| Pharyngeal muscles | |
|---|---|
 | |
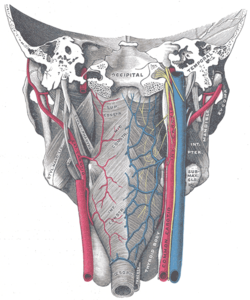 Muscles of the pharynx, viewed from behind, together with the associated vessels and nerves | |
| Details | |
| Nerve | Receives motor innervation by Vagus nerve (CN X). Stylopharyngeus receives motor innervation by Glossopharyngeal (CN IX) |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculi pharyngis, musculus constrictor pharyngis or tunica muscularis pharyngis |
| MeSH | D010609 |
| TA98 | A04.2.06.001 |
| TA2 | 2176 |
| FMA | 67169 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The pharyngeal muscles are a group of muscles that form the pharynx, which is posterior to the oral cavity, determining the shape of its lumen, and affecting its sound properties as the primary resonating cavity.
The pharyngeal muscles (involuntary skeletal) push food into the esophagus. There are two muscular layers of the pharynx: the outer circular layer and the inner longitudinal layer.
The outer circular layer includes:
During swallowing, these muscles constrict to propel a bolus downwards (an involuntary process).
The inner longitudinal layer includes:
During swallowing, these muscles act to shorten and widen the pharynx.
They are innervated by the pharyngeal branch of the vagus nerve (CN X) with the exception of the stylopharyngeus muscle which is innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX).[1]
They are primarily supplied by branches of the facial artery. Other blood supply includes the ascending pharyngeal artery, lingual artery, and ascending and descending palatine arteries.
References
- ^ Moore, KL; Dalley, AF; Agur, AMR (2018). Clinically Oriented Anatomy (8th ed.). Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer. pp. 1044–1045. ISBN 9781496347213.
