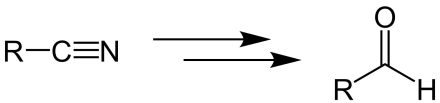
Stephen aldehyde synthesis, a named reaction in chemistry, was invented by Henry Stephen (OBE/MBE). This reaction involves the preparation of aldehydes (R-CHO) from nitriles (R-CN) using tin(II) chloride (SnCl2), hydrochloric acid (HCl) and quenching the resulting iminium salt ([R-CH=NH2]+Cl−) with water (H2O).[1][2] During the synthesis, ammonium chloride is also produced.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:9 16216 8896 517
-
Aldehydes and ketones preparation -10- Special Methods of Preparation
-
Important reactions of aromatic compounds- IITJEE chemistry
-
SUPER TRICK FOR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY REACTIONS | STEPHENS REACTION | HINDI
Transcription
Mechanism
The following scheme shows the reaction mechanism:

By addition of hydrogen chloride the used nitrile (1) reacts to its corresponding salt (2). It is believed that this salt is reduced by a single electron transfer by the tin(II) chloride (3a and 3b).[3] The resulting salt (4) precipitates after some time as aldimine tin chloride (5). Hydrolysis of 5 produces a hemiaminal (6) from which an aldehyde (7) is formed.
Substitutes that increase the electron density promote the formation of the aldimine-tin chloride adduct. With electron withdrawing substituents, the formation of an amide chloride is facilitated.[4] In the past, the reaction was carried out by precipitating the aldimine-tin chloride, washing it with ether and then hydrolyzing it. However, it has been found that this step is unnecessary and the aldimine tin chloride can be hydrolysed directly in the solution.[5]
This reaction is more efficient when aromatic nitriles are used instead of aliphatic ones. However, even for some aromatic nitriles (e. g. 2-cyanobenzoic acid ethyl ester) the yield can be low.[5]
Sonn-Müller method
In the Sonn-Müller method[6][7] the intermediate iminium salt is obtained from reaction of an amide PhCONHPh with phosphorus pentachloride.
See also
- Amide reduction
- Nitrile reduction
- Pinner reaction – a similar reaction using alcohols or amines as the nucleophile and without the reduction; generated esters, carboximidates or orthoesters.
References
- ^ Williams, Jonathan W. (1943). "β-Naphthaldehyde". Organic Syntheses. 23: 63. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.023.0063.
- ^ Stephen, Henry. (1925). "A new synthesis of aldehydes". J. Chem. Soc., Trans. 127: 1874–1877. doi:10.1039/CT9252701874.
- ^ Wang, Zerong (2009). Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents, 3 Volume Set. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, New Jersey. pp. 2659–2660. ISBN 978-0-471-70450-8.
- ^ Rabinovitz, Mordecai (1970). "Chapter 7. Reduction of the cyano group". In Rappoport, Zvi (ed.). The Cyano group (1970). PATAI'S Chemistry of Functional Groups. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., Chichester, UK. p. 308. doi:10.1002/9780470771242.ch7. ISBN 978-0-470-77124-2.
- ^ a b Wang, Zerong (2009). Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents, 3 Volume Set. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, New Jersey. pp. 2659–2660. ISBN 978-0-471-70450-8.
- ^ Adolf, Sonn; Müller, Ernst (1919). "Über eine neue Methode zur Umwandlung von Carbonsäuren in Aldehyde" [About a new method for converting carboxylic acids into aldehydes]. Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft (A and B Series). 52 (10): 1927–1934. doi:10.1002/cber.19190521002.
- ^ Williams, Jonathan W.; Witten, Charles H.; Krynitsky, John A. (1946). "o-Tolualdehyde". Organic Syntheses. 26: 97. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.026.0097.
