 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Eradacil |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.049.763 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
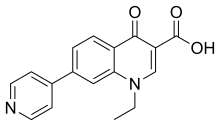
| Formula | C17H14N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 294.310 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 290 °C (554 °F) |
| |
| |
| | |
Rosoxacin (also known as acrosoxacin, tradename Eradacil) is a quinolone antibiotic indicated for the treatment of urinary tract infections and certain sexually transmitted diseases. Rosoxacin is not available in the United States.
It was developed in 1978 by George Lesher and his colleagues at Winthrop-Stearns (now part of sanofi-aventis), as an extension of the work that originally led to nalidixic acid.[1][2]
It is classified as a first generation quinolone.[3]
Synthesis

The synthesis of rosoxacin begins with a modified Hantzsch pyridine synthesis employing as component parts ammonium acetate, two equivalents of methyl propiolate, and one of 3-nitrobenzaldehyde. Oxidation of the resulting dihydropyridine (2) with nitric acid followed by saponification, decarboxylation, and reduction of the nitro group with iron and HCl acid gives aniline 3. This undergoes the classic sequence of Gould-Jacobs reaction with methoxymethylenemalonate ester to form the 4-hydroxyquinoline ring, and then alkylation with ethyl iodide and saponification of the ester to complete the synthesis of the antibacterial agent rosoxacin (4).
See also
References
- ^ Carabateas PM, Brundage RP, Gelotte KO, Gruett MD, Lorenz RR, Opalka Jr CJ, et al. (1984). "1-Ethyl-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(pyridinyl)-3-quinolinecarboxylic acids. I. Synthesis of 3- and 4-(3-aminophenyl)pyridine intermediates". Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry. 21 (6): 1849–1856. doi:10.1002/jhet.5570210654.
- ^ Carabateas PM, Brundage RP, Gelotte KO, Gruett MD, Lorenz RR, Opalka Jr CJ, et al. (1984). "1-Ethyl-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(pyridinyl)-3-quinolinecarboxylic acids. II. Synthesis". Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry. 21 (6): 1857–1863. doi:10.1002/jhet.5570210655.
- ^ Przybilla B, Georgii A, Bergner T, Ring J (1990). "Demonstration of quinolone phototoxicity in vitro". Dermatologica. 181 (2): 98–103. doi:10.1159/000247894. PMID 2173670.
- ^ US 3907808, Lescher Y, Carabateas PM, "1,4-Dihydro-4-oxo-7-pyridyl-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid derivatives", issued 23 September 1975, assigned to STWB Inc.; Chem. Abstr., 84, 43880p (1975).
