| Province of Alpes Maritimae Provincia Alpes Maritimæ | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Province of the Roman Empire | |||||||
| 63 AD–476 | |||||||
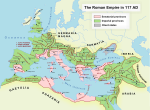
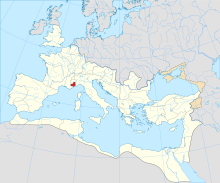 The Roman Empire c. 125 AD, with the province of Alpes Maritimae highlighted. | |||||||
| Capital | Cemenelum (63 AD – 297 AD) Ebrodunum (from 297 AD) | ||||||
| Historical era | Antiquity | ||||||
• Established by Nero | 63 AD | ||||||
• Disestablished | 476 | ||||||
| |||||||
| Today part of | France Monaco | ||||||
The Alpes Maritimae (Latin pronunciation: [ˈaɫpeːs maˈrɪtɪmae̯]; English: 'Maritime Alps') was a small province of the Roman Empire founded in 63 AD by Nero. It was one of the three provinces straddling the Alps between modern France and Italy, along with the Alpes Graiae et Poeninae and Alpes Cottiae. The Alpes Maritimae included parts of the present-day French departments of Alpes-Maritimes (in which the name survives), Alpes-de-Haute-Provence and Hautes-Alpes.[1]
The capital of the province was Cemenelum (modern Cimiez, a neighbourhood of Nice), until it was replaced by Eburodunum (modern Embrun) during the reign of Diocletian (284–305).[2]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/5Views:803902 6371 13216 80435 875
-
Scenes from the Cemenelum Site, Archeology Museum of Nice-Cimiez, France
-
The Dark Ages Explained - Part 1
-
The Austrian State of Carinthia
-
A Super Quick History of Bulgaria
-
Who was Romulus and Remus? - The Founding of Rome
Transcription
History

Following the subjugation of the local Ligurian tribes in the summer of 14 BC, the region was ruled by a praefectus civitatium, then was given Latin Rights in 63 AD and placed under the administration of a procurator. Cemenelum (modern Cimiez), the chief town of the Vediantii, became the capital of the new province.[2]
Under Diocletian (284–305), the province was extended via the incorporation of parts of Gallia Narbonensis and Alpes Cottiae, and was allocated to the praefectura Galliarum (Diocese of Vienne). The capital was transferred to Eburodunum (modern Embrun), which had been part of the Alpes Cottiae until that time.[2]
Settlements
Major settlements within the province included:
- Cemenelum (Cimiez)
- Nicaea (Nice)
- Antipolis (Antibes)
- Portus Herculis Monoeci (Monaco)
- Salinae (Castellane)
- Sanitium (Senez)
- Vintium (Vence)
After 297 the province was expanded to include:
- Ebrodunum (Embrun)
- Brigantio (Briançon)
- Brigomagus (Briançonnet)
- Civitas Rigomagensium / Rigomagus (Chorges)
References
- ^ Michael Grant, Gli imperatori romani, Roma, Newton & Compton, 1984, ISBN 88-7819-224-4.
- ^ a b c Graßl 2006.
Bibliography
- Graßl, Herbert (2006). "Alpes Maritimae". Brill's New Pauly. doi:10.1163/1574-9347_bnp_e116390.
- Morabito, Stéphane (2010). "Entre Narbonnaise et Italie : le territoire de la province des Alpes Maritimae pendant l'Antiquité romaine (I er S. av. J.-C.-V e S. apr. J.-C.)". Gallia. 67 (2): 99–124. ISSN 0016-4119. JSTOR 43608132.
44°34′21″N 6°29′37″E / 44.5724°N 6.4936°E