| The ancient Near East |
|---|
 |
This timeline tries to compile dates of important historical events that happened in or that led to the rise of the Middle East. The Middle East is the territory that comprises today's Egypt, the Persian Gulf states, Iran, Iraq, Israel and Palestine, Cyprus, Jordan, Lebanon, Oman, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. The Middle East, with its particular characteristics, was not to emerge until the late second millennium AD. To refer to a concept similar to that of today's Middle East but earlier in time, the term ancient Near East is used.
This list is intended as a timeline of the history of the Middle East. For more detailed information, see articles on the histories of individual countries. See ancient Near East for ancient history of the Middle East.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/5Views:2 229 9921 779 9833 029 7321 664 8021 280 433
-
The History of the Middle East: Every Year
-
The Story Of The Israel vs Palestine Conflict | Promises & Betrayals | Timeline
-
Timeline of World History | Major Time Periods & Ages
-
Colonel Gaddafi: Terror Of The Middle East | Evolution Of Evil | Timeline
-
The Ancient Middle East: Every Year
Transcription
Paleolithic period
- 16000 BC – Kebaran period
- 13050 to 7050 BC – Natufian culture
- 12500 BC – The world's oldest evidence of bread-making has been found at Shubayqa 1, in Jordan
- 11000 BC – The oldest known evidence of beer found in Mount Carmel
Neolithic period
- 10000 BC – Pre-Pottery Neolithic A
- 10000 BC – earliest neolithic sanctuaries at Göbekli Tepe in southern Anatolia
- 9300 BC – first cultivating of wild emmer wheat in Netiv HaGdud and other sites in Jordan by hunter gatherers[1]
- 10000 to 8800 BC — Shepherd Neolithic
9th millennium B.C.
- 8500 BC – first domestication of the cow (taurine line from the aurochs near Çayönü Tepesi in southeastern Anatolia and Dja'de el-Mughara in northern Iraq).[2]
- 8400 to 8100 BC – first settlements at Nevali Cori in Anatolia
- 8200 to 7650 BC – first domestication of emmer wheat near Damascus, Syria
8th millennium BC
- 8000 BC – human settlements at Sagalassos in southwest Anatolia
- 8000 BC – first domestication of goats from the bezoar ibex in Iran
- 8000 BC – first domestication of einkorn wheat near Karaca Dağ in southeast Anatolia.
- 8000 BC – first domestication of Durum wheat near Karaca Dağ in the Levant and the Ethiopian Highlands
- 7500 BC – Çatalhöyük, very large Neolithic and Chalcolithic settlement in southern Anatolia
- 7000 BC – Jarmo, one of the oldest agricultural communities, in northern Iraq
7th millennium BC
- 7000 to 6500 BC – early undecorated, unglazed and low-fired pottery in Hassuna
- 7000 BC — settlements in Byblos
- 7000 BC — Neolithic farmers start to move in to Europe, stimulating the European neolithic for over 3 thousand years
- 6000 to 4000 BC – invention of the potter's wheel in Mesopotamia
6th millennium BC
- 6000 BC – first irrigation and flood control in Mesopotamia and Egypt
- 6000 to 4300 BC – first sail boats in Mesopotamia[3]
- 6000 to 3000 BC — Pre-dynastic Egypt
- 5600 BC – Black Sea floods according to the Black Sea deluge theory
- 5509 BC – date of creation according to the Byzantine calendar
- 5500 BC – first large scale agriculture by the Sumerians and in the valley of the Nile
- 5500 BC – the oldest discovered Sumerian settlement at Tell el-'Oueili
- 5403 BC – expulsion from the Garden of Eden according to the Genealogies of Genesis
- 5400 BC – Eridu
- 5100 BC – first Temples in South Mesopotamia
- 5000 BC — Byblos is named a city
- 5000 BC — Aleppo is settled
- 5000 BC — Uruk
5th millennium BC
- 4500 BC – civilization of Susa and Kish in Mesopotamia
- 4570 to 4250 BC – Merimde culture on the Nile
- 4400 to 4000 BC – Badari culture on the Nile
- 4000 BC – first use of light wooden ploughs in Mesopotamia
- 4000 BC – Egyptians discover how to make bread using yeast
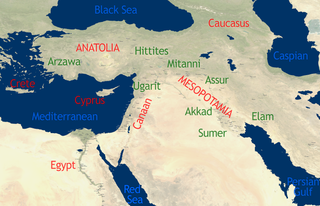
Ancient Near East
4th millennium BC
- 4000 to 3000 BC – domestication of the African wild ass in Egypt or Mesopotamia, producing the donkey
- 4000 BC – city of Ur in Mesopotamia
- 4000 to 3100 BC – Uruk period
- 4000 to 3000 BC – Naqada culture on the Nile
- 3760 BC – date of creation according to some interpretations of Jewish chronology
- 3650 BC – The foundation of the city of Gaziantep
- 3600 BC – first civilization in the world: Sumer (city-states) in modern-day southern Iraq[4]
- 3500 BC – City of Ebla in Syria is founded
- 3500 to 3000 BC – one of the first appearances of wheeled vehicles in Mesopotamia
- 3500 BC – beginning of desertification of the Sahara: the shift from a habitable region to a barren desert
