member elected December 21, 1841. Democratic gain. |
Elected on a general ticket:
|
| Eugenius A. Nisbet | Whig | 1838 | Incumbent resigned October 12, 1841. New member elected December 21, 1841. Democratic gain. | ||
| Julius Caesar Alford | Whig | 1838 | Incumbent resigned October 1, 1841. New member elected December 21, 1841. Democratic gain. | ||
Alabama
Arkansas
| District | Incumbent | This race | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Member | Party | First elected | Results | Candidates | |
| Arkansas at-large | Edward Cross | Democratic | 1838 | Incumbent reelected. |
|
Connecticut
Delaware
Florida Territory
See Non-voting delegates, below.
Georgia
Illinois
Indiana
Iowa Territory
See Non-voting delegates, below.
Kentucky
Louisiana
Maine
Maine elected its members September 14, 1840.
| District | Incumbent | This race | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Member | Party | First elected | Results | Candidates | |
| Maine 1 | |||||
| Maine 2 | |||||
| Maine 3 | |||||
| Maine 4 | |||||
| Maine 5 | |||||
| Maine 6 | |||||
| Maine 7 | |||||
| Maine 8 | Thomas Davee | Democratic | 1836 | Incumbent retired. New member elected. Whig gain. |
|
Maryland
Massachusetts
Massachusetts held its elections November 9, 1840, but one district went to a second ballot on January 4, 1841.
| District | Incumbent | This race | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Member | Party | First elected | Results | Candidates | |
| Massachusetts 1 | |||||
| Massachusetts 2 | |||||
| Massachusetts 3 | |||||
| Massachusetts 4 | William Parmenter | Democratic | 1836 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Massachusetts 5 | |||||
| Massachusetts 6 | |||||
| Massachusetts 7 | |||||
| Massachusetts 8 | |||||
| Massachusetts 9 | |||||
| Massachusetts 10 | Henry Williams | Democratic | 1838 | Incumbent lost re-election. New member elected on the second ballot. Whig gain. |
First ballot (November 9, 1840):
Second ballot (January 4, 1841):
|
| Massachusetts 11 | |||||
| Massachusetts 12 | John Quincy Adams | Whig | 1830 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
Mississippi
Elections held late, from November 1 to 2, 1841.
| District | Incumbent | This race | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Member | Party | First elected | Results | Candidates | |
| Mississippi at-large (2 seats) |
Jacob Thompson | Democratic | 1839 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Albert G. Brown | Democratic | 1839 | Incumbent retired. New member elected. Democratic hold. | ||
Michigan
| District | Incumbent | This race | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Member | Party | First elected | Results | Candidates | |
| Michigan at-large | Isaac E. Crary | Democratic | 1835 | Incumbent retired. New member elected. Whig gain. |
|
Missouri
New Hampshire
New Jersey
North Carolina
New York
Ohio
Pennsylvania
Rhode Island
South Carolina
Tennessee
Elections held late, on May 6, 1841.
| District | Incumbent | This race | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Member | Party | First elected | Results | Candidates | |
| Tennessee 1 | William B. Carter | Whig | 1835 | Incumbent retired. New member elected. Whig hold. |
|
| Tennessee 2 | Abraham McClellan | Democratic | 1837 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Tennessee 3 | Joseph L. Williams | Whig | 1837 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Tennessee 4 | Julius W. Blackwell | Democratic | 1839 | Incumbent lost re-election. New member elected. Whig gain. |
|
| Tennessee 5 | Hopkins L. Turney | Democratic | 1837 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Tennessee 6 | William B. Campbell | Whig | 1837 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Tennessee 7 | John Bell | Whig | 1827 | Incumbent retired to become Secretary of War. New member elected. Whig hold. |
|
| Tennessee 8 | Meredith P. Gentry | Whig | 1839 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Tennessee 9 | Harvey M. Watterson | Democratic | 1839 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Tennessee 10 | Aaron V. Brown | Democratic | 1839 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Tennessee 11 | Cave Johnson | Democratic | 1839 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Tennessee 12 | John W. Crockett | Whig | 1837 | Incumbent retired to become Attorney General for the 9th district. New member elected. Whig hold. |
|
| Tennessee 13 | Kit Williams | Whig | 1837 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
Vermont
Virginia
Wisconsin Territory
See Non-voting delegates, below.
Non-voting delegates
26th Congress
| District | Incumbent | This race | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Member | Party | First elected | Results | Candidates | |
| Iowa Territory at-large | William W. Chapman | Democratic | 1838 | Incumbent's term expired by law. New delegate elected in 1840. Democratic hold. |
|
27th Congress
| District | Incumbent | This race | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Member | Party | First elected | Results | Candidates | |
| Florida Territory at-large | Charles Downing | Democratic | 1836 | Incumbent re-elected on an unknown date. |
|
| Iowa Territory at-large | Augustus C. Dodge | Democratic | 1840 | Incumbent re-elected August 6, 1841. |
|
| Wisconsin Territory at-large | James D. Doty | Democratic | 1838 | Incumbent re-elected on an unknown date. |
|
See also
Notes
- ^ Includes one Independent from Virginia, and one Independent Democrat from Illinois.
