 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names |
|
| Routes of administration | Infusion |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 2.9-11 min |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| PubChem SID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChEBI | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C150H188N57O97P15 |
| Molar mass | 4806.062 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
BC-007, whose international nonproprietary name is Rovunaptabin,[1] is an oligonucleotide aptamer, a synthetic DNA compound designed to bind other chemicals.[2] BC-007 is in early-stage clinical trials as a lead compound intended for the potential treatment of heart failure or long COVID.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/5Views:606419 86979 86520 975 8451 364 505
-
GAME-CHANGING treatment for ME/CFS, Long Covid patients? All about Berlin Cures 007
-
Destroying spike protein! - COVID-19 update 60
-
Autoantikörper bei CFS und Long-CoVID? Aktuelle Forschung bei chronischem Erschöpfungssyndrom!
-
अमीर लोग ये मसाज क्यों करवाते हैं
-
The Truth About GORE-TEX
Transcription
History
Since the 1990s, the binding of G protein coupled receptors to autoantibodies (GPCR-AABs) was investigated as a possible factor in the pathology of several diseases, including heart disease.[3][4] In parallel, treatment strategies to remove GPCR-AABs were investigated, initially using proteins or peptides to bind the antibodies.[5][6]
In 2012, scientists from the Max Delbrück Center and the Charité Heart Center obtained a patent in the United States for using aptamers as a therapy or diagnosis of autoimmune diseases.[7] Beginning in 2013, the research group focused on the treatment of dilated cardiomyopathy in people positive for beta-1 adrenergic receptor autoantibodies.[8][9] In 2015–16, scientists reported that two aptamers might bind and inhibit GPCR-AABs.[10][11]
The biotechnology company Berlin Cures pursued the development of the aptamer with the nucleotide sequence GGT TGG TGT GGT TGG under the codename BC-007 for the inhibition of autoantibodies in cardiomyopathy.[12]
Properties
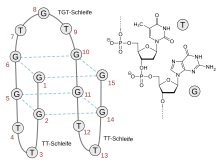
BC-007 is a 15-nucleotide single-stranded DNA molecule consisting of nine unmodified deoxy-guanosines and six corresponding deoxythymidines with the sequence 5'-GGT TGG TGT GGT TGG-3'.[2] Its three-dimensional structure allows it to wrap around the target structure of G-protein-coupled receptor autoantibodies and neutralize their activity.[2]
BC-007 is synthetic, enabling it to be produced in high volumes quickly.[13] It is stable and suited for long-term storage.[13] It has shown no side effects in early clinical studies, and does not trigger immunological responses.[2][13] As it is water soluble, it can be formulated as inhalation or as nasal spray.[13] In some human studies, it was given by intravenous infusion, displaying an in vivo half-life in blood of about 4 minutes.[2]
Research
Heart failure
The removal of pathogenic functional autoantibodies through a medical blood purification procedure, known as immunoadsorption, can stabilize heart function in people with dilated cardiomyopathy who are awaiting heart transplantation.[14][15] In 2018, a Phase I clinical trial found that BC-007 was well-tolerated, with no serious adverse events reported.[2][12] Phase IIa trials demonstrated that BC-007 could neutralize the activity of functional autoantibodies in most subjects treated.[16]
Long COVID
BC-007 is under investigation as a possible agent for treating disorders of long COVID.[17]
References
- ^ "WHO Drug Information - International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN) - Recommended INN: List 91". INN and Classification of Medical Products (INN), World Health Organization. 2024-03-25. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2024-03-25. Retrieved 2024-04-03.
- ^ a b c d e f Kolter T (2023). "BC-007". In Böckler F, Dill B, Eisenbrand G, et al. (eds.). Römpp [Online]. Georg Thieme Verlag. Archived from the original on 2023-07-23.
- ^ Matsui S, Fu ML (May 1998). "Myocardial injury due to G-protein coupled receptor-autoimmunity". Japanese Heart Journal. 39 (3): 261–274. doi:10.1536/ihj.39.261. PMID 9711178. S2CID 22133040.
- ^ Bornholz B, Wallukat G, Roggenbuck D, Schimke I (2017-02-17). "Chapter 3 - Autoantibodies Directed Against G-Protein-Coupled Receptors in Cardiovascular Diseases: Basics and Diagnostics". In Nussinovitch U (ed.). The Heart in Rheumatic, Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases. Academic Press. pp. 49–63. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-803267-1.00003-X. ISBN 978-0-12-803267-1.
