| Hormiguero cejiamarillo | ||
|---|---|---|
 | ||
| Estado de conservación | ||
 Preocupación menor (UICN 3.1)[1] | ||
| Taxonomía | ||
| Dominio: | Eukaryota | |
| Reino: | Animalia | |
| Filo: | Chordata | |
| Subfilo: | Vertebrata | |
| Infrafilo: | Gnathostomata | |
| Superclase: | Tetrapoda | |
| Clase: | Aves | |
| Superorden: | Neognathae | |
| Orden: | Passeriformes | |
| Familia: | Thamnophilidae | |
| Subfamilia: | Thamnophilinae | |
| Tribu: | Pithyini | |
| Género: | Hypocnemis | |
| Especie: |
H. hypoxantha P.L. Sclater, 1869[2] | |
| Distribución | ||
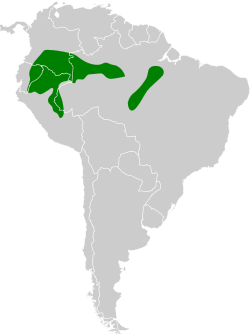 Distribución geográfica del hormiguero cejiamarillo. | ||
El hormiguero cejiamarillo[3] (en Colombia y Ecuador) (Hypocnemis hypoxantha), también denominado hormiguero de cejas amarillas o de ceja amarilla (en Perú),[4] es una especie de ave paseriforme de la familia Thamnophilidae perteneciente al género Hypocnemis. Es nativo de la región amazónica en América del Sur.
Distribución
Se distribuye desde el sureste de Colombia hasta el este de Ecuador, noreste de Perú y oeste y sureste de la Amazonia brasileña.[4]
Esta especie es consdiderada poco común y local en su hábitat natural, el sotobosque de selvas húmedas de terra firme, principalmente debajo de los 400 m de altitud.[5]
Sistemática

Descripción original
La especie H. hypoxantha fue descrita por primera vez por el ornitólogo británico Philip Lutley Sclater en 1869 bajo el mismo nombre científico; localidad tipo «alta Amazonia».[6]
Etimología
El nombre genérico femenino «Hypocnemis» proviene del griego «hupo»: de alguna forma y «knēmis o knēmidos»: armadura que protege la pierna, canillera; significando «que parece tener canilleras»;[7] y el nombre de la especie «hypoxantha», proviene del griego «hupo»: por debajo, y «xanthos»: amarillo, significando «amarillento».[8]
Taxonomía
Anteriormente era considerada especie hermana de Hypocnemis cantator, pero existe una considerable distancia genética entre ambas, lo que sugiere que la separación puede haber ocurrido algunos millones de años atrás.[6]
Subespecies
Según la clasificación del Congreso Ornitológico Internacional (IOC)[9] y Clements Checklist v.2017,[10] se reconocen dos subespecies, con su correspondiente distribución geográfica:[6]
- Hypocnemis hypoxantha hypoxantha P. L. Sclater, 1869– sur de Colombia (Putumayo hacia el este hasta Vaupés, al sur hasta Amazonas), este de Ecuador, noreste y centro este de Perú (al norte del río Marañón y este del Ucayali, hacia el sur hasta el departamento de Ucayali) y oeste de la Amazonia brasileña (norte del río Amazonas hacia el este hasta la margen occidental del río Negro, y al sur del Amazonas en las cuencas de los ríos Javari y alto Juruá).
- Hypocnemis hypoxantha ochraceiventris Chapman, 1921– sureste de la Amazonia brasileña (entre los ríos Tapajós/Teles Pires y Xingú).
Referencias
- ↑ BirdLife International (2016). «Hypocnemis hypoxantha». Lista Roja de especies amenazadas de la UICN 2017.1 (en inglés). ISSN 2307-8235. Consultado el 16 de agosto de 2017.
- ↑ Sclater, P.L. (1868). «Descriptions of some New or little known Species of Formicarians». Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London (en inglés y latín). Pt.3: 571–575. Hypocnemis hypoxantha, descripción original p.573, Ilustración pl.43. Disponible en Biodiversitas Heritage Library. ISSN 0370-2774.
- ↑ Bernis, F; De Juana, E; Del Hoyo, J; Fernández-Cruz, M; Ferrer, X; Sáez-Royuela, R; Sargatal, J (2004). «Nombres en castellano de las aves del mundo recomendados por la Sociedad Española de Ornitología (Novena parte: Orden Passeriformes, Familias Cotingidae a Motacillidae)». Ardeola. Handbook of the Birds of the World (Madrid: SEO/BirdLife) 51 (2): 491-499. ISSN 0570-7358. Consultado el 14 de marzo de 2015. P.108.
- ↑ a b Hormiguero Cejiamarillo Hypocnemis hypoxantha Sclater, PL, 1869 en Avibase. Consultada el 16 de agosto de 2017.
- ↑ Ridgely, Robert & Tudor, Guy. 2009. Hypocnemis hypoxantha, p. 362, lámina 30(10), en Field guide to the songbirds of South America: the passerines – 1.a edición – (Mildred Wyatt-World series in ornithology). University of Texas Press, Austin. ISBN 978-0-292-71748-0
- ↑ a b c Yellow-browed Antwarbler (Hypocnemis hypoxantha) en Handbook of the Birds of the World - Alive (en inglés). Consultada el 16 de agosto de 2017.
- ↑ Jobling, J. A. (2017). Hypocnemis Key to Scientific Names in Ornithology (en inglés). En: del Hoyo, J., Elliott, A., Sargatal, J., Christie, D.A. & de Juana, E. (eds.). Handbook of the Birds of the World Alive. Lynx Edicions, Barcelona. Consultado el 16 de agosto de 2017.
- ↑ Jobling, J. A. (2017) hypoxantha Key to Scientific Names in Ornithology (en inglés). En: del Hoyo, J., Elliott, A., Sargatal, J., Christie, D.A. & de Juana, E. (eds.). Handbook of the Birds of the World Alive. Lynx Edicions, Barcelona. Consultado el 16 de agosto de 2017.
- ↑ Gill, F., Donsker, D. & Rasmussen, P. (Eds.). «Antbirds». IOC – World Bird List (en inglés). Consultado el 10 de agosto de 2017. Versión 7.2. Versión/Año:
- ↑ Clements, J. F., T. S. Schulenberg, M. J. Iliff, D. Roberson, T. A. Fredericks, B. L. Sullivan & C. L. Wood (2017). The eBird/Clements checklist of Birds of the World: v2017 (Planilla Excel) (en inglés). Disponible para descarga. Ithaca, NY: Cornell Lab of Ornithology.
Enlaces externos
 Wikimedia Commons alberga una categoría multimedia sobre Hypocnemis hypoxantha.
Wikimedia Commons alberga una categoría multimedia sobre Hypocnemis hypoxantha. Wikispecies tiene un artículo sobre Hypocnemis hypoxantha.
Wikispecies tiene un artículo sobre Hypocnemis hypoxantha.- Videos, fotos y sonidos de Hypocnemis hypoxantha en The Internet Bird Collection.
- Fotos y sonidos de Hypocnemis hypoxantha en Wikiaves.
- Sonidos y mapa de distribución de Hypocnemis hypoxantha en xeno-canto.