- 3500 BC – first examples of Sumerian writing in Mesopotamia, in the cities of Uruk and Susa (cuneiform writings)
- 3500 BC – first cities in Egypt
- 3300 BC – Earliest Cuneiform writings
- 3200 BC – Iry-Hor reigns as pharaoh of Upper Egypt, the earliest historical person known by name
- 3100 BC – King Narmer unifies the Upper and Lower Egyptian Kingdoms, and gives birth to the world's first nation
- 3100 to 2686 BC – early Dynastic Period (Egypt)
- 3100 BC – Earliest hieroglyphs
- 3000 BC – The temple of Haddad in Aleppo
- 3000 to 2800 BC – Earliest evidence of Taxation found in Egypt
3rd millennium BC
- 3000 to 2000 BC – First domestication of the dromedaries in Somalia and southern Arabia
- 3000 to 2300 BC – First Kingdom of Ebla
- 2900 to 2350 BC – First ziggurats in Sumer
- 2900 to 2500 BC – First Kingdom of Mari
- 2800 BC – Beginning of Uruk's decline
- 2700 to 539 BC – Elam
- 2600 to 2350 BC – early Dynastic III period in Mesopotamia
- 2600 to 2300 BC – Kingdom of Nagar
- 2600 to 2025 BC – Early Assyrian Period
- 2575 to 2150 BC – Old Kingdom of Egypt
- 2560 BC – completion of the Great Pyramid of Giza
- 2500 BC – First use of war wagons as recorded by the Standard of Ur
- 2500 BC – First domestication of the camel in central Asia and Arabia[5][6][7]
- 2500 BC – Ur-Nina first king of Lagash
- 2500 to 2290 BC – Second Kingdom of Mari
- 2340 to 2280 BC – Reign of Sargon of Akkad, founder of the dynasty of the Akkad
- 2334 to 2154 BC – Akkadian Empire
- 2300 to 2000 BC – Second Kingdom of Ebla
- 2266 to 1761 BC – Third Kingdom of Mari
- 2254 to 2218 BC – Naram-Sin of Akkad, under whom the empire reached its maximum strength and the first taking the title "god of Akkad"
- 2200 BC – Akkad taken by the Guti
- 2112 to 2094 BC – Ur-Nammu, founder of the Third Dynasty of Ur
- 2111 to 2004 BC – Third Dynasty of Ur
- 2052 to 1570 BC – Middle Kingdom in Egypt
- 2025 to 1378 BC – Old Assyrian Empire
- 2004 BC – Elamites destroy Ur
- 2004 to 1763 BC – Rise of the Amorites who established several city-states in Mesopotamia
- 2000 to 1600 BC – Third Kingdom of Ebla
- 2000 to 1334 BC – Kingdom of Qatna
- 2000 BC – First use of the spoke-wheel by the Andronovo culture and soon after used by horse cultures of the Caucasus region in war chariots
2nd millennium BC
- 1900 BC – Hittites Old Kingdom in Anatolia
- 1800 BC – civilization in Canaan
- 1800 to 1200 BC – the emergence of the city of Ugarit when it ruled a coastal kingdom, trading with Egypt, Cyprus, the Aegean, Syria, the Hittites, and others
- 1792 to 1750 BC – the reign of Hammurabi of the First Babylonian Dynasty, extended control throughout Mesopotamia, known for the Code of Hammurabi, one of the earliest codes of law
- 1775 to 1761 BC – the reign of Zimri-Lim of Mari, extended control throughout Syria and Upper Mesopotamia, he was allied to Hammurabi
- 1763 to 1595 BC – Paleo-Babylonian Empire
- 1725 to 1550 BC – Hyksos (Canaanite) domination of Egypt
- 1600 to 1360 BC – Egyptian domination over Canaan and Syria
- 1594 BCE – Kassites take Babylon
- 1595 to 1155 BC – Kassite dynasty
- 1550 to 1077 BC – New Kingdom of Egypt
- 1500 to 1300 BC – Kingdom Mitanni, a Hurrian-speaking state in northern Syria and southeast Anatolia
- 1500 to 539 BC – Phoenicia and the spread of their alphabet from which almost all modern phonetic alphabets derived
- 1457 BC – Battle of Megiddo
- 1380 to 1336 BC – Shuppiluliuma, king of the Hittites who challenged Egypt for control of the lands between the Mediterranean and the Euphrates
- 1370 to 1200 BC – Hittite Empire
- 1350 to 1050 BC – Middle Assyrian Empire

- 1300 BC – discovery of iron smelting and smithing techniques in Anatolia or the Caucasus: start of the Iron Age
- 1300 to 125 BC – Kingdom of Edom
- 1274 BC – Battle of Kadesh between the Egyptian Empire under Ramesses II and the Hittite Empire under Muwatalli II,[8] largest chariot battle ever fought[9]
- 1259 BC – Egyptian-Hittite peace treaty, the first peace treaty ever recorded in history
- 1245 to 1208 BC – Tukulti-Ninurta I, king of Assyria, first native Mesopotamian ruler in Babylon, took on the ancient title "King of Sumer and Akkad"
- 1237 BC – Battle of Nihriya, resulting in Assyrian victory over the Hittites for control over remnants of the former empire of Mitanni in Asia Minor and the Levant
- 1234 BC – Babylon taken by the Assyrians
- 1200 to 1050 BC – Bronze Age collapse
- 1200 BC – oldest Phoenician alphabet inscription engraved on the sarcophagus of King Ahiram
- 1200 to 884 BC – Sea Peoples, conjectured groups of seafaring raiders, invaded Anatolia, Syria, Canaan, Cyprus, and Egypt
- 1200 to 546 BC – Lydian Empire
- 1200 to 732 BC – Aramaean Kingdom of Aram-Damascus
