| S21 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
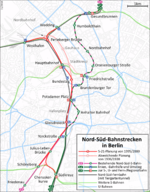 S21 route | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overview | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Line number | 6017 Westhafen–Hbf–Potsdamer Platz 6019 Wedding–Hauptbahnhof | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Track gauge | 1435 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrification | 800 V Third rail DC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
S21 is a planned second north-south route for the Berlin S-Bahn, which will connect Berlin Hauptbahnhof to the Berlin Ringbahn to both north and south. The first section is under construction and is expected to go into operation in 2024.[1]
The term was also used as a route number for a temporary service which operated during the 2006 FIFA World Cup and during service reductions in 2009.
Overview
The route creates an S-Bahn connection from the Nordring (Jungfernheide and Westhafen as well as Wedding and Gesundbrunnen) and the northern suburban railways (Kremmener Bahn from Hennigsdorf, Nordbahn from Oranienburg and Stettiner Bahn from Bernau) via the main station, Potsdamer Platz, Gleisdreieck to the Südring (Schöneberg, Südkreuz) and the southern suburban railways (Wannseebahn from Berlin-Wannsee, Anhalter Vorortbahn from Teltow and Dresdener Bahn from Blankenfelde).
The ministry in the past had created various routes:
- the Verbindungsbahn, which connected the main stations to street level in the 1850s in the south,
- the Ringbahn, which once runs around the city center, with railways for S-Bahn and other traffic,
- the Stadtbahn, which crosses the city in an east-west direction on a viaduct, also with long-distance and S-Bahn tracks.
- the North-south tunnel of the S-Bahn, without mainline tracks.
In 1917, urban planner Martin Mächler proposed in a development plan to build a tunnel between Potsdam and Anhalter Bahn and Lehrter Bahnhof. This should create construction areas for the expansion of the city center. The Lehrter station was to be developed as a Friedrich List station to a crossing station for the north-south and east-west traffic. This model was later to be realized in a modified form as a mushroom concept.
After the Second World War to the early 1950s, the remaining old station stations Lehrter Bahnhof, Potsdamer Bahnhof, Anhalter Bahnhof, Görlitzer Bahnhof and Stettiner Bahnhof (North Station) were shut down because they were heavily destroyed and West Berlin was cut off from the surrounding GDR and so had reduced long-distance traffic. The other main stations, such as the Hamburger Bahnhof, were closed in the 19th century.
All long-distance traffic in West Berlin shifted to the Stadtbahn. In East Berlin next to the light rail Lichtenberg station was connected to the main station and new connections to the north and south. The most important stations of Berlin on the urban railway line were the Ostbahnhof (to 1950: Schlesischer station, from 1987: main station, since 1998: again Ostbahnhof) in the east and the station Zoologischer Garten in the west.
After the German reunification it became clear that a rationalisation of the Berlin railway network was necessary. The Berlin-Lichtenberg station was too peripheral for much of the city, the light rail had limited capacity and a long-distance transport links to the central areas of the city in the north and south were missing.
Almost parallel to the S21 run two other railway tunnels in a north-south direction: The first north-south tunnel of Berlin S-Bahn is the tunnel section below the city center and includes the section Bornholmer road–Gesundbrunnen–Friedrichstrasse–Anhalter station–Priesterweg/Schöneberg, A link between both tunnels is planned at the stations Potsdamer Platz and Yorckstraße. The north-south long-distance railway line for long-distance and regional trains from Nordring via Hauptbahnhof to Südkreuz runs through the Nord-Süd-Fernbahn tunnel, which was commissioned in 2006.
The project is divided into several planning and realization sections, the first of which is in the concrete realization.
These are the key interchange stations of the line:
- Gesundbrunnen for the northern part of Ringbahn towards Mecklenburg and some towards the south
- Südkreuz (before 2006: S-Bahnhof Papestraße) for the southern part of Ringbahn towards Leipzig und Dresden
History
In June 1992, the Federal Ministry of Transport decided on the mushroom concept. It provided for the construction of a central station in the area of the former Lehrter station. While the area in the east-west direction had already been developed with the Berlin Stadtbahn, there was no efficient inner-city connection in a north-south direction. For this purpose, the construction of a S-Bahn line was planned, which should lead to the northwest to the Berlin Ringbahn and from the station Berlin Beusselstraße on to the airport Tegel. Towards the south a route was planned over the station Potsdamer Platz further to the Yorckstraße. A little later, the planning was supplemented by a connection to the northern Ringbahn to the east. In May 1993, it emerged that a standardized assessment of the S21 did not even come close to achieving a benefit-cost factor of 1.
