| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Ytterbium difluoride
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| F2Yb | |
| Molar mass | 211.042 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | gray crystals |
| Density | g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 1,407 °C (2,565 °F; 1,680 K) |
| Boiling point | 2,380 °C (4,320 °F; 2,650 K) |
| insoluble | |
| Structure[1] | |
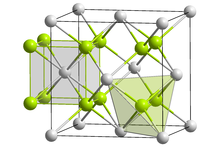
| Fluorite structure | |
| Fm3m (No. 225) | |
a = 559.93 pm
| |
Formula units (Z)
|
4 |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Ytterbium(II) chloride Ytterbium(II) iodide |
Other cations
|
Samarium(II) fluoride Europium(II) fluoride Thulium(II) fluoride |
Related compounds
|
Ytterbium(III) fluoride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Ytterbium(II) fluoride is a binary inorganic compound of ytterbium and fluorine with the chemical formula YbF2.[2][3][4]
Synthesis
Ytterbium(II) fluoride can be obtained by reacting ytterbium(III) fluoride with ytterbium or hydrogen.
- 2YbF3 + Yb → 3YbF2
- 2YbF3 + H2 → 2YbF2 + 2HF
Physical properties
Ytterbium(II) fluoride is a gray solid and crystallizes in the so-called fluorite type analogous to calcium fluoride with a unit cell a axis of 559.46 pm. In the crystal structure of ytterbium(II) fluoride, the Yb2+ cation is surrounded by eight F− anions in the form of a cube, which is tetrahedrally surrounded by four Yb2+.[5]
References
- ^ Greis, Ortwin; Haschke, John M. (1982). "Chapter 45 Rare earth fluorides". Handbook on the Physics and Chemistry of Rare Earths Volume 5. Vol. 5. Elsevier. pp. 387–460. doi:10.1016/s0168-1273(82)05008-9. ISBN 9780444863751. ISSN 0168-1273.
- ^ Meyer, G.; Morss, L. R. (6 December 2012). Synthesis of Lanthanide and Actinide Compounds. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 57. ISBN 978-94-011-3758-4. Retrieved 5 April 2023.
- ^ Yaws, Carl (6 January 2015). The Yaws Handbook of Physical Properties for Hydrocarbons and Chemicals: Physical Properties for More Than 54,000 Organic and Inorganic Chemical Compounds, Coverage for C1 to C100 Organics and Ac to Zr Inorganics. Gulf Professional Publishing. p. 807. ISBN 978-0-12-801146-1. Retrieved 5 April 2023.
- ^ Macintyre, Jane E. (23 July 1992). Dictionary of Inorganic Compounds. CRC Press. p. 3160. ISBN 978-0-412-30120-9. Retrieved 5 April 2023.
- ^ Reckeweg, Olaf; DiSalvo, Francis J. (1 December 2017). "Single-crystal structure refinement of YbF2 with a remark about YbH2". Zeitschrift für Naturforschung B. 72 (12): 995–998. doi:10.1515/znb-2017-0147. ISSN 1865-7117. S2CID 102902501. Retrieved 5 April 2023.
