| Pretracheal fascia | |
|---|---|
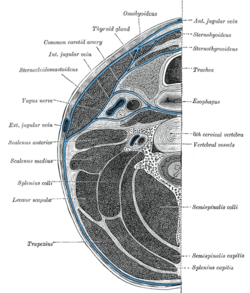 Section of the neck at about the level of the sixth cervical vertebra. Showing the arrangement of the fascia coli. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | lamina praetrachealis fasciae cervicalis |
| TA98 | A04.2.05.004 |
| TA2 | 2212 |
| FMA | 46559 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The pretracheal fascia is a layer of the deep cervical fascia at the front of the neck. It attaches to the hyoid bone above, and - extending down into the thorax - blends with the fibrous pericardium below. It encloses the thyroid gland and parathyroid glands, trachea, and esophagus.[1] It extends medially in front of the carotid vessels. It assists in forming the carotid sheath.
The back portion of the pretracheal fascia is known as the buccopharyngeal fascia.[1]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:19 7444 9151 659
-
Cervical fascia
-
Deep Cervical Fascia - 2 | Pretracheal Fascia | Prevertebral Fascia | Carotid Sheath
-
3D4 - 2.0 Neck Fascia
Transcription
Structure
The pretracheal fascia is continued behind the depressor muscles of the hyoid bone. After enveloping the thyroid gland, it is prolonged in front of the trachea to meet the corresponding layer of the opposite side. The pretracheal layer of the deep cervical fascia passes in front of the carotid sheath (i.e., common carotid artery, internal jugular vein, and vagus nerve) and in front of the cervical viscera (larynx, oesophagus, and pharynx). The muscular layer ensheathes the infrahyoid muscles.
Above, the pretracheal fascia is fixed to the hyoid bone. Below, it is carried downward in front of the trachea and large vessels at the root of the neck, and ultimately blends with the fibrous pericardium.[2]
The pretracheal fascia is fused on either side with the prevertebral fascia, and with it completes the compartment containing the larynx and trachea, the thyroid gland, and the pharynx and esophagus.[2]
Function
The pretracheal fascia encloses the thyroid gland, and is responsible for its movement during deglutition.
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 390 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 390 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ a b Morton, David A. (2019). The Big Picture: Gross Anatomy. K. Bo Foreman, Kurt H. Albertine (2nd ed.). New York. p. 266. ISBN 978-1-259-86264-9. OCLC 1044772257.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ a b Thompson, Stevan H.; Yeung, Alison Y. (2016-01-01), Hupp, James R.; Ferneini, Elie M. (eds.), "4 - Anatomy Relevant to Head, Neck, and Orofacial Infections", Head, Neck, and Orofacial Infections, St. Louis: Elsevier, pp. 60–93, doi:10.1016/b978-0-323-28945-0.00004-1, ISBN 978-0-323-28945-0, retrieved 2020-11-10
External links
- Sagittal Section Showing Deep Cervical Fascial Layers
- Infrahyoid Cross-Section Showing Layers of Deep Cervical Fascia
- "Anatomy diagram: 25420.000-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2014-01-01.
