| Claisen condensation | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Named after | Rainer Ludwig Claisen | ||||||||||||
| Reaction type | Condensation reaction | ||||||||||||
| Reaction | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Conditions | |||||||||||||
| Typical solvents | R'-OH
| ||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||
| Organic Chemistry Portal | claisen-condensation | ||||||||||||
| RSC ontology ID | RXNO:0000043 | ||||||||||||
The Claisen condensation is a carbon–carbon bond forming reaction that occurs between two esters or one ester and another carbonyl compound in the presence of a strong base. The reaction produces a β-keto ester or a β-diketone.[1] It is named after Rainer Ludwig Claisen, who first published his work on the reaction in 1887.[2][3][4] The reaction has often been displaced by diketene-based chemistry, which affords acetoacetic esters.[5]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:36 51523 36313 761
-
Claisen Condensation Reaction Mechanism - Organic Chemistry
-
Claisen Condensation Reaction Mechanism by Leah4sci
-
Claisen Condensation Product Shortcut by Leah4sci
Transcription
Requirements
At least one of the reagents must be enolizable (have an α-proton and be able to undergo deprotonation to form the enolate anion). There are a number of different combinations of enolizable and nonenolizable carbonyl compounds that form a few different types of Claisen.
The base used must not interfere with the reaction by undergoing nucleophilic substitution or addition with a carbonyl carbon. For this reason, the conjugate sodium alkoxide base of the alcohol formed (e.g. sodium ethoxide if ethanol is formed) is often used, since the alkoxide is regenerated. In mixed Claisen condensations, a non-nucleophilic base such as lithium diisopropylamide, or LDA, may be used, since only one compound is enolizable. LDA is not commonly used in the classic Claisen or Dieckmann condensations due to enolization of the electrophilic ester.
The alkoxy portion of the ester must be a relatively good leaving group. Methyl and ethyl esters, which yields methoxide and ethoxide, respectively, are commonly used.
Types
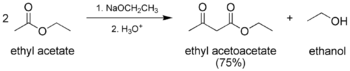
- The classic Claisen condensation, a self-condensation between two molecules of a compound containing an enolizable ester.
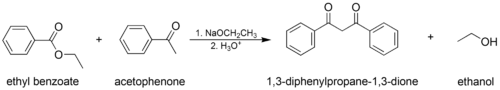
- The mixed (or "crossed") Claisen condensation, where one enolizable ester or ketone and one nonenolizable ester are used.
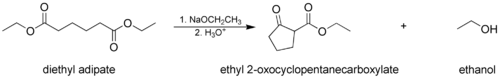
- The Dieckmann condensation, where a molecule with two ester groups reacts intramolecularly, forming a cyclic β-keto ester. In this case, the ring formed must not be strained, usually a 5- or 6-membered chain or ring.
- Retro-Claisen condensation is the reverse of the title reaction, i.e., the base-induced cleavage of 2-ketoesters
Mechanism

In the first step of the mechanism, an α-proton is removed by a strong base, resulting in the formation of an enolate anion, which is made relatively stable by the delocalization of electrons. Next, the carbonyl carbon of the (other) ester is nucleophilically attacked by the enolate anion. The alkoxy group is then eliminated (resulting in (re)generation of the alkoxide), and the alkoxide removes the newly formed doubly α-proton to form a new, highly resonance-stabilized enolate anion. Aqueous acid (e.g. sulfuric acid or phosphoric acid) is added in the final step to neutralize the enolate and any base still present. The newly formed β-keto ester or β-diketone is then isolated. Note that the reaction requires a stoichiometric amount of base as the removal of the doubly α-proton thermodynamically drives the otherwise endergonic reaction. That is, Claisen condensation does not work with substrates having only one α-hydrogen because of the driving force effect of deprotonation of the β-keto ester in the last step.

|
| animation |
See also
- Aldol condensation
- Stobbe condensation
- Fatty acid synthesis
- Polyketide synthase
- Dieckmann condensation
References
- ^ Carey, F. A. (2006). Organic Chemistry (6th ed.). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-111562-5.
- ^ Claisen, L.; Claparede, A. (1881). "Condensationen von Ketonen mit Aldehyden". Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft. 14 (2): 2460–2468. doi:10.1002/cber.188101402192.
- ^ Claisen, L. (1887). "Ueber die Einführung von Säureradicalen in Ketone". Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft. 20 (1): 655–657. doi:10.1002/cber.188702001150.
- ^ Hauser, C. R.; Hudson, B. E. Jr. (1942). "The Acetoacetic Ester Condensation and Certain Related Reactions". Organic Reactions. 1: 266–302. doi:10.1002/0471264180.or001.09. ISBN 0471264180.
- ^ Riemenschneider, Wilhelm; Bolt, Hermann M. (2005). "Esters, Organic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. doi:10.1002/14356007.a09_565.pub2. ISBN 3527306730.
External links
- "Claisen Condensation". Organic Chemistry Portal.