| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Hafnium(IV) iodide
| |
| Other names
hafnium tetraiodide, tetraiodohafnium
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.150.349 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| HfI4 | |
| Molar mass | 686.11[1] |
| Appearance | red-orange[1] |
| Density | 5.60 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | 449 °C (840 °F; 722 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 394 °C (741 °F; 667 K)[1] (sublimes) |
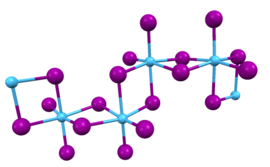
| Structure | |
| Monoclinic, mS40 | |
| C2/c, No. 15[2] | |
a = 1.1787 nm, b = 1.1801 nm, c = 1.2905 nm
| |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Hafnium(IV) fluoride Hafnium(IV) chloride Hafnium(IV) bromide |
Other cations
|
Titanium(IV) iodide Zirconium(IV) iodide |
Related compounds
|
Hafnium(III) iodide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Hafnium(IV) iodide is the inorganic compound with the formula HfI4. It is a red-orange, moisture sensitive, sublimable solid that is produced by heating a mixture of hafnium with excess iodine.[2] It is an intermediate in the crystal bar process for producing hafnium metal.
In this compound, the hafnium centers adopt octahedral coordination geometry. Like most binary metal halides, the compound is a polymeric. It is one-dimensional polymer consisting of chains of edge-shared bioctahedral Hf2I8 subunits, similar to the motif adopted by HfCl4. The nonbridging iodide ligands have shorter bonds to Hf than the bridging iodide ligands.[2]
References
- ^ a b c d e Haynes, William M., ed. (2011). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (92nd ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. p. 4.66. ISBN 1-4398-5511-0.
- ^ a b c Krebs, B.; Sinram, D. (1980). "Hafniumtetrajodid HfI4: Struktur und eigenschaften. Ein neuer AB4-strukturtyp". Journal of the Less Common Metals. 76 (1–2): 7–16. doi:10.1016/0022-5088(80)90005-3.
