| Styloid process (temporal) | |
|---|---|
 Right side of the skull. Styloid process shown in red | |
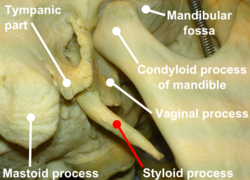 Right temporal bone and mandible (styloid process labeled at bottom) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | processus styloideus ossis temporalis |
| TA98 | A02.1.06.047 |
| TA2 | 683 |
| FMA | 52877 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The temporal styloid process is a slender bony process of the temporal bone extending downward and forward from the undersurface of the temporal bone[1] just below the ear.[citation needed] The styloid process gives attachments to several muscles, and ligaments.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/5Views:1 051185 3242 1533 8544 940
-
STYLOID PROCESS IN 10 MINUTES
-
Temporal Bone - Definition, Location & Parts - Human Anatomy | Kenhub
-
Styloid Process (Temporal, Radius, & Ulna Bone)
-
Styloid apparatus
-
Styloidectomy, excision of styloid process, eagle's syndrome
Transcription
Structure
The styloid process is a slender and pointed bony process of the temporal bone projecting anteroinferiorly from the inferior surface of the temporal bone[1] just below the ear.[citation needed] Its length normally ranges from just under 3 cm to just over 4 cm. It is usually nearly straight, but may be curved in some individuals.[1]
Its proximal (tympanohyal) part is ensheathed by the tympanic part of the temporal bone (vaginal process), whereas its distal (stylohyal) part gives attachment to several structures.[1]
Attachments
The styloid process gives attachments to several muscles, and ligaments.[1] It serves as an anchor point for several muscles associated with the tongue and larynx.[citation needed]
- stylohyoid ligament[citation needed]
- stylomandibular ligament[citation needed]
- styloglossus muscle (innervated by the hypoglossal nerve)[citation needed]
- stylohyoid muscle (innervated by the facial nerve)[citation needed]
- stylopharyngeus muscle (innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve)[citation needed]
Relations
The parotid gland is situated laterally to the styloid process, the external carotid artery passes by its apex, the facial nerve crosses its base, and the attachment of the stylopharyngeus muscle separates it from the internal jugular vein medially.[1]
Clinical significance
A small percentage of the population will suffer from an elongation of the styloid process and stylohyoid ligament calcification. This condition is also known as Eagle syndrome. The tissues in the throat rub on the styloid process during the act of swallowing with resulting pain along the glossopharyngeal nerve. There is also pain upon turning the head or extending the tongue. Other symptoms may include voice alteration, cough, dizziness, migraines, occipital neuralgia, pain in teeth and jaw and sinusitis or bloodshot eyes.[citation needed]
Development
The styloid process arises from endochondral ossification of the cartilage from the second pharyngeal arch.[citation needed]
Additional images
-
Animation. Temporal styloid process shown in red.
-
Left temporal bone.
-
Inferior surface of left temporal bone. Styloid process shown in red.
-
External and middle ear, opened from the front. Right side. (Label for styloid process is bottom center.)
-
Left temporal bone. Outer surface. (Styloid process visible at center bottom.)
-
Articulation of the mandible. Medial aspect.
-
Extrinsic muscles of the tongue. Left side.
-
Dissection of the muscles of the palate from behind.
-
Styloid process.Base of skull.
References
- ^ a b c d e f Gray's anatomy : the anatomical basis of clinical practice. Susan Standring (Forty-second ed.). [New York]. 2021. p. 737. ISBN 978-0-7020-7707-4. OCLC 1201341621.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) CS1 maint: others (link)
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 145 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 145 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Anatomy photo:22:os-0407 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- "Anatomy diagram: 25420.000-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2015-02-26.
- "Anatomy diagram: 34257.000-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2012-07-22.









