| Perivitelline space | |
|---|---|
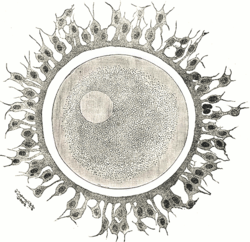 Human ovum. The zona pellucida is seen as a thick clear girdle surrounded by the cells of the corona radiata. The perivitelline space is between the zona pellucida and the oocyte membrane. | |
| Anatomical terminology |
The perivitelline space is the space between the zona pellucida and the cell membrane of an oocyte or fertilized ovum.[1] In the slow block to polyspermy, the cortical granules released from the ovum are deposited in the perivitelline space. Polysaccharides released in the granules cause the space to swell, pushing the zona pellucida farther from the oocyte.[1] The hydrolytic enzymes released by the granules cause the zona reaction, which removes the ZP3 ligands from the zona pellucida.[1]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:220 164381 2283 493
-
General Embryology - Detailed Animation On Fertilization
-
How to Get Pregnant with ICSI? Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection Procedure Step by Step Video IVF
-
Ovulation, Fate of ovum and ovarian follicle [General Embryology, Female Reproductive Physiology]
Transcription
when ejaculation occurs during intercourse approximately 200 million sperm or spermatozoa are deposited into the vagina they swim through the cervix propelled by with whip-like motions of their tails or Flagela after which muscular contractions of the uterus direct them to the uterine tubes this process usually takes between 30 minutes and two hours only around 200 spermatozoa will reach the secondary oocyte in the uterine tube and of these only one will fertilize it fertilization cannot occur until two processes have taken place capacitation and the acrosomal reaction these can take several hours capacitation is not fully understood but secretions from the uterus wall and uterine tube destabilize the plasma membrane surrounding the head the spermatozoa or acrosome resulting in the membrane becoming more fluid which helps to prepare the spermatozoa for the events a fertilization the spermatozoa become hyperactive their flagella beat more frequently and their heads move laterally the capacitated spermatozoa moved through the corona radiata a dense layer of granulosa cells surrounding the oocyte and come into contact with the zona pellucida the zona pellucida expresses specific receptor proteins called ZP3 which bind to proteins expressed in the heads of the spermatozoa the binding ZP3 triggers the acrosome reaction during which the enzymatic contents of the acrosome are released these enzymes help to digest a path through the zona pellucida allowing the spermatozoa to enter the perivitelline space and reach the plasma membrane of the secondary oocyte with which it fuses to ensure that only one spermatozoa and penetrates the zona pellucida infuses with the oocyte membrane fusion of the spermatozoon and oocyte membranes activates a fast and a slow block to polyspermy during fast blocked polyspermy after fusion the oocyte membrane depolarizes preventing other spermatozoa from fusing with it slow block to polyspermy is also stimulated by this depolarization during slow block to polyspermy a wave of intracellular calcium is released causing small cortical granules beneath the oocyte membrane to release their contents renderings ZP3 inactive and making the zona pellucida impermeable upon the spermatozoon entering the oocyte undergoes meiosis II and further develops into the female pro nucleus during this time the sperm develops into the male pro nucleus and the two Pro nuclei fuse to form a single diploid nucleus or zygote
Clinical importance
Clinically, the perivitelline space is relevant because it is where the polar body lodges after meiosis.
References
External links
- Histology image: 14805loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University
