| Boyland–Sims oxidation | |
|---|---|
| Named after | Eric Boyland Peter Sims |
| Reaction type | Organic redox reaction |
| Identifiers | |
| RSC ontology ID | RXNO:0000181 |
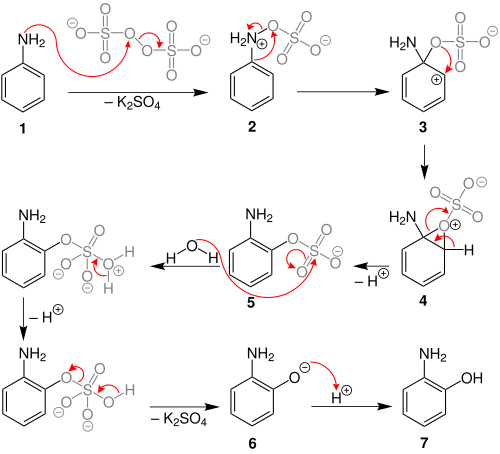
The Boyland–Sims oxidation is the chemical reaction of anilines with alkaline potassium persulfate, which after hydrolysis forms ortho-hydroxyl anilines.[1][2][3] The reaction is generally performed in water at room temperatures or below, using equimolar quantities of reagents.

The ortho-isomer is formed predominantly. However, the para-sulfate is formed in small amounts with certain anilines.[4]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/2Views:787594
-
1000 name reaction
-
Easy Explanation of Named Reactions (Part-10) | Organic Chemistry | Target IIT-JAM 2021
Transcription
Scope and mechanism
The reaction is disadvantaged by moderate to low chemical yields, but is simple to perform and uses mild conditions. Some competitive oxidation of the nitrogen has been observed.[3]
Behrman has shown that the first intermediate in the Boyland–Sims oxidation is the formation of an arylhydroxylamine-O-sulfate (2).[5] Rearrangement of this zwitterionic intermediate forms the ortho- sulfate (5), which then hydrolyses to form the ortho-hydroxyl aniline.
See also
References
- ^ Boyland, E.; Manson, D.; Sims, Peter (1953). "729. The preparation of o-aminophenyl sulphates". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed): 3623. doi:10.1039/jr9530003623.
- ^ Boyland, E.; Sims, Peter (1954). "The oxidation of some aromatic amines with persulphate". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed): 980. doi:10.1039/jr9540000980.
- ^ a b Behrman, E. J. (1988). "The Persulfate Oxidation of Phenols and Arylamines (The Elbs and the Boyland-Sims Oxidations)". Org. React. 35: 421–511. doi:10.1002/0471264180.or035.02. ISBN 0471264180.
- ^ Boyland, E.; Sims, P.; Williams, D. C. (1956). "The oxidation of tryptophan and some related compounds with persulphate". Biochem. J. 62 (4): 546–50. doi:10.1042/bj0620546. PMC 1215958. PMID 13315210.
- ^ Behrman, E. J. (1992). "The ortho-para ratio and the intermediate in the persulfate oxidation of aromatic amines (the Boyland-Sims oxidation)". J. Org. Chem. 57 (8): 2266–2270. doi:10.1021/jo00034a016.
Further reading
- Behrman, Edward J. (2014). "On the Mechanism of the Boyland-Sims Oxidation". Progress in Reaction Kinetics and Mechanism. Science Reviews 2000 Ltd. 39 (3): 308–310. doi:10.3184/146867814X14062204626705. S2CID 101779652. Archived from the original on 2016-07-16. Retrieved 2015-11-06.