In the Berlin Senate, which was governed at that time by a grand coalition, there were different views on the project. The CDU with its Transport Senator Herwig Haase endorsed the concept; The SPD with the building Senator Wolfgang Nagel declined because of the high cost. After the federal government was not ready to finance the project, the Berlin Senate decided on October 5, 1993, to renounce the immediate construction of the track. Also on a free-keeping of the route waived the Senate by order of November 30, 1993. The project cost around one billion marks at the time. A year later, Haase tried to achieve a free-standing of the route and the construction of individual inputs in the area Potsdamer Platz, but failed initially. In early 1995, however, the Senate resolution was revised in the House of Representatives and decided to keep the planned route, after even the SPD faction had opposed the decision of the Bausenators. However, the decision at that time contained only one route clearing at the northern end of the line in the direction of the east, but not to the western loop.
In the autumn of 1999, the Berlin Senate assured Deutsche Bahn to pre-finance the shell construction of the connection from the Nordring to the Lehrter Bahnhof (the later main station). In the construction of the long-distance railway tunnel and the underground station part also appropriate facilities for the rapid-transit railway were to be established. At that time Deutsche Bahn assumed that the S21 could go into operation together with the mainline tunnel in mid-2005. However, the unclear financing caused further delays in construction. At the beginning of 2001, the Confederation stated that it still considered the route unnecessary and did not want to finance it. In contrast, the Berlin Senate continued to consider a north-south connection to the new central station to be important. The Deutsche Bahn also saw the construction of the S21 as a priority.
Former services

| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The two former services were operated with 15 kV, 16.7 Hz AC overhead lines, while all other S-Bahn lines in Berlin were and are operated with 800 V DC third rail. It was operated by Deutsche Bahn.
First operation in 2006
S21 service was introduced with the opening of the Berlin North-South mainline and the new Berlin Hauptbahnhof central station, while the 2006 FIFA World Cup took place in Germany. DBAG Class 423 trains were used, these trains were borrowed from the Munich, Stuttgart and Frankfurt S-Bahn networks. The first S21 service was discontinued on July 11, 2006.
Second operation in 2009
In 2009 the S-Bahn service had to be strongly shortened due to lack of rolling stock. As a replacement and addition for the North-South S-Bahn route (S1, S2, S25 service), the S21 ran again. Some S21 trains were extended to Hennigsdorf as a replacement for S25. This time, trains of the Munich, Stuttgart and Rhine-Ruhr S-Bahn networks were used.
Future
The second North-South route (third rail) is planned since the 1930s. This route has the working title S21, but the route will not be exclusively served by the S21 service. A first part was planned to be opened in 2017, connecting Berlin's central station with the northern part of the circle line. An S21 shuttle train will operate between Hauptbahnhof and Gesundbrunnen.
With the opening of the second section Hauptbahnhof – Potsdamer Platz, there will be changes. S1 which goes from Oranienburg to Wannsee will be diverted via the second north-south line, the first north-south line will still have S2, S25, and S26. Finally, the S85 that was terminating at Pankow, will be diverted at Schönhauser Allee via the Berliner Ringbahn, then Berlin Hauptbahnhof, Potsdamer Platz, Yorckstraße (Großgörschenstraße), Schöneberg, Steglitz and terminating at Zehlendorf via S1 to increase frequencies on the Wannsee line.
The S21 will be introduced from Jungfernheide to Potsdamer Platz via Berlin Hauptbahnhof when it opens.
References
- ^ "S-Bahn-Tunnel zum Hauptbahnhof: Jetzt wird er noch später fertig". Berliner Zeitung. 23 August 2023. Retrieved 23 August 2023.
External links
- (in German) Klaus Kurpjuweit, "Licht für den Tunnel" Der Tagesspiegel Aug. 12, 2013. p. 11 online
- (in English) S21
- (in German) S 21 Wechselstrom-S-Bahn
- (in German) Service in 2009

