| Ischial tuberosity | |
|---|---|
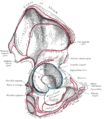
 Capsule of hip-joint (distended). Posterior aspect. (Ischial tuberosity visible at bottom left.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | tuber ischiadicum, tuberositas ischiadica |
| TA98 | A02.5.01.204 |
| TA2 | 1342 |
| FMA | 17010 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The ischial tuberosity (or tuberosity of the ischium, tuber ischiadicum), also known colloquially as the sit bones or sitz bones,[1] or as a pair the sitting bones,[2] is a large posterior bony protuberance on the superior ramus of the ischium. It marks the lateral boundary of the pelvic outlet.
When sitting, the weight is frequently placed upon the ischial tuberosity.[3] The gluteus maximus provides cover in the upright posture, but leaves it free in the seated position.[4] The distance between a cyclist's ischial tuberosities is one of the factors in the choice of a bicycle saddle.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:113 36074 426469
-
Ischial Tuberosity pain treatment - Dr. Ross Hauser
-
What causes ischial tuberosity pain (butt pain)?
-
Classifying Ischial Tuberosity Avulsion Fractures by Ossification Stage and Tendon Attachment
Transcription
Divisions
The tuberosity is divided into two portions: a lower, rough, somewhat triangular part, and an upper, smooth, quadrilateral portion.
- The lower portion is subdivided by a prominent longitudinal ridge, passing from base to apex, into two parts:
- The outer gives attachment to the adductor magnus
- The inner to the sacrotuberous ligament
- The upper portion is subdivided into two areas by an oblique ridge, which runs downward and outward:
- From the upper and outer area the semimembranosus arises
- From the lower and inner, the long head of the biceps femoris and the semitendinosus
Additional images
-
Muscles of the gluteal and posterior femoral regions, with ischial tuberosity highlighted in red
-
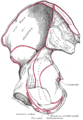
Right hip bone. External surface.
-
Right hip bone. Internal surface.
-
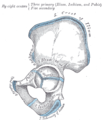
Plan of ossification of the hip bone
-
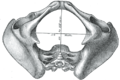
Diameters of inferior aperture of lesser pelvis (female)
-
Right hip-joint from the front
-
-
Anterior view of the pelvis with the ischial tuberosity labelled in the lower part of the image
See also
Notes
- ^ M.D, John R. Schultz (October 28, 2019). "Sit Bones Pain (aka Sitz Bone)". Centeno-Schultz Clinic. Retrieved April 12, 2020.
- ^ Sills, Franklyn (2004). Craniosacral Biodynamics: The Primal Midline and the Organization of the Body (revised, illustrated ed.). Berkeley, CA: North Atlantic Books. p. 99. ISBN 1-55643-390-5.
- ^ Goossens (2005), pp 895–982
- ^ Platzer (2004), p 236
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 235 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 235 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Goossens R, Teeuw R, Snijders C (2005). "Sensitivity for pressure difference on the ischial tuberosity". Ergonomics. 48 (7): 895–902. doi:10.1080/00140130500123647. PMID 16076744. S2CID 854065.
- Platzer, Werner (2004). Color Atlas of Human Anatomy, Vol. 1: Locomotor System (5th ed.). Thieme. ISBN 3-13-533305-1.
External links
- pelvis at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (pelvisposterior, pelvislateral, pelvisinside)