| Nasociliary nerve | |
|---|---|
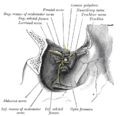
 Nerves of the orbit, and the ciliary ganglion. Side view. (Nasociliary is at center.) | |
 Nerves of septum of nose. Right side. (Nasociliary is rightmost yellow line.) | |
| Details | |
| From | Ophthalmic nerve |
| To | posterior ethmoidal nerve, anterior ethmoidal nerve, long ciliary nerves, infratrochlear nerve, communicating branch to ciliary ganglion |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervus nasociliaris |
| TA98 | A14.2.01.025 |
| TA2 | 6204 |
| FMA | 52668 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The nasociliary nerve is a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) (which is in turn a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)). It is intermediate in size between the other two branches of the ophthalmic nerve, the frontal nerve and lacrimal nerve.[1]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:4 180497676
-
The Ciliary ganglion
-
Orbital Cavity
-
Anatomy of ciliary ganglion
Transcription
Structure
Course
The nasociliary nerve enters the orbit via the superior orbital fissure,[citation needed] through the common tendinous ring,[1] and between the two heads of the lateral rectus muscle and between the superior and inferior rami of the oculomotor nerve.[citation needed] It passes across the optic nerve (CN II) along with the ophthalmic artery. It then runs obliquely beneath (inferior to) the superior rectus muscle and superior oblique muscle to the medial wall of the orbital cavity whereupon it emits the posterior ethmoidal nerve, and the anterior ethmoidal nerve.[1]
Branches
Branches of the nasociliary nerve include:[1]
- posterior ethmoidal nerve
- anterior ethmoidal nerve
- long ciliary nerves
- infratrochlear nerve
- communicating branch to ciliary ganglion
Function
The branches of the nasociliary nerve provide sensory innervation to structures surrounding the eye such as the cornea, eyelids, conjunctiva, ethmoid air cells and mucosa of the nasal cavity.[citation needed]
Clinical significance
Clinical assessment
Since both the short and long ciliary nerves carry the afferent limb of the corneal reflex, one can test the integrity of the nasociliary nerve (and, ultimately, the trigeminal nerve) by examining this reflex in the patient. Normally both eyes should blink when either cornea (not the conjunctiva, which is supplied by the adjacent cutaneous nerves) is irritated. If neither eye blinks, then either the ipsilateral nasociliary nerve is damaged, or the facial nerve (CN VII, which carries the efferent limb of this reflex) is bilaterally damaged. If only the contralateral eye blinks, then the ipsilateral facial nerve is damaged. If only the ipsilateral eye blinks, then the contralateral facial nerve is damaged.[citation needed]
Additional images
-
Nerves of the orbit. Seen from above.
-
Distribution of the maxillary and mandibular nerves, and the submaxillary ganglion.
-
Dissection showing origins of right ocular muscles, and nerves entering by the superior orbital fissure.
-
Pathways in the ciliary ganglion.
-
Extrinsic eye muscle. Nerves of orbita. Deep dissection.
References
- ^ a b c d Standring, Susan (2020). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (42nd ed.). New York. p. 782. ISBN 978-0-7020-7707-4. OCLC 1201341621.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 888 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 888 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Anatomy figure: 29:03-08 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "A deeper dissection of the right orbit from a superior approach."
- lesson9 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (nasalseptumner)
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (V)
- MedEd at Loyola GrossAnatomy/h_n/cn/cn1/cnb1.htm