| Vesicular appendages of epoöphoron | |
|---|---|
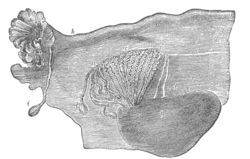 Broad ligament of adult, showing epoöphoron. (From Farre, after Kobelt.) a, a. Epoöphoron formed from the upper part of the Wolffian body. b. Remains of the uppermost tubes sometimes forming appendices. c. Middle set of tubes. d. Some lower atrophied tubes. e. Atrophied remains of the Wolffian duct. f. The terminal bulb or hydatid. h. The uterine tube, originally the duct of Müller. i. Appendix attached to the extremity. l. The ovary. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | appendices vesiculosae epoöphori appendices vesiculosæ[1] hydatids of Morgagni[1] |
| TA98 | A09.1.05.004 |
| TA2 | 3543 |
| FMA | 18696 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Vesicular appendages of the epoöphoron are small pedunculated vesicles of the fimbriae of the uterine tube, or connected to the broad ligament. They were described by Giovanni Battista Morgagni and are remnants of the cranial part of the mesonephric duct. Typically they are asymptomatic.
In the male, remnants of the paramesonephric duct may be present as well and are also known as appendix of testis or hydatid of Morgagni.
They are rarely absent, and are attached either to the free margin of the mesosalpinx or to one of the fimbriae, and are pedunculated vesicles, filled with fluid, about the size of a small pea. The pedicles frequently attain a considerable length.[1]
See also
References
- ^ a b c Sobotta, Johannes (1906). Atlas and text-book of human anatomy (3 v.2 ed.). Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders Company. p. 148.
External links
