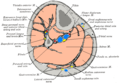
| Extensor hallucis longus muscle | |
|---|---|
 The mucous sheaths of the tendons around the ankle. Lateral aspect. (Ext. hall. long. labeled at upper left.) | |
 Animation | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Arises from the middle portion of the fibula on the anterior surface and the interosseous membrane |
| Insertion | Inserts on the dorsal side of the base of the distal phalanx of the big toe |
| Artery | Anterior tibial artery |
| Nerve | Deep fibular nerve, L5 (L4-S1) |
| Actions | Extends (raises) the big toe and assists in dorsiflexion of the foot at the ankle. Also is a weak evertor/invertor |
| Antagonist | Flexor hallucis longus, flexor hallucis brevis |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus extensor hallucis longus |
| TA98 | A04.7.02.040 |
| TA2 | 2650 |
| FMA | 22533 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The extensor hallucis longus muscle is a thin skeletal muscle, situated between the tibialis anterior and the extensor digitorum longus. It extends the big toe and dorsiflects the foot. It also assists with foot eversion and inversion.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/5Views:26 0457 0868 2758 89636 586
-
Extensor Hallucis Longus Muscle - Origin, Insertion, Innervation & Function | Kenhub
-
Functions of the extensor hallucis longus muscle (preview) - 3D Human Anatomy | Kenhub
-
Anatomy Of The Extensor Hallucis Longus Muscle - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
-
Anatomy Of The Extensor Digitorum Longus Muscle - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
-
Extensor Digitorum Longus Muscle - Origins & Function - Human Anatomy | Kenhub
Transcription
Hey, everyone. It’s Matt from Kenhub! And in this tutorial, we will discuss the anatomy and function of the extensor hallucis longus. The extensor hallucis longus or in Latin, “musculus extensor hallucis longus,” is one of three anterior muscles that function as extensors at the lower leg. They lie within the anterior compartment located at the ventrolateral region of the lower leg where they form its surface structure. Their tendons are particularly prominent on the dorsum of the foot. The extensor hallucis longus has its origin at the medial side of the fibula and interosseous membrane. It merges into a tendon above the superior extensor retinaculum as well. Its insertion is the distal phalanx of the big toe. All anterior muscles are innervated by the deep fibular nerve, also called the deep peroneal nerve. The main function of the anterior muscles of the lower leg is the dorsal extension of the upper ankle joint. In addition, the extensor hallucis longus is partly responsible for the lifting of the toes or the extension of the first, middle, and end joints. Due to the course of the tendons, the anterior muscles also contribute to the movement of the lower ankle joint. The extensor hallucis longus can provide both an inversion and eversion of the ankle joint depending on the initial situation. This video is more fun than reading a textbook, right? If you want more videos, interactive quizzes, articles, and an atlas of human anatomy, click on the “Take me to Kenhub” button. It is time to say goodbye to your old textbooks and say hello to your new anatomy learning partner, Kenhub! See you there! https://www.kenhub.com
Structure
The muscle ends as a tendon of insertion. The tendon passes through a distinct compartment in the inferior extensor retinaculum of foot. It crosses anterior tibial vessels lateromedially near the bend of the ankle.[citation needed] In the foot, its tendon is situated at along the medial side of the dorsum of the foot.[1] Opposite the metatarsophalangeal articulation, the tendon gives off a thin prolongation on either side, to cover the surface of the joint. An expansion from the medial side of the tendon is usually inserted into the base of the proximal phalanx.[citation needed]
Origin
The extensor hallucis longus muscle arises from the middle portion of[2] the anterior surface[citation needed] of the fibula and adjacent interosseous membrane of the leg.[3] Its origin is medial to the origin of the extensor digitorum longus muscle.[citation needed]
Insertion
The muscle inserts at the base of the distal phalanx of the great toe.[4]
Nerve supply
The muscle receives motor innervation from the deep fibular nerve (L5)[3] (a branch of common fibular nerve).
Relations
The anterior tibial vessels and deep fibular nerve pass between this muscle and the tibialis anterior muscle.
Variation
Occasionally united at its origin with the extensor digitorum longus.
The extensor ossis metatarsi hallucis, a small muscle, sometimes found as a slip from the extensor hallucis longus, or from the tibialis anterior, or from the extensor digitorum longus, or as a distinct muscle; it traverses the same compartment of the transverse ligament with the extensor hallucis longus.
Actions/movements
The muscle extends/dorsiflects the big toe (primary action), and dorsiflects the foot (secondary action).[3]
Additional Images
-
Cross-section through middle of leg. (Extensores longi digitorum et hallucis labeled at upper left.)
-
Dorsum of Foot. Deep dissection.
-
Dorsum of Foot. Deep dissection.
-
Ankle joint. Deep dissection. Medial view
-
Ankle joint. Deep dissection. Lateral view.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 481 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 481 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Sinnatamby, Chummy (2011). Last's Anatomy (12th ed.). p. 144. ISBN 978-0-7295-3752-0.
- ^ Sinnatamby, Chummy (2011). Last's Anatomy (12th ed.). p. 144. ISBN 978-0-7295-3752-0.
- ^ a b c Sinnatamby, Chummy (2011). Last's Anatomy (12th ed.). p. 144. ISBN 978-0-7295-3752-0.
- ^ Sinnatamby, Chummy (2011). Last's Anatomy (12th ed.). p. 144. ISBN 978-0-7295-3752-0.
External links
- Anatomy photo:15:st-0402 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The Leg: Muscles"
- University of Washington