| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
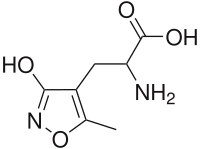
| IUPAC name
2-Amino-3-(3-hydroxy-5-methyl-isoxazol-4-yl)propanoic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| MeSH | AMPA |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H10N2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 186.167 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid, better known as AMPA, is a compound that is a specific agonist for the AMPA receptor, where it mimics the effects of the neurotransmitter glutamate.[1]
There are several types of glutamatergic ion channels in the central nervous system including AMPA, kainic acid and N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA) channels. In the synapse, these receptors serve very different purposes. AMPA can be used experimentally to distinguish the activity of one receptor from the other in order to understand their differing functions.[2] AMPA generates fast excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSP).[1] AMPA activates AMPA receptors that are non-selective cationic channels allowing the passage of Na+ and K+ and therefore have an equilibrium potential near 0 mV.
AMPA was first synthesized, along with several other ibotenic acid derivatives, by Krogsgaard-Larsen, Honoré, and others toward differentiating glutamate sensitive receptors from aspartate sensitive receptors.[3]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:5 7424 953239 304
-
AMPA Receptors Part 1
-
¿Qué es un AMPA
-
SHEIKH KISHK AMPA USIA MZITO MTOTO RAMADHAN AMBAE ANAKIPAJI CHA KUTOA DA'AWA
Transcription
See also
References
- ^ a b Purves, Dale; George J. Augustine; David Fitzpatrick; William C. Hall; Anthony-Samuel LaMantia; James O. McNamara & Leonard E. White (2008). Neuroscience (4th ed.). Sinauer Associates. pp. 128–33. ISBN 978-0-87893-697-7.
- ^ Dinh, L; Nguyen T; Salgado H; Atzori M (2009). "Norepinephrine homogeneously inhibits alpha-amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionate- (AMPAR-) mediated currents in all layers of the temporal cortex of the rat". Neurochem Res. 34 (11): 1896–906. doi:10.1007/s11064-009-9966-z. PMID 19357950. S2CID 25255160.
- ^ Krogsgaard-Larsen, P; Honore T; Hansen JJ; Curtis DR; Lodge D (1980). "New class of glutamate agonist structurally related to ibotenic acid". Nature. 284 (5751): 64–66. Bibcode:1980Natur.284...64K. doi:10.1038/284064a0. PMID 6101908. S2CID 4252428.
