| Redlichiina Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|
| |
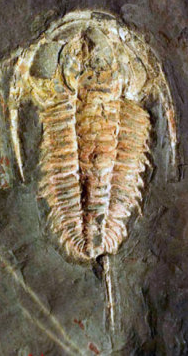
| Redlichia takooensis , a member of the trilobite suborder Redlichiina. Lower Cambrian Emu Shale Kangaroo Island, South Australia | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | †Trilobita |
| Order: | †Redlichiida |
| Suborder: | †Redlichiina Richter, 1932 |
| Superfamilies | |
| |
Redlichiina is a suborder of the order Redlichiida of Trilobites. The suborder contains three superfamilies: Emuelloidea, Redlichioidea and Paradoxidoidea. These trilobites are some of the oldest trilobites known. They originated at the beginning of the Cambrian Period and disappeared (possibly by evolving into members of the Ptychopariida order) at the end of the middle Cambrian.
Physiology

Cephalon: Opisthoparian facial sutures. Early forms tend to have tapering, conical glabella with furrows extending far backwards while later forms with glabella expanding forwards to inflated frontal lobe. The hypostome is conterminant (e.g., Redlichia) or natant (e.g., Dolerolenus). The rostral plate is narrower than in suborder Olenellina, bound by rostral and connective sutures.
Thorax: Fulcrate or non-fulcrate, typically with many segments (60+ in an Emmuelid). The axis is infrequently spine-bearing.
Pygidium: Typically small, but can be larger and with many segments.
References
- Hagadorn, J.W. (2002). "Burgess Shale-type Localities: The global picture". In Bottjer, D.J.; W. Etter; J.W. Hagadorn; C.M. Tang (eds.). Exceptional Fossil Preservation -- A Unique View on the Evolution of Marine Life. Columbia University Press. ISBN 0231102542.
- Greg Edgecombe and the Australian Museum. "Australian Trilobites: A Species List and Bibliography". Retrieved August 23, 2005.
- Sam Gon III. "A guide to the Orders of Trilobites". Retrieved August 23, 2005.
- Nedin, C. (1995). "The Emu Bay Shale, a Lower Cambrian fossil Lagerstätte, Kangaroo Island, South Australia". Memoirs of the Association of Australasian Palaeontologists. 18: 31–40.
- Simpson, Dave. "Trilobites of South Australia". Archived from the original on February 19, 2006. Retrieved August 23, 2005.
