In organic chemistry, a homologation reaction, also known as homologization, is any chemical reaction that converts the reactant into the next member of the homologous series. A homologous series is a group of compounds that differ by a constant unit, generally a methylene (−CH2−) group. The reactants undergo a homologation when the number of a repeated structural unit in the molecules is increased. The most common homologation reactions increase the number of methylene (−CH2−) units in saturated chain within the molecule.[1] For example, the reaction of aldehydes or ketones with diazomethane or methoxymethylenetriphenylphosphine to give the next homologue in the series.
Examples of homologation reactions include:
- Kiliani-Fischer synthesis, where an aldose molecule is elongated through a three-step process consisting of:
- Nucleophillic addition of cyanide to the carbonyl to form a cyanohydrin
- Hydrolysis to form a lactone
- Reduction to form the homologous aldose
- Wittig reaction of an aldehyde with methoxymethylenetriphenylphosphine, which produces a homologous aldehyde.
- Arndt–Eistert reaction is a series of chemical reactions designed to convert a carboxylic acid to a higher carboxylic acid homologue (i.e. contains one additional carbon atom)
- Kowalski ester homologation, an alternative to the Arndt-Eistert synthesis. Has been used to convert β-amino esters from α-amino esters through an ynolate intermediate.[2]
- Seyferth–Gilbert homologation in which an aldehyde is converted to a terminal alkyne and then hydrolyzed back to an aldehyde.
Some reactions increase the chain length by more than one unit. For example, the DeMayo reaction can be considered a two-carbon homologation reaction.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:14 0415 3073 539
-
The Arndt-Eistert Reaction: Reaction mechanism chemistry tutorial.
-
3 Carboxylic Acid & its derivatives Arndt eistert, Curtius, HVZ, Hoffmann reaction
-
Arndt Eistert Synthesis
Transcription
Chain reduction
Likewise the chain length can also be reduced:
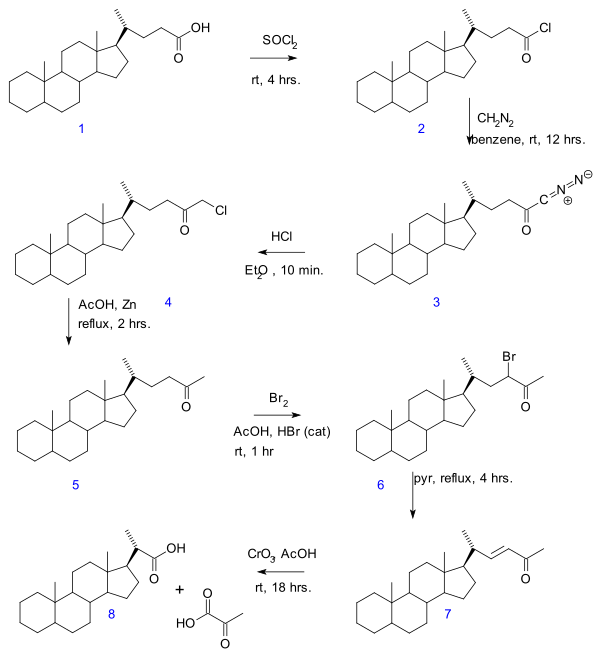
- In the Gallagher–Hollander degradation (1946) pyruvic acid is removed from a linear aliphatic carboxylic acid yielding a new acid with 2 carbon atoms less.[3] The original publication concerns the conversion of bile acid in a series of reactions: acid chloride (2) formation with thionyl chloride, diazoketone formation (3) with diazomethane, chloromethyl ketone formation (4) with hydrochloric acid, organic reduction of chlorine to methylketone (5), ketone halogenation to 6, elimination reaction with pyridine to enone 7 and finally oxidation with chromium trioxide to bisnorcholanic acid 8.
- In the Hooker reaction (1936) an alkyl chain in a certain naphthoquinone (phenomenon first observed in the compound lapachol) is reduced by one methylene unit as carbon dioxide in each potassium permanganate oxidation.[4][5]

- Mechanistically oxidation causes ring-cleavage at the alkene group, extrusion of carbon dioxide in decarboxylation with subsequent ring-closure.
See also
References
- ^ Encyclopedia of Inorganic Chemistry doi:10.1002/0470862106.id396
- ^ D. Gray, C. Concellon and T. Gallagher (2004). "Kowalski Ester Homologation. Application to the Synthesis of β-Amino Esters". J. Org. Chem. 69 (14): 4849–4851. doi:10.1021/jo049562h. PMID 15230615.
- ^ Vincent P. Hollander and T. F. Gallagher PARTIAL SYNTHESIS OF COMPOUNDS RELATED TO ADRENAL CORTICAL HORMONES. VII. DEGRADATION OF THE SIDE CHAIN OF CHOLANIC ACID J. Biol. Chem., Mar 1946; 162: 549 - 554 Link
- ^ On the Oxidation of 2-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone Derivatives with Alkaline Potassium Permanganate Samuel C. Hooker J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1936; 58(7); 1174-1179. doi:10.1021/ja01298a030
- ^ On the Oxidation of 2-Hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone Derivatives with Alkaline Potassium Permanganate. Part II. Compounds with Unsaturated Side Chains Samuel C. Hooker and Al Steyermark J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1936; 58(7); pp 1179 - 1181; doi:10.1021/ja01298a031