- ^ There was 1 Independent and 1 Independent Democrat.
- ^ a b Including one Independent Democrat elected to Illinois's 2nd congressional district.
- ^ Includes 3 plural districts
- ^ Includes 5 plural districts
- ^ a b Robert M. T. Hunter was elected as an Independent in Virginia's 9th congressional district, and so is not included in the figures here. Hunter had previously run in earlier elections as a Whig.
- ^ Includes 1 plural district
- ^ Changed from district
References
- ^ Dubin 1998, p. 129.
- ^ Martis 1989, p. 98.
- ^ CQGuide, p. 974.
- ^ Dubin 1998, p. 128.
- ^ Martis 1989, p. 96.
- ^ "Our Campaigns - NY District 26 - Special Election Race - May 11, 1841". OurCampaigns.com.
- ^ "Our Campaigns - NY District 26 - Special Election Race - Nov 01, 1841". OurCampaigns.com.
- ^ "Our Campaigns - GA At-Large - Special Election Race - Dec 21, 1841". OurCampaigns.com. Retrieved December 18, 2020.
- ^ Guide to U.S. Elections. Vol. II (6th ed.). Washington, D.C.: CQ Press. 2010. p. 996. ISBN 9781604265361. LCCN 2009033938. OCLC 430736650.
- ^ "Our Campaigns - ME District 8 Race - Sep 14, 1840".
- ^ "Our Campaigns - MA District 4 Race - Nov 09, 1840". www.ourcampaigns.com.
- ^ "Our Campaigns - MA District 10 - 1st Trial Race - Nov 09, 1840". www.ourcampaigns.com. Retrieved October 9, 2020.
- ^ "Our Campaigns - MA District 10 - 2nd Trial Race - Jan 04, 1841". www.ourcampaigns.com. Retrieved October 9, 2020.
- ^ "Our Campaigns - MA District 12 Race - Nov 09, 1840". www.ourcampaigns.com.
- ^ "MS - At Large". Our Campaigns. Retrieved March 7, 2021.
- ^ "MI - District 01 Race - Nov 03, 1840". Our Campaigns. January 11, 2010. Retrieved June 27, 2022.
- ^ "TN - District 01". Our Campaigns. Retrieved February 13, 2021.
- ^ "TN - District 02". Our Campaigns. Retrieved February 13, 2021.
- ^ "TN - District 03". Our Campaigns. Retrieved February 13, 2021.
- ^ "TN - District 04". Our Campaigns. Retrieved February 13, 2021.
- ^ "TN - District 05". Our Campaigns. Retrieved February 13, 2021.
- ^ "TN - District 06". Our Campaigns. Retrieved February 13, 2021.
- ^ "TN - District 07". Our Campaigns. Retrieved February 13, 2021.
- ^ "TN - District 08". Our Campaigns. Retrieved February 13, 2021.
- ^ "TN - District 09". Our Campaigns. Retrieved February 13, 2021.
- ^ "TN - District 10". Our Campaigns. Retrieved February 13, 2021.
- ^ "TN - District 11". Our Campaigns. Retrieved February 13, 2021.
- ^ "TN - District 12". Our Campaigns. Retrieved February 13, 2021.
- ^ "TN - District 13". Our Campaigns. Retrieved February 13, 2021.
- ^ Pelzer, Louis (1908). Shambaugh, Benjamin F. (ed.). "The Early Democratic Party of Iowa". Iowa Journal of History and Politics. 6 (1). Iowa City, Iowa: State Historical Society of Iowa: 15. hdl:2027/uc1.31210017304112. Retrieved December 18, 2020.
- ^ Pelzer, Louis (1908). Shambaugh, Benjamin F. (ed.). "The Early Democratic Party of Iowa". Iowa Journal of History and Politics. 6 (1). Iowa City, Iowa: State Historical Society of Iowa: 16. hdl:2027/uc1.31210017304112. Retrieved December 18, 2020.
Bibliography
- Dubin, Michael J. (March 1, 1998). United States Congressional Elections, 1788-1997: The Official Results of the Elections of the 1st Through 105th Congresses. McFarland and Company. ISBN 978-0786402830.
- Martis, Kenneth C. (January 1, 1989). The Historical Atlas of Political Parties in the United States Congress, 1789-1989. Macmillan Publishing Company. ISBN 978-0029201701.
- Moore, John L., ed. (1994). Congressional Quarterly's Guide to U.S. Elections (Third ed.). Congressional Quarterly Inc. ISBN 978-0871879967.
- "Party Divisions of the House of Representatives* 1789–Present". Office of the Historian, House of United States House of Representatives. Retrieved January 21, 2015.
External links
- Office of the Historian (Office of Art & Archives, Office of the Clerk, U.S. House of Representatives)