- 1190 BC – Hattusha, capital of the Hittites, taken by the Sea Peoples
- 1184 BC – Fall of Troy
- 1180 to 700 BC – Neo-Hittite kingdoms also known as Syro-Hittite states
- 1155 BC – Babylon taken by Elamites
- 1100 to 539 BC – Neo-Elamite period
- 1087 BC – Babylon destroyed by Assyrians
- 1070 BC to 350 AD – Cushites, an ancient African Nubian kingdom in Sudan
- 1102 to 850 BC – estimated period in which Homer lived
- 1069 to 664 BC – Third Intermediate Period of Egypt
- 1050 to 930 BC – Kingdom of Israel
- 1041 BC – King David captures Jerusalem, designates it the capital of the united Kingdom of Israel
- 1004 BC – King Solomon lays the foundation for the First Temple
1st millennium BC
- 927 BC – Jerusalem becomes the capital of the (southern) Kingdom of Judah after the split of the United Monarchy
- 884 to 858 BC – Ashurnasirpal II, king of Assyria, embarked on a vast program of expansion, known for his harshness, moved his capital to the city of Kalhu (Nimrod)
- 884 to 612 BC – Neo-Assyrian Empire
- 800 to 480 BC – Archaic period in Greece with the rise of the city-states, Greek colonies, and Epic Greek poetry: onset of Classical Antiquity
- 776 BC – first Olympic Games
- 745 to 727 BC – Tiglath-Pileser III, king of Assyria who introduced advanced civil, military, and political systems into the empire
- 711 BC – Sargon II conquers the kingdom of Israel and exiles the inhabitants of Samaria
- 710 BC – Sargon II captures Babylonia
- 689 BCE – Babylon destroyed by Sennacherib, king of the Assyria
- 677 BC – Esarhaddon, king of Assyria, defeats the rebellion of Abdi-Milkutti, the king of the Phoenician state of Sidon
- 678 to 549 BC – Median Empire
- 672 to 525 BC – Twenty-sixth dynasty of Egypt
- 667 BC – Ashurbanipal, king of Assyria, defeated the 25th Dynasty king Taharqa near Memphis
- 626 to 539 BC – Chaldean Empire (Neo-Babylonian Empire)
- 624 to 545 BC – Thales of Miletus, first philosopher in Ancient Greek philosophy, founder of the Milesian school
- 612 BC – Fall of Nineveh by a coalition Babylonians, Medes, Persians, Chaldeans, Scythians, and Cimmerians, leading to the destruction of the Neo-Assyrian Empire
- 605 BC – Battle of Carchemish between the Babylonians and the Egyptians allied with the remnants of the Assyrian army
- 609 BC – Battle of Megiddo (609 BC) between Necho II and Josiah of Judea
- 597 BC – King Nebuchadnezzar II of Babylon capturing Jerusalem
- 587 BC – King Nebuchadnezzar II of Babylon destroys Jerusalem and Solomon's Temple
- 570 to 495 BC – Pythagoras, founder of Pythagoreanism
- 600 or 576 – 530 BC – Cyrus the Great conquered Babylon and created the Persian Achaemenid Empire
- 550 to 330 BC – Achaemenid Empire
- 547 BC – Battle of Pteria between the Lydian Empire and the Achaemenid empire
- 539 BC – Fall of Babylon
- 537 BC – Cyrus allows the Israelites to return from the Babylonian captivity and rebuild the Temple
- 522 to 486 BC – reign of Darius the Great, third king of the Persian Achaemenid Empire
- 516 BC – completion of the Second Temple
- 510 to 323 BC – Classical Greek period with large annexations by the Persian Empire and a powerful influence on the Roman Empire and western civilization
- 500 BC – Ionian Revolt
- 499 to 449 BC – Greco-Persian Wars, finally won by the Greek city-states
- 480 to 479 BC – Xerxes invades Greece, start of Second Persian invasion of Greece
- 477 BC – founding of the Delian League, an association of Greek city-states under Athenian hegemony
- 431 to 404 BC – Peloponnesian War between Sparta and Athens leading to the end of Athens' hegemony and weakening of Greece
- 353 to 350 BC – Mausoleum at Halicarnassus is built in Lydia, one of the seven wonders of the ancient world
- 334 to 262 BC – Zeno of Citium, Founder of the Stoic school of philosophy
- 330 BC – Alexander the Great conquered Persia
- 323 to 31 BC – Hellenistic period with Greek influence in Europe, Africa, and Asia, in the arts, exploration, literature, theatre, architecture, music, mathematics, philosophy, and science
- 316 to 240 AD – Arcesilaus, founder of Academic skepticism
- 300 BC – Foundation of the city of Antioch by Seleucus I Nicator
- 279 to 206 BC – Chrysippus of Soli, creator of the first system of Propositional logic
- 247 BC to 224 AD – Parthian Empire
- 230 to 140 BC – Diogenes of Babylon, scholarch of the Stoic school in Athens in 2nd century BC
- 190 to 120 BC – Hipparchus, mathematician, astronomer and geographer from Bithynia who studied at Alexandria and Babylon. He discovered Axial precession, and gave the first tables of chords, analogous to modern tables of sine values, and used them to solve problems in trigonometry and spherical trigonometry.
