| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Cobalt(III) acetylacetonate, tris(acac) cobalt
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.040.464 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H21CoO6 | |
| Molar mass | 356.260 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | green solid |
| Density | 1.41 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 213 °C (415 °F; 486 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Danger | |
| H302, H317, H334 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P272, P280, P285, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P341, P321, P330, P333+P313, P342+P311, P363, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Tris(acetylacetonato)cobalt(III) is the coordination complex with the formula Co(C5H7O2)3. Often abbreviated Co(acac)3, it is a green, diamagnetic solid that is soluble in organic solvents, but not in water. Owing to its solubility in organic solvents, tris(acetylacetonato)cobalt(III) is used to produce homogeneous catalysts by reduction.[1]
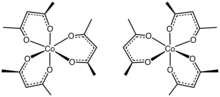
Structure
The structure of the complex has been confirmed by X-ray crystallography. The three acac− ligands bind in a bidentate fashion to cobalt, defining an octahedral complex.[2] The solid is isomorphous with tris(acetylacetonato)iron(III), tris(acetylacetonato)manganese(III), and tris(acetylacetonato)aluminium. With D3-symmetry, these complexes are chiral and often can be resolved into the individual enantiomers.
Synthesis and reactions
Tris(acetylacetonato)cobalt(III) is prepared by the reaction of cobalt(II) carbonate and acetylacetone in the presence of hydrogen peroxide:[3]
- 2 CoCO3 + 6 CH3COCH2COCH3 + H2O2 → 2 Co(O2C3Me2H)3 + 2 CO2 + 4 H2O
One distinctive aspect of Co(acac)3 is its susceptibility toward electrophilic aromatic substitution, by which protons on the central carbon are replaced with diverse electrophiles (Me = methyl):[4]
- Co(O2C3Me2H)3 + 3 NO2+ → Co(O2C3Me2NO2)3 + 3 H+
References
- ^ Mayo, Peter D.; Tam, William (2002). "Tris(acetoacetonyl)cobalt". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rn00084. ISBN 0-471-93623-5.
- ^ Arslan, Evrim; Lalancette, Roger A.; Bernal, Ivan (2017). "An Historic and Scientific Study of the Properties of Metal(III) Tris-acetylacetonates". Structural Chemistry. 28: 201–212. doi:10.1007/s11224-016-0864-0. S2CID 99668641.
- ^ Bryant, Burl E.; Fernelius, W. Conard (1957). Cobalt(III) Acetylacetonate. Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 5. pp. 188–189. doi:10.1002/9780470132364.ch53. ISBN 978-0-470-13236-4.
- ^ Shalhoub, George M. (1980). "Co(acac)3 Synthesis, Reactions, and Spectra: An Experiment for General Chemistry". Journal of Chemical Education. 57 (7): 525. Bibcode:1980JChEd..57..525S. doi:10.1021/ed057p525.
