| Mulato-Getudo Fault | |
|---|---|
| Mulato-Jetudo Fault, Falla de Mulato-Jetudo | |
| Etymology | Mulatos & Jetudo Rivers |
| Coordinates | 05°20′35″N 74°51′23″W / 5.34306°N 74.85639°W |
| Country | |
| Region | Andean |
| State | Antioquia, Caldas, Tolima |
| Cities | Mariquita |
| Characteristics | |
| Range | Central Ranges, Andes |
| Part of | Andean oblique faults |
| Length | 187.3 km (116.4 mi) |
| Strike | 016.7 ± 9 |
| Dip | West |
| Dip angle | High to medium |
| Displacement | <0.2 mm (0.0079 in)/yr |
| Tectonics | |
| Plate | North Andean |
| Status | Inactive |
| Type | Oblique thrust fault |
| Movement | Reverse sinistral |
| Age | Quaternary |
| Orogeny | Andean |
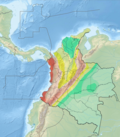
The Mulato-Getudo or Mulato-Jetudo Fault (Spanish: Falla de Mulato-Jetudo) is a sinistral oblique thrust fault in the departments of Tolima, Caldas and Antioquia in central Colombia. The fault has a total length of 187.3 kilometres (116.4 mi) and runs along an average north-northeast to south-southwest strike of 016.7 ± 9 in the Middle Magdalena Valley and along the western foothills of the Central Ranges of the Colombian Andes.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/1Views:1 873
-
বাংলাদেশ ও বিশ্ব পরিচয় - (অধ্যায়-১) পূর্ব ও পশ্চিম পাকিস্তানের মধ্যে বৈষম্য - সপ্তম শ্রেণি
Transcription
Etymology
The fault is named after the Mulatos and Jetudo Rivers, left tributaries of the Magdalena River.[1]
Description
The Mulato-Getudo Fault, in some parts called Jetudo Fault,[2] extends along the eastern foothills of the Central Ranges of the Colombian Andes, where it marks the abrupt break in slope of the east-tilted Tertiary erosion surface of the Cordillera and the flat alluvial plains of the Magdalena River in the Middle Magdalena Valley. The fault forms a regional-scale degraded fault escarpment with an outstanding break in slope. It offsets Pliocene to Quaternary deposits and an extensive tilted erosional surface of probable Miocene to Pliocene age (pre-Mesa Formation, older than 1.5 Ma). The northern half of the fault is characterised by aligned drainages and broad valleys.[1] The fault possibly underlies the Honda Group south of the La Miel River.[3]
See also
References
Bibliography
- Paris, Gabriel; Michael N. Machette; Richard L. Dart, and Kathleen M. Haller. 2000a. Map and Database of Quaternary Faults and Folds in Colombia and its Offshore Regions, 1–66. USGS. Accessed 2017-09-18.
Maps
- Barrero L., Darío, and Carlos J. Vesga O. 2009. Plancha 188 - La Dorada - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Gómez, J.; N.E. Montes; Á. Nivia, and H. Diederix. 2015. Plancha 5-09 del Atlas Geológico de Colombia 2015 – 1:500,000, 1. Servicio Geológico Colombiano. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Paris, Gabriel; Michael N. Machette; Richard L. Dart, and Kathleen M. Haller. 2000b. Map of Quaternary Faults and Folds of Colombia and Its Offshore Regions, 1. USGS. Accessed 2017-09-18.
Further reading
- Page, W.D. 1986. Seismic geology and seismicity of Northwestern Colombia, 1–200. San Francisco, California, Woodward-Clyde Consultants Report for ISA and Integral Ltda., Medellín.