- 163 BC to 72 AD – Kingdom of Commagene
- 150 to 75 BC – Zeno of Sidon, Epicurean philosopher known through his pupil, Philodemus
- 132 BC to 214 AD – Kingdom of Osroene
- 125 to 68 BC – Antiochus of Ascalon, the pioneer of Middle Platonism
- 110 to 40/35 BC – Philodemus Epicurean philosopher and poet, author of ethics, theology, rhetoric, music, poetry and history of philosophical schools
- 100 to 44 BC – Julius Caesar
- 92 BC to 629 AD – Roman–Persian Wars
- 64 BC to 24 AD – Strabo, Greek geographer, philosopher, and historian from Pontus, Asia Minor
- 63 BC – Romans annex all of Asia Minor, Syria and Judea under Pompey
- 48 BC to 642 AD – Destruction of the Library of Alexandria, one of the largest and most significant libraries of the ancient world
- 31 BC – Emergence of the Roman Empire as signified by the Battle of Actium
- 30 BC – Romans annex Egypt
- 20 BC to 50 AD – Philo of Alexandria, prominent Hellenistic Jewish philosopher
- 4 BC – Birth of Jesus of Nazareth
1st millennium AD
- 27/30 AD – The ministry of Jesus of Nazareth starts
- 30 to 100 AD – Apostolic Age, onset of Christianity
- 37 to 100 AD – Josephus, Famous first century Roman-Jewish philosopher-historian
- 50 AD – Apollodorus of Damascus, Syrian architect and engineer who introduced several Eastern innovations to the Roman Imperial style, such as making the dome a standard
- 60 to 120 AD – Nicomachus, a Neopythagorean who wrote about the mystical properties of numbers, and author of Introduction to Arithmetic and Manual of Harmonics in Greek
- 66 to 136 AD – Jewish–Roman wars and Jewish diaspora
- 129 to 216 AD – Galen, a physician, surgeon and philosopher in the Roman Empire from Pergamon, Asia Minor
- 135 AD – Roman Emperor Hadrian renamed Iudaea Province into Syria Palaestina
- 150 AD – Albinus, Platonist philosopher, teacher of Galen
- 160 to 210 AD – Sextus Empiricus, Pyrrhonist philosopher and physician most likely from Alexandria, author of most preserved accounts of Pyrrhonism
- 175 242 AD – Ammonius Saccas, one of the founders of Neoplatonism
- 184 to 253 – Origen, early Christian scholar and Church Father
- 200 AD – Alexander of Aphrodisias, Peripatetic philosopher, author of Prior Analytics, Topics, Meteorology, Sense and Sensibilia, and Metaphysics
- 2nd century AD to 241 AD – Kingdom of Hatra
- 204/5 to 270 – Plotinus, the author of the Enneads, one of the founders of Neoplatonism
- 240 AD – Diogenes Laërtius, biographer of ancient Greek philosophers, author of Lives and Opinions of Eminent Philosophers, a principal source for the history of ancient Greek philosophy.
- 285 to 628 AD – Byzantine–Sasanian wars
- 300 to 602 AD – Kingdom of the Lakhmids
- 330 to 1453 AD – Byzantine Empire, continuation of the Roman Empire in the east, until it fell to the Ottoman Empire
- 376 AD – large-scale irruption of Goths and others, and the subsequent onset of the Fall of the Western Roman Empire
- 394 AD – Theodosius I suppressed the Olympic Games as part of the campaign to impose Christianity as the state religion
- 412 to 485 AD – Proclus a Greek Neoplatonist philosopher who set forth one of the most elaborate and fully developed systems of Neoplatonism
- 5th century to 437 AD – Syrianus, Neoplatonist philosopher, author of a commentary on the Metaphysics of Aristotle and Plato's Timaeus
- 450 to 520 – Isidore of Alexandria one of the last Neoplatonist philosophers
- 458 to 538 AD – Damascius, the last of Neoplatonist philosophers
- 490 to 560 AD – Simplicius of Cilicia, Neoplatonist philosopher and commentator on Aristotle's de Caelo, Physica Auscultatio, and Categories, as well as a commentary upon the Enchiridion of Epictetus.
