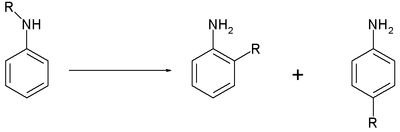
The Hofmann–Martius rearrangement in organic chemistry is a rearrangement reaction converting an N-alkylated aniline to the corresponding ortho and / or para aryl-alkylated aniline. The reaction requires heat, and the catalyst is an acid like hydrochloric acid.[1][2]
When the catalyst is a metal halide the reaction is also called the Reilly–Hickinbottom rearrangement.[3]
The reaction is also known to work for aryl ethers and two conceptually related reactions are the Fries rearrangement and the Fischer–Hepp rearrangement. Its reaction mechanism centers around dissociation of the reactant with the positively charged organic residue R attacking the aniline ring in a Friedel–Crafts alkylation.
In one study this rearrangement was applied to a 3-N(CH3)(C6H5)-2-oxindole:[4][5]
The reaction is named after German chemists August Wilhelm von Hofmann and Carl Alexander von Martius.
See also
- Friedel–Crafts alkylation-like reactions:
References
- ^ Hofmann, A. W.; Martius, C. A. (1871). "Methylirung der Phenylgruppe im Anilin". Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft. 4 (2): 742. doi:10.1002/cber.18710040271.
- ^ Hofmann, A. W. (1872). "Umwandlung des Anilins in Toluidin". Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft. 5 (2): 720–722. doi:10.1002/cber.18720050241.
- ^ Reilly, J.; Hickinbottom, W. J. (1920). "XV.—Intramolecular rearrangement of the alkylarylamines: Formation of 4-amino-n-butylbenzene". J. Chem. Soc. 117: 103–137. doi:10.1039/ct9201700103.
- ^ Magnus, Philip; Turnbull, Rachel (2006). "Thermal and Acid-Catalyzed Hofmann–Martius Rearrangement of 3-N-Aryl-2-oxindoles into 3-(Arylamino)-2-oxindoles". Organic Letters. 8 (16): 3497–9. doi:10.1021/ol061191z. PMID 16869644.
- ^ heating 1 in toluene at 80 °C gives 30% 2-o (ortho) and 37% 2-p (para)