| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Hydroxy-N,N,N-trimethylethan-1-aminium chloride | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.596 |
| E number | E1001(iii) (additional chemicals) |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
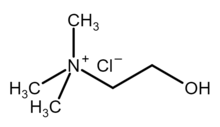
| [(CH3)3NCH2CH2OH]+Cl− | |
| Molar mass | 139.62 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White hygroscopic crystals |
| Melting point | 302 °C (576 °F; 575 K) (decomposes) |
| very soluble (>650 g/L)[1] | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Corrosive |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Danger | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Choline chloride is an organic compound with the formula [(CH3)3NCH2CH2OH]+Cl−. It is a quaternary ammonium salt, consisting of choline cations ([(CH3)3NCH2CH2OH]+) and chloride anions (Cl−). It is a bifunctional compound, meaning, it contains both a quaternary ammonium functional group and a hydroxyl functional group. The cation of this salt, choline, occurs in nature in living beings.[2] Choline chloride is a white, water-soluble salt used mainly in animal feed.[3]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:1 68712 930722
-
What Is Choline Supplement and What Can It Do?
-
🐓 Poultry Farming Business Plan Documentary For Poultry Feed || Broiler Feed Formulation Basic ||
-
Ask Dr. J - Should people take Magnesium & Choline for life or only when their pH is low?
Transcription
Synthesis
In the laboratory, choline can be prepared by methylation of dimethylethanolamine with methyl chloride.
Choline chloride is mass-produced with world production estimated at 160 000 tons in 1999.[3] Industrially, it is produced by the reaction of ethylene oxide, hydrogen chloride, and trimethylamine,[4] or from the pre-formed salt:[5]
Choline chloride can also be made by treating trimethylamine with 2-chloroethanol.[6]
- (CH3)3N + ClCH2CH2OH → [(CH3)3NCH2CH2OH]+Cl−
Applications
It is an important additive in feed especially for chickens where it accelerates growth. It forms a deep eutectic solvent with urea, ethylene glycol, glycerol, and many other compounds.
It is also used as a clay control additive in fluids used for hydraulic fracturing.[7]
Related salts
Other commercial choline salts are choline hydroxide and choline bitartrate. In foodstuffs, the compound is often present as phosphatidylcholine.
References
- ^ "Chemical Safety Information from Intergovernmental Organizations - Choline Chloride" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-07-12.
- ^ "Choline". Micronutrient Information Center, Linus Pauling Institute, Oregon State University. February 2015. Retrieved 11 November 2019.
- ^ a b Matthias Frauenkron; Johann-Peter Melder; Günther Ruider; Roland Rossbacher; Hartmut Höke (2002). "Ethanolamines and Propanolamines". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a10_001. ISBN 3527306730.
- ^ title=Johnson Matthey Process Technology - Choline chloride licensed process
- ^ "Choline chloride" (PDF). Screening Information Data Set (SIDS) for High Production Volume Chemicals. IPCS INCHEM. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-07-12. Retrieved 2009-11-10.
- ^ Kirk RE, et al. (2000). Kirk-Othmer encyclopedia of chemical technology. Vol. 6 (4th ed.). John Wiley & Sons. pp. 100–102. ISBN 9780471484943.
- ^ "What Chemicals Are Used". FracFocus. Archived from the original on 2 July 2020. Retrieved 19 September 2014.