- 490 to 570 AD – John Philoponus, an Alexandrian philologist, Aristotelian commentator and Christian theologian, one of the first to propose a "theory of impetus" similar to the modern concept of inertia over Aristotelian dynamics
- 512 to 602 AD – Justinian dynasty of Eastern Roman Empire
Islamic Middle East
1st millennium AD


- 570 – Birth of Muhammad
- 573 - Birth of Abu Bakr
- 585 - Birth of Umar
- 573/576 - Birth of Uthman
- 601 – Birth of Ali
- 614 – Persecution of the Muslims by the Quraish (Migration to Abyssinia)
- 616 – Second migration to Abyssinia
- 620 – Ascension to the heavens
- 622 – Constitution of Medina, establishment of the first Islamic state
- 624: Battle of Badr, expulsion of the Bani Qainuqa Jews from Medina
- 626 – Siege of Constantinople
- 629 to 1050 – Arab–Byzantine wars
- 630 – Conquest of Mecca
- 632 – Death of Muhammad, Designation of the successor of Muhammad
- 632 to 661 – Rashidun Caliphate
- 633 to 651 – Muslim conquest of Persia
- 634 to 641 – Muslim conquest of the Levant (Syria)
- 639 to 642 – Muslim conquest of Egypt
- 642 to 799 – Khazar-Arab Wars weaken the Umayyad army and contribute to the eventual fall of the dynasty
- 642 to 870 – Islamic conquest of Afghanistan
- 656 to 661 – First Fitna (First Islamic Civil War)
- 660 – Construction of the Great Mosque of Kufa
- 661 to 750 – Umayyad Caliphate
- 670 to 742 – Muslim conquest of North Africa
- 674 – Siege of Constantinople (674–678) by the Umayyads against the Byzantines
- 680 – The Battle of Karbala takes place, martyrdom of Husayn ibn Ali, the grandson of the Prophet Muhammad
- 680 to 692 – Second Fitna (Second Islamic Civil War)
- 711 to 718 – Umayyad conquest of Hispania
- 711 to 714 – Muslim conquest in the Indian subcontinent
- 717 to 718 – Siege of Constantinople (717-718)
- 719 to 759 – Umayyad invasion of Gaul
- 738 – Caliphate campaigns in India
- 746 to 750 – Abbasid Revolution
- 750 to 1258 – Abbasid Caliphate
- 750 to 950 – Jabir ibn Hayyan, or anonymous authors writing under this name, pioneered organic chemistry
- 766 to 869 – Habash al-Hasib al-Marwazi, the first mathematician to describe the trigonometric ratios: sine, cosine, tangent and cotangent
- 770 to 840 – Khwarizmi, developed algebra
- 800 to 870 – Ahmad ibn Muhammad ibn Kathir al-Farghani, One of the prominent scientists involved in the calculation of the diameter of the Earth by the measurement of the meridian arc length along others
- 801 to 873 – Al-Kindi, promoter of Greek and Hellenistic philosophy, introduced Indian numerals
- 810 – House of Wisdom set up in Baghdad, where Greek and Indian mathematical and astronomy works were translated into Arabic
- 821 to 979 – Iranian Intermezzo
- 821 to 873 – Tahirid dynasty in Iran, Afghanistan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan
- 827 to 902 – Muslim conquest of Sicily
- 836 to 901 – Thabit Ibn Qurra, discovered a theorem which enables pairs of amicable numbers to be found
- 847 to 871 – Emirate of Bari
- 850 to 934 – Abu Zayd al-Balkhi, pioneer of mental health, medical psychology, cognitive psychology, cognitive therapy, psychophysiology and psychosomatic medicine
- 858 to 929 – Al-Battani, Syrian Arab mathematician and astronomer who introduced a number of trigonometric relations such as tan θ
- 861 to 1003 – Saffarid dynasty, an Iranian Persian empire
- 864 to 930 – Al-Razi, advocate of hygiene and patients' psychology, wrote on alkali, caustic soda, soap, glycerine and naphtha in "Book of the Secret of Secrets"
- 872 to 950/951 – Al-Farabi (Alpharabius), pioneered social psychology and consciousness studies
- 874 to 941 – Minor Occultation of the Mahdi
- 875/819 to 999 – Samanid dynasty, an Iranian empire
- 895 to 1004 – Hamdanid dynasty of Aleppo and Mosul
- 899 to 976 – Qarmatian revolution
- 909 – Abdullah al-Mahdi Billah, founded the Fatimid Caliphate
- 909 to 1171 – Fatimid Caliphate, originally based in Tunisia, spanned a vast area of the Arab lands, ultimately made Egypt its centre
- 928 – Construction of Al-Hakim Mosque
- 929 to 1031 – Caliphate of Córdoba, with the Iberian peninsula as an integral province, ruled from Damascus
- 934 – Imad al-Dawla rise to power and establishment of the Buyid dynasty
- 934 to 1062 – Buyid dynasty in Iran
- 936 to 1013 – Al-Zahrawi, pioneer of surgery
- 941 – The Major Occultation of the Mahdi starts
- 942 to 979 – Sallarid dynasty in Iran, Azerbaijan and Armenia
- 945 – Sayf al-Dawla rise to power
- 965 to 1091 – Emirate of Sicily
- 965 to 1040 – Ibn al-Haytham, Founded experimental psychology, psychophysics, phenomenology and visual perception as well as optics and experimental physics.
