| Raduga Kh-15 (NATO reporting name: AS-16 'Kickback') | |
|---|---|
 Raduga Kh-15 | |
| Type | Air-launched ballistic missile Air-to-ground missile Anti-radiation missile (Kh-15P) Anti-ship missile (Kh-15S) |
| Place of origin | Soviet Union |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1980 |
| Used by | Russia |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Raduga |
| Designed | 1974–1980 |
| Manufacturer | Dubna Machine-building Plant |
| Produced | 1980 |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 1,200 kg (2,650 lb) |
| Length | 478 cm (15 ft 8 in) |
| Diameter | 45.5 cm (17.9 in) |
| Wingspan | 92 cm (36.2 in) maximum |
| Warhead | conventional or nuclear |
| Warhead weight | 150 kg (331 lb) |
| Blast yield | 300 kt |
| Engine | solid-fuel RDTT-160 |
Operational range | 300 km (160 nmi) |
| Flight ceiling | 40,000 m (130,000 ft) |
| Maximum speed | Up to Mach 5[1] |
Guidance system | inertial guidance, active radar homing, or anti-radiation missile |
Launch platform | Tu-22M3, [1] |
The Raduga Kh-15 or RKV-15 (Russian: Х-15; NATO: AS-16 "Kickback"; GRAU:) is a Russian hypersonic aero-ballistic air-to-ground missile carried by the Tupolev Tu-22M and other bombers. Originally developed as a standoff nuclear air-to-ground missile similar to the U.S. Air Force's AGM-69 SRAM, versions with conventional warheads have been developed.
As of early 2019, it was uncertain whether the Kh-15 was in service, with rumors that it had been retired or placed in storage.[2]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/5Views:2 393 0063 990 2652 609202 4823 041 438
-
The US's Problem with Hypersonic Missiles
-
Russia’s Decoy Cruise Missile
-
Harpoon VS Kh-59 Cruise Missile
-
Hypersonic Kinzhal Missile Footage In Ukraine
-
S-550 anti-satellite missile: can you see it? #shorts
Transcription
Development
In 1967, MKB Raduga started developing the Kh-2000 as a replacement for the Kh-22 (NATO reporting name AS-4 Kitchen) heavy anti-shipping missile.[1] Development of the Kh-15 started some time in the early 1970s.[3] The sophistication of the design made it suitable for other roles, and a nuclear-tipped version was developed in tandem with the conventionally armed variant.[1] An upgrade under development was cancelled in 1991, but reports in 1998 suggested an upgraded Kh-15 might be fitted to Su-35 (Flanker-E) tactical aircraft.[3]
Design
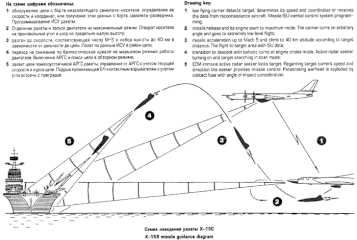
The Kh-15 climbs to an altitude of about 40,000 m (130,000 ft) and then dives in on the target, accelerating to a speed of about Mach 5.[1]
Operational history
It entered service in 1980. It can be carried by the Su-33, Su-34, Tu-95MS-6 'Bear-H', Tu-22M3 'Backfire C', and Tu-160 'Blackjack'.[4]
Variants
- Kh-15 (RKV-15) - the original version with nuclear warhead and inertial guidance
- Kh-15P - passive seeker for anti-radar use
- Kh-15S - active radar seeker for anti-shipping use[1]
Operators
Current
Former
 Soviet Union - Passed onto successor states
Soviet Union - Passed onto successor states
Similar weapons
- KSR-5 (AS-6 'Kingfish') - heavy anti-surface missile carried under the wings of Tu-22M
- Kh-59 (AS-13 'Kingbolt') - ASM for tactical aircraft, up to 285 km range
- Kh-37 (updated version of AS-20 'Kayak') - land attack version of subsonic Kh-35 Anti-Ship missile, 250 km range
- AGM-69 SRAM - 1000 kg US missile with up to 170 km range
Photo Gallery
-
Kh-15 from rear
-
Mission profile
Notes
- ^ a b c d e f "Kh-15, RKV-15 (AS-16 'Kickback')", Jane's Air-Launched Weapons, 2008-08-01, archived from the original on 2019-10-18, retrieved 2009-02-03
- ^ Kristensen, Hans M.; Korda, Matt (4 March 2019). "Russian nuclear forces, 2019". Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists. 75 (2): 73–84. Bibcode:2019BuAtS..75b..73K. doi:10.1080/00963402.2019.1580891.
- ^ a b "Kh-15 (AS-16 'Kickback'/RKV-15)", Jane's Strategic Weapon Systems, 2008-09-02, archived from the original on 2019-10-18, retrieved 2009-02-06
- ^ "АО "Корпорация Тактическое Ракетное Вооружение"". Archived from the original on 2014-08-06. Retrieved 2016-08-25.
References
- Gordon, Yefim (2004). Soviet/Russian Aircraft Weapons Since World War Two. Hinckley, England: Midland Publishing. ISBN 1-85780-188-1.
- Healey, John K. (January–February 2004). "Retired Warriors: 'Cold War' Bomber Legacy". Air Enthusiast. No. 109. pp. 75–79. ISSN 0143-5450.