| Leucoantocianina | ||
|---|---|---|
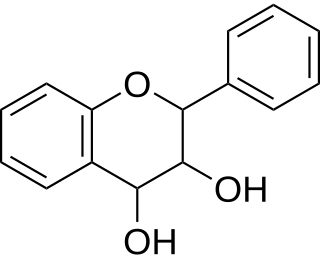 | ||
| Nombre IUPAC | ||
| 2-phenyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromene-3,4-diol | ||
| General | ||
| Otros nombres | Flavan-3,4-diol | |
| Fórmula molecular | C15H14O3 | |
| Identificadores | ||
| ChEBI | 60835 | |
| PubChem | 5318979 | |
|
C1=CC=C(C=C1)C2C(C(C3=CC=CC=C3O2)O)O
| ||
| Propiedades físicas | ||
| Masa molar | 242,26 g/mol | |
| Valores en el SI y en condiciones estándar (25 ℃ y 1 atm), salvo que se indique lo contrario. | ||
Leucoantocianina (flavan-3,4-dioles) son compuestos químicos incoloros relacionados con antocianidinas y antocianinas. Leucoantocianinas se pueden encontrar en Anadenanthera peregrina y en varias especies de Nepenthes incluyendo N. burbidgeae, N. muluensis, N. rajah, N. tentaculata, y N. × alisaputrana.[1]
Tales compuestos incluyen:
- Leucocyanidin
- leucodelfinidina
- Leucofisetinidin
- Leucomalvidin
- Leucopelargonidin
- Leucopeonidin
- leucorobinetinidin
- Melacacidin
- Teracacidin de Acacia obtusifolia y Acacia maidenii[2]
Leucoantocianidinas han demostrado ser intermedios en la biosíntesis de antocianidina en las flores de Matthiola incana.[3]
Metabolism
Leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase utiliza flavan-3 ,4-dioles para producir 3-hydroxyanthocyanidins.[4] El gen que codifica la enzima (PpLDOX) se ha identificado en el melocotón[5] y ha sido estudiado en Vitis vinifera.[6]
Referencias
- ↑ Adam, J. H., R. Omar & C. C. Wilcock 2002. Phytochemical screening of flavonoids in three hybrids of Nepenthes (Nepenthaceae) and their putative parental species from Sarawak and Sabah. OnLine Journal of Biological Sciences 2(9): 623–625. doi 10.3923/jbs.2002.623.625
- ↑ Flavan derivatives. XIX. Teracacidin and isoteracacidin from Acacia obtusifolia and Acacia maidenii heartwoods; Phenolic hydroxylation patterns of heartwood flavonoids characteristic of sections and subsections of the genus Acacia. JW Clark-Lewis and I Dainis, Australian Journal of Chemistry, 20(10), pp. 2191-2198, doi 10.1071/CH9672191
- ↑ Leucoanthocyanidins as intermediates in anthocyanidin biosynthesis in flowers of Matthiola incana R. Br. Werner Heller, Lothar Britsch, Gert Forkmann and Hans Grisebach, 1984
- ↑ «leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase on mondofacto.com». Archivado desde el original el 4 de marzo de 2012. Consultado el 6 de abril de 2014.
- ↑ Leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase gene (PpLDOX): a potential functional marker for cold storage browning in peach, E. A. Ogundiwin, C. P. Peace, C. M. Nicolet, V. K. Rashbrook, T. M. Gradziel, F. A. Bliss, D. Parfitt and C. H. Crisosto, 2008
- ↑ Regulation of the leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase gene expression in Vitis vinifera, Gollop R; Farhi S.; Perl A. 2001