- 970 – foundation of Al-Azhar University, oldest Islamic institution for higher studies
- 980 to 1037 – Avicenna, pioneer of neuropsychiatry, thought experiment, self-awareness and self-consciousness
- 990 to 1081 – Numayrid dynasty of Harran and Raqqa
- 990 to 1096 – Uqaylid dynasty of Mosul
2nd millennium AD
- 1004 – House of Knowledge built by the Fatimid caliph Al-Hakim bi-Amr Allah, said to have contained more than 1,600,000 books
- 1024 to 1080 – Mirdasid dynasty of Aleppo
- 1037 to 1194 – arrival of the Turkish Seljuq Empire, and the subsequent end of Arab dominance
- 1044 or 1048 to 1123 – Al-Khayyam gave a classification of cubic equations with geometric solutions using conic sections, extracted roots using the Indian decimal system
- 1096 to 1487 – Crusades; four crusader states are established in the region for more than two centuries: The County of Edessa (1097–1150); the Principality of Antioch (1098–1287), the County of Tripoli (1102–1289), and the Kingdom of Jerusalem (1099–1291).
- 1100 to 1166 – Muhammad al-Idrisi, known for having drawn some of the most advanced ancient world maps
- 1105 to 1185 – Ibn Tufail, pioneer of tabula rasa and nature versus nurture, author of the first Philosophical novel
- 1126 to 1198 – Averroes pioneer of Parkinson disease, philosophical commentator
- 1136 to 1206 – Ismail al-Jazari, Muslim polymath: a scholar, inventor, mechanical engineer, artisan and artist from Jazira. He described the crankshaft that transforms continuous rotary motion into a linear reciprocating motion.
- 1147 to 1269 – Almohad Caliphate, a Moroccan Berber Muslim movement, started by Ibn Tumart among the Masmuda
- 1171 to 1260 – Ayyubid dynasty
- 1192 to 1489 – Kingdom of Cyprus
- 1201 to 1274 – Nasir al-Din al-Tusi, Persian polymath who created very accurate tables of planetary motion, an updated planetary model, and critiques of Ptolemaic astronomy. He is often considered the creator of trigonometry as a mathematical discipline in its own right, and he is believed to have influenced Copernican heliocentrism
- 1204 – Sack of Constantinople by the crusaders
- 1213 to 1288 – Ibn Al-Nafis, discovered the lesser circulatory system of the heart and the lungs, and described the mechanism of breathing and its relation to the blood
- 1218 to 1221 – Mongol conquest of Khwarezmia marked the beginning of the Mongol conquest of the Islamic states
- 1241 to 1244 – Mongol invasions of Anatolia
- 1250 to 1517 – Mamluk Sultanate of Cairo
- 1258 – Forces of the Mongol Empire sack Baghdad and destroy the House of Wisdom, marking the end of the Islamic Golden Age
- 1260 to 1323 – Mongol invasions of the Levant
- 1260 – First major defeat the Mongols suffer at Battle of Ain Jalut, Mongol invasion of the Levant is halted
- 1261 to 1517 – Abbasid Caliphate in Cairo, symbolic title
- 1275 – Hasan al-Rammah, Arab chemist and engineer who studied gunpowders and explosives, and sketched prototype instruments of warfare, including the first torpedo. He also invented new types of gunpowder, and he invented a new type of fuse and two types of lighters
- 1299 to 1923 – rise of the Ottoman Empire
- 1300 – deportation of the last Muslims from Lucera, Italy
- 1303 – Battle of Marj al-Saffar, defeat for the Mongols, which put an end to Ghazan Khan's invasions of Syria
- 1332 to 1406 – Ibn Khaldun, set the basis of social sciences such as demography, cultural history, historiography, philosophy of history, sociology and economics
- 1347 – a fleet of Genoese trading ships fleeing Caffa (Theodosia) reached the port of Messina and spreads the Black Death
- 1380 – al-Kashi, contributed to development of decimal fractions for approximating algebraic numbers and real numbers such as pi
- 1393 to 1449 – Ulugh Beg commissions an observatory at Samarqand in Uzbekistan
- 1394 to 1465 – Appearance of the Arquebus, ancestor of modern firearms, in the Ottoman Empire and Europe
- 1453 – Fall of Constantinople
- 1453 to 1550 – Classical Age of the Ottoman Empire
- 1501 to 1736 – Safavid Iran
- 1516 to 1517 – Ottoman-Mamluk War, Ottomans seize Cairo in 1517
- 1526 to 1585 – Taqi ad-Din Muhammad ibn Ma'ruf, a Syrian polymath who built the Constantinople observatory, the largest observatory of the medieval world. He described a steam turbine with the practical application of rotating a spit in 1551. He also had his own method of finding coordinates of stars that was most precise at the time, and he proved the law of reflection observationally. He authored more than ninety books on a variety of different subjects
