| Northern Tai | |
|---|---|
| Northern Zhuang | |
| Geographic distribution | Southern China |
| Linguistic classification | Kra–Dai |
| Subdivisions |
|
| Glottolog | nort3180 |
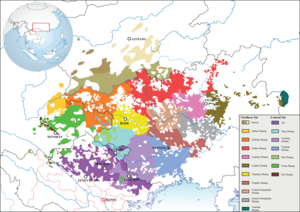 Distribution of Northern Tai and Central Tai languages (Zhuang, Tay-Nung and Bouyei included) | |
The Northern Tai languages are an established branch of the Tai languages of Southeast Asia. They include the northern Zhuang languages and Bouyei of China, Tai Mène of Laos and Yoy of Thailand.
Languages
Ethnologue
Ethnologue distinguishes the following languages:[1]
- Saek (Laos and northeast Thailand; listed outside Tai proper in the Ethnologue classification, though said to be similar to Tai Maen, which is listed as Northern Tai)
- Tai Maen (Laos)
- Yoy (Thailand) [?][2]
- Bouyei (Buyi) (China) (including the language of the Giáy people of Vietnam)
- Central Hongshuihe Zhuang
- Eastern Hongshuihe Zhuang
- Guibei Zhuang
- Yei Zhuang
- Lianshan Zhuang
- Liujiang Zhuang
- Liuqian Zhuang
- Yongbei Zhuang
- Youjiang Zhuang
(See varieties of Zhuang.)
Yoy is elsewhere classified as Southwestern Tai, and E, which is a mixed language Northern Tai-Chinese language.
Longsang Zhuang, a recently described Northern Tai language, is spoken Longsang Township, Debao County, Guangxi, China. Hezhang Buyi is a moribund Northern Tai language of northwestern Guizhou that is notable for having a Kra substratum.
Pittayaporn (2009)
Pittayaporn (2009:300) distinguishes a similar group of Zhuang varieties as group "N", defined by the phonological shifts *ɯj, *ɯw → *aj, *aw.[3] He moves the prestige dialect of Zhuang, the Wuming dialect, from the Northern Tai Yongbei Zhuang to Yongnan Zhuang – purportedly Central Tai – as it lacks these shifts. The various languages and localities Pittayaporn includes in group N, along with their Ethnologue equivalents, are:
- Saek
- Bouyei 布依 (including the language of the Giáy people of Vietnam)
- Yei Zhuang 剥隘
- (Wenshan Zhuang and Miao Autonomous Prefecture, Yunnan)
- (Baise, Guangxi)
- (Nanning Prefecture, Guangxi)
- (Guigang Prefecture, Guangxi)
- Laibin 来宾 Prefecture, Guangxi = Hongshuihe Zhuang (south Laibin), Liujiang Zhuang (north Laibin)
- (Hechi Prefecture, Guangxi)
- (Liuzhou Prefecture, Guangxi)
- Longsheng 龙胜县, Guilin 桂林, Guangxi = Guibei Zhuang
- Dong'an 东安县, Yongzhou 永州, Hunan
- Lianshan 连山县, Qingyuan 清远, Guangdong = Lianshan Zhuang
Vocabulary
Some examples of lexical and phonological differences between Northern Tai and Central-Southwestern Tai:[4]
| Gloss | p-North Tai | p-Central Tai | p-Southwest Tai |
|---|---|---|---|
| ‘tiger’ | *kuːk | *sɯə | *sɯə |
| ‘thorn’ | *ʔon | *n̥aːm | *n̥aːm |
| ‘crow’ | *ʔaː | *kaː | *kaː |
| ‘steam, vapor’ | *soːj | *ʔjaːj | *ʔaːj |
| ‘to tear’ | *siːk | *cʰiːk | *cʰiːk |
| ‘knife’ | *mit | *miːt | *miːt |
References
- ^ "Tai-Kadai, Kam-Tai, Be-Tai, Tai-Sek, Tai". Ethnologue. Archived from the original on 2012-10-18. Retrieved 2011-11-30.
- ^ Pittayaporn classified Yoy as Southwestern Tai, but does not provide supporting analysis.
- ^ Pittayaporn, Pittayawat (2009). The Phonology of Proto-Tai (Ph.D. thesis). Cornell University. hdl:1813/13855.
- ^ Norquest, Peter (2021). "Classification of (Tai-)Kadai/Kra-Dai languages". In Sidwell, Paul; Jenny, Mathias (eds.). The Languages and Linguistics of Mainland Southeast Asia. Berlin: De Gruyter Mouton. pp. 225–246. doi:10.1515/9783110558142-013. ISBN 978-3-11-055814-2.
