| Chitagá-Pamplona Fault | |
|---|---|
| Falla de Chitagá-Pamplona | |
| Etymology | Chitagá, Pamplona |
| Coordinates | 07°32′34.2″N 72°36′30.4″W / 7.542833°N 72.608444°W |
| Country | |
| Region | Andean |
| State | Norte de Santander, Boyacá |
| Cities | Pamplona, Chitagá |
| Characteristics | |
| Range | Eastern Ranges, Andes Catatumbo Basin |
| Part of | Andean oblique faults |
| Length | 192.5 km (119.6 mi) |
| Strike | 355.2 ± 30 |
| Dip | Variable |
| Dip angle | Variable |
| Displacement | 0.2–1 mm (0.0079–0.0394 in)/yr |
| Tectonics | |
| Plate | North Andean |
| Status | Inactive |
| Type | Oblique strike-slip fault |
| Movement | Reverse sinistral |
| Rock units | Floresta & Río Negro Formations |
| Age | Pleistocene |
| Orogeny | Andean |
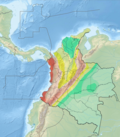
The Chitagá-Pamplona Fault (Spanish: Falla de Chitagá-Pamplona) is an inactive sinistral oblique thrust fault in the departments of Norte de Santander and Boyacá in northeastern Colombia. The fault has a total length of 192.5 kilometres (119.6 mi) and runs along an average north to south strike of 355.2 ± 30, but varies in orientation from northwest-southeast in the south to northeast-southwest in the north. The fault cross-cuts the northern part of the Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes and the Catatumbo Basin.
Etymology
The fault was named after Chitagá and Pamplona, Norte de Santander.[1]
Description
The Chitagá-Pamplona Fault parallels the Morronegro-Las Mercedes Fault System and places Paleozoic rocks on the west against Tertiary and Cretaceous rocks on the east. The structural behavior of the fault is very similar to faults of the Morronegro-Las Mercedes Fault System. Both faults are believed to be an extension of the Boconó Fault and associated faults of the Venezuelan Andes.[1] The fault starts in northernmost Boyacá in the municipality Chiscas, just north of the Sierra Nevada del Cocuy, where it places the Devonian Floresta Formation in the hanging wall against the Cretaceous Río Negro Formation in the footwall.[2]
Activity
A rate between 0.2 and 1 millimetre (0.0079 and 0.0394 in) per year is estimated for the fault, considered inactive. The fault was probably active in the Pleistocene, at an estimated range of between 1.6 Ma and 750 ka.[3]
See also
References
Bibliography
- Paris, Gabriel; Michael N. Machette; Richard L. Dart, and Kathleen M. Haller. 2000a. Map and Database of Quaternary Faults and Folds in Colombia and its Offshore Regions, 1–66. USGS. Accessed 2017-09-18.
Maps
- Daconte B., Rommel, and Rosalba Salinas E. 1982. Plancha 122 - Río Cobugón - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2018-06-01.
- Paris, Gabriel; Michael N. Machette; Richard L. Dart, and Kathleen M. Haller. 2000b. Map of Quaternary Faults and Folds of Colombia and Its Offshore Regions, 1. USGS. Accessed 2017-09-18.