- 1550 to 1700 – Transformation of the Ottoman Empire
- 1700 to 1789 – Ottoman ancien régime
- 1709 to 1738 – Hotak dynasty of Iran and Afghanistan
- 1751 to 1794 – Zand dynasty of Iran
Contemporary Middle East
2nd millennium AD
- 1789 to 1925 – Qajar Iran
- 1798 – Napoleon Bonaparte leads a campaign in Egypt and Syria
- 1828 to 1914 – Decline and modernization of the Ottoman Empire
- 1828 – Al-Waqa'i' al-Misriyya, oldest newspaper ever established in Egypt
- 1830 to 1950 – Nahda or "Arab cultural renaissance"
- 1831 to 1833 – First Egyptian-Ottoman War, Egypt under Muhammad Ali seizes the Levantine provinces
- 1834 to 1835 – Syrian Peasant Revolt takes place in the Levant, but is suppressed
- 1837 – The first newspaper in Iran, Kaghaz-i Akhbar (The Newspaper), was created for the government by Mirza Saleh Shirazi
- 1838 – 1838 Druze revolt
- 1839 to 1841 – Egypt loses control over the Levantine provinces after the Second Egyptian-Ottoman War
- 1840 – Oriental Crisis of 1840
- 1840 – Convention of London
- 1851 – Darul Funun, one of the oldest modern universities in the Middle East, is established by Amir Kabir
- 1860 – Al-Jinan, an Arabic-language political and literary bi-weekly magazine established in Beirut by Butrus al-Bustani, continues until 1886
- 1860 – 1860 Mount Lebanon civil war
- 1861 – Mount Lebanon Mutasarrifate is established
- 1862 to 1892 – development of the internal combustion engine rivals the steam engine, and ultimately makes petroleum an important political factor in the following century
- 1869 – Construction of the Suez Canal is completed
- 1875 – Al-Ahram, second oldest and widest newspaper in circulation in Egypt is established
- 1882 – British troops occupy Cairo, Egypt becomes British protectorate
- 1888 – Ibrahim al-Yaziji, a Lebanese Christian writer, philologist, poet and journalist published a rich modern Arabic translation of the Bible. His works were also crucial to the establishment of the Arabic typewriter
- 1909 to 1921 – Arab nationalist organizations Al-Fatat and Al-'Ahd are established to liberate and unify Arab territories that were under Ottoman rule
- 1914 to 1918 – Middle Eastern theatre of World War I
- 1917 – Arthur Balfour, Foreign Minister of Great Britain, in a letter to Lord Rothschild, gives British government approval to Zionist's goal of building a "national home" in Palestine
- 1918 to 1922 – Defeat and dissolution of the Ottoman Empire
- 1918 – Britain and France occupy former Ottoman Empire lands
- 1919 to 1921 – Franco-Syrian War
- 1919 to 1923 – Asia Minor Catastrophe reshapes Anatolia, as continuous fighting incorporates the newly founded Republic of Turkey, Armenia, France, Greece
- 1920 – Iraqi revolt against the British
- 1922 – Egypt is granted nominal independence from the United Kingdom.
- 1922 to 1923 – Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon and British Mandate of Palestine and the Emirate of Transjordan come into effect.
- 1924 – Abolition of the Caliphate as part of Atatürk's Reforms
- 1925 to 1927 – Great Syrian Revolt against the French Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon
- 1925 – Sheikh Said rebellion of Kurds against Turkey
- 1925 – Deposition of the Qajar dynasty of Iran
- 1927 to 1930 – Ararat rebellion of Kurds, as Republic of Ararat is declared, but dissolved upon defeat
- 1932 – Kingdom of Saudi Arabia declared in unification of Najd and Hejaz
- 1933 to 1936 – Tribal revolts in Iraq of Assyrians in Simele, Shia in the south and Kurds in the north
- 1934 – Saudi–Yemeni War
- 1935 – Persia becomes Iran
- 1936 to 1939 – Arab revolt in Palestine
- 1937 – Dersim rebellion, is the largest uprising of the Kurds against Turkey, massive casualties
- 1939 to 1945 – Mediterranean and Middle East Theatre of World War II
- 1946 – Emirate of Transjordan becomes Kingdom of Jordan (named Transjordan until 1948)
- 1946 – Kurdish Republic of Mahabad declared along with Azerbaijan People's Government, but defeated by Iranian military forces and dissolved
- 1947 – UN General Assembly proposes to divide Palestine into an Arab and Jewish state
- 1948 – Israel declares independence and Arab–Israeli war erupts
- 1952 – After a revolution in Egypt the monarchy is overthrown
- 1953 – The coup d'état in Iran
- 1954 – Gamal Abdel Nasser becomes president of Egypt
- 1954 – Central Treaty Organization
- 1956 – Suez Crisis
- 1961 – First Iraqi–Kurdish War erupts in north Iraq.
