| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
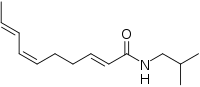
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2E,6Z,8E)-N-(2-Methylpropyl)deca-2,6,8-trienamide | |
| Other names
Affinin
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H23NO | |
| Molar mass | 221.344 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Spilanthol (Affinin) is a fatty acid amide isolated from Acmella oleracea.[1] It is believed to be responsible for the local anesthetic properties of the plant.[2]
Spilanthol permeates the human skin[3] and the inside lining of the cheeks in the mouth (buccal mucosa),[4] resulting in local as well as systemic pharmacological concentrations. In the skin and in the pancreas, spilanthol has also been shown to exert anti-inflammatory effects.[5] The underlying mechanism involves inhibition of nitric oxide production due to reduced expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase enzyme (iNOS) in macrophages. Transcription factor array experiments revealed that spilanthol inhibits the activation of several transcription factors (NFκB, ATF4, FOXO1, IRF1, ETS1, and AP-1) which may explain the effect of spilanthol on gene expression.[5]
The antihypertensive effect of Spilanthol was blocked by CB1 antagonist Rimonabant and TRPV1 antagonist Capsazepine suggesting Spilanthol mediates some activity by interaction with the cannabinoid receptors and TRPV1 channels.[6]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:19 2379431 324
-
Soxhlet extraction
-
Acmella oleracea
-
Acmella oleracea - Toothache Plant
Transcription
See also
References
- ^ Ramsewak, RS; Erickson, AJ; Nair, MG (1999). "Bioactive N-isobutylamides from the flower buds of Spilanthes acmella". Phytochemistry. 51 (6): 729–32. Bibcode:1999PChem..51..729R. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(99)00101-6. PMID 10389272.
- ^ Spelman, Kevin; Depoix, Delphine; McCray, Megan; Mouray, Elisabeth; Grellier, Philippe (2011). "The Traditional Medicine Spilanthes acmella, and the Alkylamides Spilanthol and Undeca-2E-ene-8,10-diynoic Acid Isobutylamide, Demonstrate in Vitro and in Vivo Antimalarial Activity". Phytotherapy Research. 25 (7): 1098–101. doi:10.1002/ptr.3395. PMC 3374932. PMID 22692989.
- ^ Boonen, Jente; Baert, Bram; Roche, Nathalie; Burvenich, Christian; De Spiegeleer, Bart (2010). "Transdermal behaviour of the N-alkylamide spilanthol (affinin) from Spilanthes acmella (Compositae) extracts". Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 127 (1): 77–84. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2009.09.046. PMID 19808085.
- ^ Boonen, Jente; Baert, Bram; Burvenich, Christian; Bondeel, Phillip; De Saeger, Sarah; De Spiegeleer, Bart (2010). "LC-MS profiling of N-alkylamides in Spilanthes acmella extract and the transmucosal behaviour of its main bio-active spilanthol". Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 53 (3): 243–249. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2010.02.010. PMID 20227845.
- ^ a b Bakondi, Edina; Singh, Salam Bhopen; Hajnády, Zoltán; Nagy-Pénzes, Máté; Regdon, Zsolt; Kovács, Katalin; Hegedűs, Csaba; Madácsy, Tamara; Maléth, József; Hegyi, Péter; Demény, Máté Á (2019-09-03). "Spilanthol Inhibits Inflammatory Transcription Factors and iNOS Expression in Macrophages and Exerts Anti-inflammatory Effects in Dermatitis and Pancreatitis". International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 20 (17): E4308. doi:10.3390/ijms20174308. ISSN 1422-0067. PMC 6747447. PMID 31484391.
- ^ Luz-Martínez, Beatriz A.; Marrero-Morfa, Dailenys; Luna-Vázquez, Francisco J.; Rojas-Molina, Alejandra; Ibarra-Alvarado, Cesar (2024). "Affinin, isolated from Heliopsis longipes, induces an antihypertensive effect that involves CB1 cannabinoid receptors and TRPA1 and TRPV1 channels activation". Planta Medica. doi:10.1055/a-2244-8855. PMID 38219731. S2CID 266983561.
