| Northwest Solomonic | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | Solomon Islands |
| Linguistic classification | Austronesian
|
| Proto-language | Proto-Northwest Solomonic |
| Glottolog | nort3225 |
The family of Northwest Solomonic languages is a branch of the Oceanic languages. It includes the Austronesian languages of Bougainville and Buka in Papua New Guinea, and of Choiseul, New Georgia, and Santa Isabel (excluding Bugotu) in Solomon Islands.
The unity of Northwest Solomonic and the number and composition of its subgroups, along with its relationship to other Oceanic groups, was established in pioneering work by Malcolm Ross.[1]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/5Views:47 528312 271541 304498 3931 567 540
-
Austronesian languages: A Family Across Oceans
-
Ancient Languages of the Middle East
-
Geography Now! SOLOMON ISLANDS!
-
How to sign the alphabet in British Sign Language (BSL) - Right handed - Signer point of view
-
THE ONLY AFRICAN COUNTRY OF MIXED RACE (BLACK-ASIAN) PEOPLE : The Malagasy.
Transcription
Languages
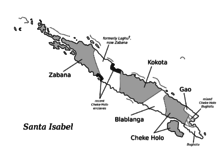
Northwest Solomonic languages group as follows:[2]
- Nehan – North Bougainville linkage
- Piva–Bannoni family: Piva (Lawunuia), Bannoni
- Mono–Uruavan family: Mono-Alu, Torau, Uruava
- Choiseul linkage: Babatana (including Sisingga)–Ririo, Vaghua–Varisi
- New Georgia – Ysabel family
- New Georgia linkage: Simbo (Simbo Island), Roviana–Kusaghe, Marovo, Hoava, Vangunu (Vangunu Island), Nduke (Kolombangara Island), Ghanongga (Ranongga Island), Lungga (Ranongga Island), Ughele (North Rendova Island)
- Ysabel linkage: Zabana (Kia)–Laghu†, Kokota–Zazao (Kilokaka)–Blablanga, Gao–Cheke Holo (Maringe, Hograno)
In addition, the extinct Kazukuru language was probably one of the New Georgia languages. The unclassified extinct language Tetepare might have also been one of the New Georgia languages, if it was Austronesian at all.
Basic vocabulary
Basic vocabulary in many Northwest Solomonic languages is aberrant, and many forms do not have Proto-Oceanic cognates.[4] Below, Ririo, Zabana, and Maringe are compared with two Southeast Solomonic languages. Aberrant forms are in bold.
English arm ear liver bone skin louse Proto-Oceanic *lima *taliŋa *qate *suRi *kulit *kutu Ririo karisi ŋgel tutuen punda kapat utu Zabana kame taliŋa kola huma kafu gutu Maringe lima khuli khebu knubra guli theli Gela lima kuli ate huli gui-guli gutu Arosi rima kariŋa rogo su-suri ʔuri-ʔuri kote
Notes
- ^ See Ross (1988).
- ^ Lynch, John; Malcolm Ross; Terry Crowley (2002). The Oceanic languages. Richmond, Surrey: Curzon. ISBN 978-0-7007-1128-4. OCLC 48929366.
- ^ distinct language per Bill Palmer
- ^ Pawley, Andrew. Explaining the Aberrant Austronesian Languages of Southeast Melanesia: 150 Years of Debate. Journal of the Polynesian Society, The, Vol. 115, No. 3, Sept 2006: 215-258.
References
- Ross, Malcolm D. (1988). Proto Oceanic and the Austronesian languages of Western Melanesia. Canberra: Pacific Linguistics.
Further reading
- Bill Palmer (2005). North West Solomonic materials. University of Surrey, UK.
- Bill Palmer (2010). [1]. University of Newcastle, Australia.
- Tryon, Darrell T. & B. D. Hackman. 1983. Solomon Islands Languages: An Internal Classification. (Pacific Linguistics: Series C, 72.) Canberra: Research School of Pacific and Asian Studies, Australian National University
- Data set derived from Tryon & Hackman (1983): Greenhill, Simon, & Robert Forkel. (2019). lexibank/tryonsolomon: Solomon Islands Languages (Version v3.0). Zenodo. doi:10.5281/zenodo.3535809
