The femoral head (femur head or head of the femur) is the highest part of the thigh bone (femur). It is supported by the femoral neck.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:45 06513 8765 594
-
AVN Femoral Head Causes, Trauma To The Hip - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
-
Avascular necrosis of the hip and the blood supply to the femoral head.
-
Osteonecrosis of the Hip (femoral head) - Avascular Necrosis
Transcription
Structure
The head is globular and forms rather more than a hemisphere, is directed upward, medialward, and a little forward, the greater part of its convexity being above and in front.
The femoral head's surface is smooth. It is coated with cartilage in the fresh state, except over an ovoid depression, the fovea capitis, which is situated a little below and behind the center of the femoral head, and gives attachment to the ligament of head of femur.
The thickest region of the articular cartilage is at the centre of the femoral head, measuring up to 2.8 mm.[1]
The diameter of the femoral head is usually larger in men than in women.
Fovea capitis
The fovea capitis is a small, concave depression within the head of the femur that serves as an attachment point for the ligamentum teres (Saladin). It is slightly ovoid in shape and is oriented "superior-to-posteroinferior. (Cerezal)" This orientation might be favorable for the tensed fibers of the ligamentum teres. The fovea capitis is located "slightly posterior and inferior to the center of the articular surface of the femoral head (Cerezal)" Unlike the head of the femur, the fovea capitis lacks any hyaline cartilage. The fovea capitis may contain vascular canals in two-thirds of individuals, but "their contribution to femoral head vascularity varies. (Cerezal)"
Clinical significance
If there is a fracture of the neck of the femur, the blood supply through the ligament becomes crucial. The head of the femur is relevant to orthopedic surgery because it can undergo avascular necrosis and consequent osteochondritis dissecans. The femoral head is removed in total hip replacement surgery.
Additional images
-
Radiograph of a healthy human hip joint
-
Gross pathology specimen of the head of the femur with some synovium attached at the bottom and the ligament attached at the top. Ruler in centimeters at left side.
-
Right femur. Anterior surface.
-
Left hip-joint, opened by removing the floor of the acetabulum from within the pelvis.
-
The obturator externus.
-
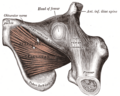
Hip joint. Lateral view. Femur head
-
Hip joint. Lateral view. Femur head
References
- ^ Mechlenburg, I.; Nyengaard, J.R.; Gelineck, J.; Soballe, K. (April 2007). "Cartilage thickness in the hip joint measured by MRI and stereology – a methodological study". Osteoarthritis and Cartilage. 15 (4): 366–371. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2006.10.005. PMID 17174117.
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 243 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 243 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Cerezal, Luis. "Anatomy, Biomechanics, Imaging, and Management of Ligamentum Teres Injuries." RadioGraphica. RSNA, Oct. 2010. Web. Nov. 2015.
- Saladin, Kenneth S. Anatomy & Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function. 6th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2007. 300–302. Print.
External links
- Cross section image: pembody/body15a—Plastination Laboratory at the Medical University of Vienna