- 1963 – Ba'ath Party comes to power in Iraq under the leadership of General Ahmad Hasan al-Bakr and Colonel Abdul Salam Arif
- 1964 – Abdul Rahman Arif stages military coup in Iraq against the Ba'th Party and brings his brother, Abdul Salam Arif, to power
- 1967 – Six-Day War, Israel occupies the Sinai Peninsula, Golan Heights, West Bank and Gaza Strip
- 1967 – Kurds revolt in Western Iran, the revolt is crushed
- 1968 – Ba'athists stage second military coup under General Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr, Saddam Hussein is made vice president of Iraq
- 1970 – Gamal Abdel Nasser dies; Anwar Sadat becomes president of Egypt
- 1971 – The Aswan High Dam is completed with Soviet help in finance and construction; independence of Kuwait, Qatar, Bahrain and the UAE
- 1973 – Yom Kippur War
- 1974 – The PLO is allowed to represent the people of Palestine in the UN
- 1974 to 1975 – Second Iraqi–Kurdish War
- 1975 to 1990 – Lebanese Civil War
- 1976 – Syria invades Lebanon
- 1978 – Camp David Accords
- 1979 – Saddam Hussein becomes president of Iraq; Iranian Revolution; Egypt–Israel peace treaty
- 1981 to 1989 – Iran–Iraq War results in 1–1.25 million casualties, Iraq uses chemical weapons against Iran and rebel Kurds; large scale economic devastation and surge in oil prices affect the global world economy
- 1981 – Assassination of Anwar Sadat
- 1982 – Israel invades Lebanon
- 1987 to 1990 – First Intifada
- 1990 – Iraq invades Kuwait
- 1991 – The Gulf War
- 1993 – Oslo Accords
- 1994 – 1994 civil war in Yemen
3rd millennium AD
- 2000 – Israeli troops leave Lebanon; Second Intifada
- 2001 – Members of al-Qaeda attacked sites in the U.S., this event is known as 9/11
- 2003 – United States invades and occupies Iraq
- 2004 – Houthi insurgency in Yemen
- 2005 – Syrian troops leave Lebanon as a result of the Cedar Revolution
- 2006 – The 2006 Israel-Lebanon conflict; Saddam Hussein executed for crimes against humanity
- 2010 – Arab Spring, which culminates in the Syrian Civil War with involvement of many regional powers to either support the Syrian opposition or the ruling Ba'ath party
- 2012 – The first MERS outbreak.
- 2014 – ISIS rises in Iraq and Syria; rival groups try to overthrow Syrian president
- 2015 – The Saudi intervention in Yemen
- 2017 – ISIS is defeated in Raqqa and Mosul, all control of territories in Syria and Iraq cease by 2019
- 2020 – COVID-19 pandemic, Assassination of Qasem Soleimani, Abraham Accords
- 2023 – Israel-Hamas war begins
See also
- History of the Middle East
- Cities of the ancient Near East
- Empires:
- Mesopotamia:
- Anatolia:
- Canaan:
- Egypt:
- Ancient Egypt: 3000 BC to 332 BC
- Ptolemaic Egypt: 332 BC to 30 BC
- Roman Egypt: 30 BC to 639 AD
- History of Arab Egypt: 639 to 1517
- History of Ottoman Egypt: 1517 to 1805
- Egypt under Mehemet Ali and his successors: 1805 to 1882
- History of Modern Egypt: since 1882
- Iran:
- Arabia:
- Timeline of Islamic history
- Timeline of Jewish history
- Timeline of the region of Palestine
- History of pottery in the Southern Levant
- British foreign policy in the Middle East
- United States foreign policy in the Middle East
References
- ^ "Which Society Cultivated Wheat First?".
- ^ McTavish, E.J., Decker, J.E., Schnabel, R.D., Taylor, J.F. and Hillis, D.M.year=2013 (2013). "New World cattle show ancestry from multiple independent domestication events". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110 (15): E1398–406. Bibcode:2013PNAS..110E1398M. doi:10.1073/pnas.1303367110. PMC 3625352. PMID 23530234.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Carter, Robert (2012). "19". In Potts, D.T. (ed.). A companion to the archaeology of the ancient Near East. Ch 19 Watercraft. Chichester, West Sussex: Wiley-Blackwell. pp. 347–354. ISBN 978-1-4051-8988-0. Retrieved 8 February 2014.
- ^ King, Leonid W. (2015) "A History of Sumer and Akkad" (ISBN 1522847308)
- ^ Mukasa-Mugerwa, E. (1981). The Camel (Camelus Dromedarius): A Bibliographical Review. International Livestock Centre for Africa Monograph. Vol. 5. Ethiopia: International Livestock Centre for Africa. pp. 1, 3, 20–21, 65, 67–68.
- ^ Scarre, Chris (15 September 1993). Smithsonian Timelines of the Ancient World. London: D. Kindersley. p. 176. ISBN 978-1-56458-305-5.
Both the dromedary (the seven-humped camel of Arabia) and the Bactrian camel (the two-humped camel of Central Asia) had been domesticated since before 2000 BC.
- ^ Bulliet, Richard (20 May 1990) [1975]. The Camel and the Wheel. Morningside Book Series. Columbia University Press. p. 183. ISBN 978-0-231-07235-9.
As has already been mentioned, this type of utilization [camels pulling wagons] goes back to the earliest known period of two-humped camel domestication in the third millennium B.C.
—Note that Bulliet has many more references to early use of camels - ^ near the modern village of Al-Houz in Syria's Al-Qusayr District. see Kitchen, K. A., "Ramesside Inscriptions", volume 2, Blackwell Publishing Limited, 1996, pp. 16–17.
- ^ Eggenberger, David (1985). An Encyclopedia of Battles. Dover Publications. p. 214. ISBN 9780486249131.