| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Mercuric azanide chloride
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.292 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Hg(NH2)Cl | |
| Molar mass | 252.065 g/mol |
| Appearance | White powder of small prisms[1] |
| Odor | None[2] |
| Density | 5.7 g/cm3[1] |
| Boiling point | Sublimes[3] |
| 1.4 g/L (cold); decomposes if hot[1] | |
| Solubility | Soluble in warm hydrochloric, nitric and acetic acids, sodium thiosulfate[3] or ammonium carbonate solution; insoluble in ethanol[2] |
| Pharmacology | |
| D08AK01 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[4] | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H300, H310, H330, H373, H410 | |
| P260, P262, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P284, P301+P316, P302+P352, P304+P340, P316, P319, P320, P321, P330, P361+P364, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | Non-combustible |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
|
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Mercuric amidochloride is an inorganic compound with the formula Hg(NH2)Cl.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/4Views:2 01255 179218 762155 234
-
Mercuric Chloride and Potassium Iodide ( Reaction )
-
Qualitative Analysis of Group I Cations
-
Bayer Admire insecticide | Imidacloprid 70% WG | systemic insecticide #TAACचैनल
-
Imidacloprid 17.8 SL की पूरी जानकारी || Full information about Imidacloprid || Evergreen world
Transcription
Preparation and properties
It arises from the reaction of mercury(II) chloride and ammonia (Calomel reaction), where the resulting mercuric amidochloride is highly insoluble.
- HgCl2 + 2 NH3 → HgCl(NH2) + [NH4]Cl
It forms white crystals in the shape of small prisms. It tastes earthy and metallic, but is a deadly poison and should not be ingested.[2]
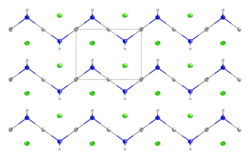
At the molecular level, it organizes as a zig-zag 1-dimensional polymer (HgNH2)n with chloride counterions.[5][6]

It is stable in air, but darkens on exposure to light.[7] It does not melt, even at dull red heat, instead subliming[3] and decomposing to gaseous mercury, hydrogen chloride, and nitrogen oxides.[8] Consequently sealed containers with this chemical may explode when heated.[9]
This substance is a deadly poison,[2] although not a carcinogen.[10] It is toxic unto lethality by inhalation, ingestion or dermal absorption. In lesser cases, it may instead cause dermatitis and skin lesions[7] or corrode the mucous membranes.[failed verification] If improperly handled, may cause dangerous environmental pollution, in soil, water bodies and air.[11]
Addition of base converts it into "Millon's base" (named after Eugène Millon), which has the formula Hg2(OH)N·xH2O. A variety of related amido and nitrido materials with chloride, bromide, and hydroxide are known.[12][page needed]
Uses
Before the toxicity of mercury was revealed, mercuric amidochloride, then known as "ammoniated mercury" or "white precipitate", was used as a topical skin antiseptic, especially impetigo, dermatomycosis and other certain dermatoses.[13] It was also used for scaling in psoriasis, to treat pruritus ani, and against pinworm and ringworm infection (especially in dogs), against crab louse infestation,[7] against lesions on the body and near eyes, against bumblefoot infection on poultry, and as a disinfectant.[11][13] Chronic use of this medication can lead to systemic mercury poisoning. Since less toxic medications are available now, to treat those conditions, there is no need to use mercuric amidochloride as a medication anymore.[7][13]
See also
- Merbromin, also known as "Mercurochrome", another antiseptic mercury compound
- Thiomersal, another antiseptic mercury compound
References
- ^ a b c Weast, Robert C., ed. (1991) [1988]. Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (1st student ed.). Boca Raton: CRC Press. p. B-42. ISBN 0-8493-0740-6. LCCN 87-26820.
- ^ a b c d Hawley, Gessner G. (1981). "Mercury, ammoniated". The Condensed Chemical Dictionary (10th ed.). New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold / Litton Educational. p. 657. ISBN 0-442-23244-6. LCCN 80-29636.
- ^ a b c "Mercuric Chloride, Ammoniated". The Merck Index. Royal Society of Chemistry. As cited in "Mercuric Ammonium Chloride", Hazardous Substances Databank entry #1175.
- ^ European Chemicals Agency. Entry 233-335-8 in Classification and Labeling database. Accessed 22 April 2024.
- ^ Wells, A. F. (1984), Structural Inorganic Chemistry (5th ed.), Oxford: Clarendon Press, pp. 1166–1169, ISBN 0-19-855370-6
- ^ Lipscomb, W. N. (1951). "The structure of mercuric amidochloride, HgNH2Cl". Acta Crystallographica. 4 (3): 266–8. doi:10.1107/S0365110X51000866.
- ^ a b c d Harvey, Stewart H. (1990). "Antimicrobial drugs". In Gennaro, Alfonso R. (ed.). Pharmaceutical Sciences (18th ed.). Easton, PA: Mack. p. 1172. ISBN 0-912-734-04-3. LCCN 60-53334.
- ^ Lewis, R. J. (1996). Sax's Dangerous Properties of Industrial Materials, 9th ed. Vols. 1-3. New York, NY: Van Nostrand Reinhold. p. 2121. As cited in HSDB.
- ^ North American transport authorities (2016). Emergency Response Guidebook. Neenah, WI: J. J. Keller. pp. 129, 240–241.
- ^ American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (2008). Threshold Limit Values for Chemical Substances and Physical Agents and Biological Exposure Indices. Cincinnati, OH. p. 37. As cited in HSDB.
- ^ a b National Library of Medicine. "Ammoniated mercury" entry in PubChem (database). Accessed 22 April 2024
- ^ Holleman, Arnold Frederik; Wiberg, Egon (2001), Wiberg, Nils (ed.), Inorganic Chemistry, translated by Eagleson, Mary; Brewer, William, San Diego/Berlin: Academic Press/De Gruyter, ISBN 0-12-352651-5
- ^ a b c Aberer W, Gerstner G, Pehamberger H (September 1990). "Ammoniated mercury ointment: outdated but still in use". Contact Dermatitis. 23 (3): 168–71. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0536.1990.tb04778.x. PMID 2149317. S2CID 20467204.