- ^ Wallukat G, Müller J, Hetzer R (November 2002). "Specific removal of beta1-adrenergic autoantibodies from patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy". The New England Journal of Medicine. 347 (22): 1806. doi:10.1056/NEJM200211283472220. PMID 12456865.
- ^ Doesch AO, Konstandin M, Celik S, Kristen A, Frankenstein L, Hardt S, et al. (2009-07-09). "Effects of protein A immunoadsorption in patients with advanced chronic dilated cardiomyopathy". Journal of Clinical Apheresis. 24 (4): 141–149. doi:10.1002/jca.20204. PMID 19591221. S2CID 5566530.
- ^ Büttner, Bettina (2012). "Technology offer - Aptamers for the Treatment and Diagnosis of Diseases Seropositive for Autoantibodies - Ref. No.: CH553" (PDF). Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2023-04-23.
- ^ Haberland A, Wallukat G, Schimke I (March 2013). "The patent situation concerning the treatment of diseases associated with autoantibodies directed against G-protein-coupled receptors". Pharmaceutical Patent Analyst. 2 (2): 231–248. doi:10.4155/ppa.12.88. PMID 24237028.
- ^ Patel PA, Hernandez AF (July 2013). "Targeting anti-beta-1-adrenergic receptor antibodies for dilated cardiomyopathy". European Journal of Heart Failure. 15 (7): 724–729. doi:10.1093/eurjhf/hft065. PMC 3707431. PMID 23639780.
- ^ Haberland A, Holtzhauer M, Schlichtiger A, Bartel S, Schimke I, Müller J, et al. (October 2016). "Aptamer BC 007 - A broad spectrum neutralizer of pathogenic autoantibodies against G-protein-coupled receptors". European Journal of Pharmacology. 789: 37–45. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.06.061. PMID 27375076.
- ^ Wallukat G, Müller J, Haberland A, Berg S, Schulz A, Freyse EJ, et al. (January 2016). "Aptamer BC007 for neutralization of pathogenic autoantibodies directed against G-protein coupled receptors: A vision of future treatment of patients with cardiomyopathies and positivity for those autoantibodies". Atherosclerosis. 244: 44–47. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2015.11.001. PMID 26584137.
- ^ a b "Berlin Cures Announces Successful Completion of Phase 1 Study of BC 007 for the Treatment of Cardiomyopathy". BioSpace. 2018-08-22. Archived from the original on 2023-05-30. Retrieved 2023-05-30.
- ^ a b c d Lang, Carolin (2020-07-08). "Wirkstoff-Kandidat auf DNA Basis - Mit James Bond gegen Covid-19" [Drug candidate based on DNA - Fighting Covid-19 with James Bond]. Pharmazeutische Zeitung (PZ) - Die Zeitschrift der deutschen Apotheker (in German). Avoxa - Mediengruppe Deutscher Apotheker GmbH. ISSN 0031-7136. Archived from the original on 2020-07-08. Retrieved 2024-04-09.
- ^ Werner S, Wallukat G, Becker NP, Wenzel K, Müller J, Schimke I, Wess G (June 2020). "The aptamer BC 007 for treatment of dilated cardiomyopathy: evaluation in Doberman Pinschers of efficacy and outcomes". ESC Heart Failure. 7 (3): 844–855. doi:10.1002/ehf2.12628. PMC 7261533. PMID 32212256.
- ^ Dandel M, Wallukat G, Englert A, Lehmkuhl HB, Knosalla C, Hetzer R (December 2012). "Long-term benefits of immunoadsorption in β(1)-adrenoceptor autoantibody-positive transplant candidates with dilated cardiomyopathy". European Journal of Heart Failure. 14 (12): 1374–1388. doi:10.1093/eurjhf/hfs123. PMID 22892122.
- ^ Düngen HD, Dordevic A, Felix SB, Pieske B, Voors AA, McMurray JJ, Butler J (January 2020). "β1-Adrenoreceptor Autoantibodies in Heart Failure: Physiology and Therapeutic Implications". Circulation. Heart Failure. 13 (1): e006155. doi:10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.119.006155. PMID 31957469. S2CID 210831160.
- ^ Becker NP, Haberland A, Wenzel K, Göttel P, Wallukat G, Davideit H, et al. (May 2020). "A Three-Part, Randomised Study to Investigate the Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics and Mode of Action of BC 007, Neutraliser of Pathogenic Autoantibodies Against G-Protein Coupled Receptors in Healthy, Young and Elderly Subjects". Clinical Drug Investigation. 40 (5): 433–447. doi:10.1007/s40261-020-00903-9. PMC 7181550. PMID 32222912.
