| Ácido aminometilfosfónico | ||
|---|---|---|
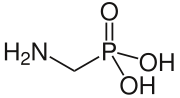 | ||
| Nombre IUPAC | ||
| Ácido (aminometil)fosfónico | ||
| General | ||
| Otros nombres | AMPA | |
| Fórmula semidesarrollada | H2NCH2P(O)(OH)2 | |
| Fórmula molecular | CH6NO3P | |
| Identificadores | ||
| Número CAS | 1066-51-9[1] | |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL41873 | |
| KEGG | C11033 | |
| Propiedades físicas | ||
| Masa molar | 11 104 g/mol | |
| Punto de fusión | 120 °C (393 K) | |
| Propiedades químicas | ||
| Acidez | 0,4 pKa | |
| Valores en el SI y en condiciones estándar (25 ℃ y 1 atm), salvo que se indique lo contrario. | ||
El aminofosfonato ácido aminometilfosfónico (AMPA) es un ácido orgánico débil con un grupo fosfonato. Es uno de los principales productos de degradación del herbicida glifosato.[2] El AMPA tiene baja toxicidad, que es comparable a la del glifosato.[3] Se ha encontrado que puede ser descompuesto de manera natural en el suelo[4] o transformado en ácido fosfórico mediante la acción bacteriana[5][6] y finalmente a dióxido de carbono y fosfato inorgánico.[7]
Referencias
- ↑ Número CAS
- ↑ Environmental Fate of Glyphosate Archivado el 20 de abril de 2012 en Wayback Machine., Jeff Schuette, Department of Pesticide Regulation, California
- ↑ Pesticide Residues in Food - 1997, FAO Panel of Experts on Pesticide Residues in Food and the Environment and the WHO Core Assessment Group
- ↑ K. A. Barrett and M. B. McBride. Oxidative Degradation of Glyphosate and Aminomethylphosphonate by Manganese Oxide. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2005, 39 (23), pp 9223–9228
- ↑ Pipke R, Amrhein N. (1988) Isolation and characterization of a mutant of Arthrobacter sp. strain GLP-1 which utilizes the herbicide glyphosate as its sole source of phosphorus and nitrogen. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 54(11): 2868-2870.
- ↑ Forlani G, Mangiagalli A, Nielsen E, Suardi CM. (1999) Degradation of the phosphonate herbicide glyphosate in soil: Evidence for a possible involvement of unculturable microorganisms. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 31: 991-997
- ↑ Backgrounder: Glyphosate does not degrade to phosphorous acid in the environment. Monsanto. 2005
