HCH3(CH2)16CO2
He
LiCH3 (CH2 )16 CO2 <link href="mw-data:TemplateStyles:r1123817410" rel="mw-deduplicated-inline-style"/><span class="chemf nowrap">Be(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">16</sub>CO<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub></span>
B(CH3(CH2)16CO2)<sub>3</sub>
<link href="mw-data:TemplateStyles:r1123817410" rel="mw-deduplicated-inline-style"/><span class="chemf nowrap">NH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">4</sub>CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">16</sub>CO<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub></span>,
-O-
Ne
NaCH3 (CH2 )16 CO2 Mg(CH3 (CH2 )16 CO2 )2 <link href="mw-data:TemplateStyles:r1123817410" rel="mw-deduplicated-inline-style"/><span class="chemf nowrap">Al(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">16</sub>CO<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub></span>
<link href="mw-data:TemplateStyles:r1123817410" rel="mw-deduplicated-inline-style"/><span class="chemf nowrap">Si(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">16</sub>CO<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">4</sub></span>
<link href="mw-data:TemplateStyles:r1123817410" rel="mw-deduplicated-inline-style"/><span class="chemf nowrap">P(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">16</sub>CO<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub></span>
Ar
KCH3 (CH2 )16 CO2 Ca(CH3 (CH2 )16 CO2 )2
<link href="mw-data:TemplateStyles:r1123817410" rel="mw-deduplicated-inline-style"/><span class="chemf nowrap">Sc(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">16</sub>CO<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub></span>
Ti
V
Cr(CH3(CH2)16CO2)<sub>2</sub>
Mn
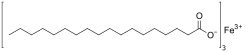
Fe(CH3(CH2)16CO2)<sub>2</sub>Fe(CH3(CH2)16CO2)3
Co(CH3 (CH2 )16 CO2 )2 Ni(CH3 (CH2 )16 CO2 )2 Cu(CH3 (CH2 )16 CO2 )2 Zn(CH3 (CH2 )16 CO2 )2 <link href="mw-data:TemplateStyles:r1123817410" rel="mw-deduplicated-inline-style"/><span class="chemf nowrap">Ga(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">16</sub>CO<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub></span>
Ge
<link href="mw-data:TemplateStyles:r1123817410" rel="mw-deduplicated-inline-style"/><span class="chemf nowrap">As(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">16</sub>CO<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub></span>
Kr
<link href="mw-data:TemplateStyles:r1123817410" rel="mw-deduplicated-inline-style"/><span class="chemf nowrap">RbCH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">16</sub>CO<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub></span>
Sr(CH3 (CH2 )16 CO2 )2
<link href="mw-data:TemplateStyles:r1123817410" rel="mw-deduplicated-inline-style"/><span class="chemf nowrap">Y(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">16</sub>CO<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub></span>
Zr(CH3 (CH2 )16 CO2 )3 Nb
Tc
Ru
Rh
<link href="mw-data:TemplateStyles:r1123817410" rel="mw-deduplicated-inline-style"/><span class="chemf nowrap">Pd(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">16</sub>CO<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub></span>
AgCH3 (CH2 )16 CO2 Cd(CH3 (CH2 )16 CO2 )2 <link href="mw-data:TemplateStyles:r1123817410" rel="mw-deduplicated-inline-style"/><span class="chemf nowrap">In(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">16</sub>CO<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub></span>
Sn
<link href="mw-data:TemplateStyles:r1123817410" rel="mw-deduplicated-inline-style"/><span class="chemf nowrap">Sb(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">16</sub>CO<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub></span>
Te
Xe
CsCH3 (CH2 )16 CO2 <link href="mw-data:TemplateStyles:r1123817410" rel="mw-deduplicated-inline-style"/><span class="chemf nowrap">Ba(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">16</sub>CO<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub></span>
*
<link href="mw-data:TemplateStyles:r1123817410" rel="mw-deduplicated-inline-style"/><span class="chemf nowrap">Lu(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">16</sub>CO<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub></span>
Hf
Ta
Re
Os
Ir
<link href="mw-data:TemplateStyles:r1123817410" rel="mw-deduplicated-inline-style"/><span class="chemf nowrap">AuCH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">16</sub>CO<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub></span>
<link href="mw-data:TemplateStyles:r1123817410" rel="mw-deduplicated-inline-style"/><span class="chemf nowrap">Hg<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">16</sub>CO<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub></span>,Hg(CH3 (CH2 )16 CO2 )2
<link href="mw-data:TemplateStyles:r1123817410" rel="mw-deduplicated-inline-style"/><span class="chemf nowrap">TlCH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">16</sub>CO<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub></span>
Pb(CH3 (CH2 )16 CO2 )2 <link href="mw-data:TemplateStyles:r1123817410" rel="mw-deduplicated-inline-style"/><span class="chemf nowrap">Bi(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">16</sub>CO<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub></span>
Po
At
Rn
Fr
Ra
**
Lr
Rf
Db
Sg
Bh
Hs
Mt
Ds
Rg
Cn
Nh
Fl
Mc
Lv
Ts
Og
*
La(CH3 (CH2 )16 CO2 )3 Ce(CH3 (CH2 )16 CO2 )3 Pr
Nd
Pm
<link href="mw-data:TemplateStyles:r1123817410" rel="mw-deduplicated-inline-style"/><span class="chemf nowrap">Sm(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">16</sub>CO<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub></span>
<link href="mw-data:TemplateStyles:r1123817410" rel="mw-deduplicated-inline-style"/><span class="chemf nowrap">Eu(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">16</sub>CO<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub></span>
<link href="mw-data:TemplateStyles:r1123817410" rel="mw-deduplicated-inline-style"/><span class="chemf nowrap">Gd(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">16</sub>CO<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub></span>
Tb
<link href="mw-data:TemplateStyles:r1123817410" rel="mw-deduplicated-inline-style"/><span class="chemf nowrap">Dy(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">16</sub>CO<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub></span>
<link href="mw-data:TemplateStyles:r1123817410" rel="mw-deduplicated-inline-style"/><span class="chemf nowrap">Ho(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">16</sub>CO<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub></span>
Er
Tm
<link href="mw-data:TemplateStyles:r1123817410" rel="mw-deduplicated-inline-style"/><span class="chemf nowrap">Yb(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">16</sub>CO<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub></span>
**
<link href="mw-data:TemplateStyles:r1123817410" rel="mw-deduplicated-inline-style"/><span class="chemf nowrap">Ac(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">16</sub>CO<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub></span>
<link href="mw-data:TemplateStyles:r1123817410" rel="mw-deduplicated-inline-style"/><span class="chemf nowrap">Th(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">16</sub>CO<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">4</sub></span>
Pa
<link href="mw-data:TemplateStyles:r1123817410" rel="mw-deduplicated-inline-style"/><span class="chemf nowrap">UO<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">3</sub>(CH<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">16</sub>CO<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub>)<sub class="template-chem2-sub">2</sub></span>
Np
Pu
Am
Cm
Bk
Cf
Es
Fm
Md
No