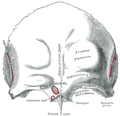
The zygomatic processes (aka. malar) are three processes (protrusions) from other bones of the skull which each articulate with the zygomatic bone. The three processes are:[1]
- Zygomatic process of frontal bone from the frontal bone
- Zygomatic process of maxilla from the maxilla
- Zygomatic process of temporal bone from the temporal bone
The term zygomatic derives from the Greek Ζυγόμα, zygoma, meaning "yoke". The zygomatic process is occasionally referred to as the zygoma, but this term usually refers to the zygomatic bone or occasionally the zygomatic arch.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:7 2492 2976 491
-
Frontal, maxilla, and zygomatic bones
-
Zygomatic arch
-
Apófisis cigomática y hueso malar. Zygomatic Process and Zygomatic Bone
Transcription
Zygomatic process of frontal bone
| Zygomatic process of frontal bone | |
|---|---|
 Frontal bone at birth (Zygomatic process visible at lower right) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | processus zygomaticus ossis frontalis |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The supraorbital margin of the frontal bone ends laterally in its zygomatic process, which is strong and prominent, and articulates with the zygomatic bone. The zygomatic process of the frontal bone extends from the frontal bone laterally and inferiorly.
Zygomatic process of maxilla
| Zygomatic process of maxilla | |
|---|---|
 Zygomatic process shown in red | |
 Left zygomatic bone in situ (Zygomatic process of maxilla is shown in yellow.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | processus zygomaticus maxillae |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The zygomatic process of the maxilla[2] is a rough triangular eminence, situated at the angle of separation of the anterior, zygomatic, and orbital surfaces.
- In front it forms part of the anterior surface.
- Behind it is concave, and forms part of the infratemporal fossa.
- Above it is rough and serrated for articulation with the zygomatic bone.
- Below it presents the prominent arched border which marks the division between the anterior and infratemporal surfaces.
Zygomatic process of temporal bone
| Zygomatic process of temporal bone | |
|---|---|
 Zygomatic process shown in red | |
 Articulation of the mandible. Lateral aspect (Zygomatic process visible at center) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | processus zygomaticus ossis temporalis |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The zygomatic process of the temporal bone is a long, arched process projecting from the lower part of the squamous portion of the temporal bone. It articulates with the zygomatic bone.
This process is at first directed lateralward, its two surfaces looking upward and downward; it then appears as if twisted inward upon itself, and runs forward, its surfaces now looking medialward and lateralward.
The superior border is long, thin, and sharp, and serves for the attachment of the temporal fascia.
The inferior border, short, thick, and arched, has attached to it some fibers of the masseter.
The lateral surface is convex and subcutaneous. The medial surface is concave, and affords attachment to the masseter.
The anterior end is deeply serrated and articulates with the zygomatic bone. The posterior end is connected to the squama by two roots, the anterior and posterior roots:
- The posterior root, a prolongation of the upper border, is strongly marked; it runs backward above the external auditory meatus.
- The anterior root, continuous with the lower border, is short but broad and strong; it is directed medialward and ends in a rounded eminence, the articular tubercle (eminentia articularis).
Processes of the zygomatic bone
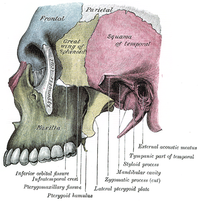
The zygomatic bone itself has four processes, namely the frontosphenoidal, orbital, maxillary and temporal processes.
The frontosphenoidal process is thick and serrated. The cranial suture between the frontal and zygomatic bone is found here. On its orbital surface, just within the orbital margin and about 11 mm below the zygomaticofrontal suture is a tubercle of varying size and form, but present in 95 per cent of skulls (Whitnall 43). This tubercle is not seen in the picture.
The orbital process is a thick, strong plate, projecting backward and medialward from the orbital margin. It is the gloomy area beneath the lac(rimal) and ethmoidal bones in the image.
The maxillary process presents a rough, triangular surface which articulates with the maxilla. It is the area below "zygomatic" in the image.
The temporal process, long, narrow, and serrated, articulates with the zygomatic process of the temporal. It is the process to the right of "zygomatic" in the image.
Additional images
-
Frontal bone: outer surface
-
Zygomatic process of frontal bone
-
Zygomatic process of maxilla
-
Zygomatic process of the temporal bone
See also
References
- ^ Marieb & Hoehn's (2010) Human Anatomy & Physiology
- ^ Google Books: zygomatic process of the maxilla: Exercises in Oral Radiology and Interpretation – E-Book (Elsevier Health Sciences, Dec 12, 2003, by Robert P. Langlais) – Retrieved 2018-08-26
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Photo – look for #6
- "Anatomy diagram: 34256.000-1". Roche Lexicon – illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2012-12-27.
- Anatomy photo:22:os-1904 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center – "Osteology of the Skull: The Maxilla"