
Pterocarpans are derivatives of isoflavonoids found in the family Fabaceae. It is a group of compounds which can be described as benzo-pyrano-furano-benzenes (i.e. 6H-[1]benzofuro[3,2-c]chromene skeleton) which can be formed by coupling of the B ring to the 4-one position.[1]
2'-hydroxyisoflavone reductase is the enzyme responsible for the conversion in Cicer arietinum[2] and glyceollin synthase for the production of glyceollins, phytoalexins in soybean.[3]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/4Views:3475 4986 6361 502
-
Loan Calculator : Constant Amortization
-
Phytoalexin ||most important||
-
GPAT 2022 | MARATHON CLASS- 37 | RESIN TANNIN CARBOHYDRATE MARINE DRUGS AND FIBER
-
Concept of Phytoalexins in Urdu / Hindi . Lecture no = 16
Transcription
Known compounds
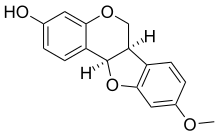


- Bitucarpin A and B, isolated from the aerial parts of Mediterranean plants Bituminaria morisiana and Bituminaria bituminosa[4]
- Erybraedin A and B, isolated from the stems of Erythrina subumbrans[5] and C, isolated from the leaves of Bituminaria morisiana[6]
- Erythrabyssin II, erystagallin A, erythrabissin-1, and erycristagallin isolated from the stems of Erythrina subumbrans[5]
- Glycinol, glyceollidin I and II, glyceollins (glyceollin I, II, III and IV), found in the soybean (Glycine max)[7][8]
- Glycyrrhizol A, isolated from the root of the Chinese licorice plant (Glycyrrhiza uralensis)
- Maackiain, isolated from the roots of Maackia amurensis subsp. Buergeri[9]
- Medicarpin, found in Medicago truncatula
- Morisianine, isolated from the seeds of Bituminaria morisiana[10]
- Orientanol A, isolated from the wood of Erythrina orientalis[11]
- Phaseolin, found in French bean seeds[12]
- Pisatin, found in Pisum sativum[13]
- Striatine, isolated from aerial parts of Mundulea striata[14]
- Trifolirhizin, found in Sophora flavescens
References
- ^ Pterocarpans on the National Library of Medicine – Medical Subject Headings
- ^ Tiemann, Karin; Hinderer, Walter; Barz, Wolfgang (23 March 1987). "Isolation of NADPH:isoflavone oxidoreductase, a new enzyme of Pterocarpan phytoalexin biosynthesis in cell suspension cultures of Cicer arietinum". FEBS Letters. Wiley. 213 (2): 324–328. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(87)81515-6. ISSN 0014-5793.
- ^ Welle R, Grisebach H (1988). "Induction of phytoalexin synthesis in soybean: enzymatic cyclization of prenylated pterocarpans to glyceollin isomers". Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 263 (1): 191–8. doi:10.1016/0003-9861(88)90627-3. PMID 3369863.
- ^ Pistelli, Luisa; Noccioli, Cecilia; Appendino, Giovanni; Bianchi, Federica; Sterner, Olov; Ballero, Mauro (2003). "Pterocarpans from Bituminaria morisiana and Bituminaria bituminosa". Phytochemistry. Elsevier BV. 64 (2): 595–598. doi:10.1016/s0031-9422(03)00190-0. ISSN 0031-9422. PMID 12943781.
- ^ a b Rukachaisirikul, Thitima; Innok, Phongsak; Aroonrerk, Nuntana; Boonamnuaylap, Woraluk; Limrangsun, Saranya; Boonyon, Chanakan; Woonjina, Umpawan; Suksamrarn, Apichart (2007). "Antibacterial Pterocarpans from Erythrina subumbrans". Journal of Ethnopharmacology. Elsevier BV. 110 (1): 171–175. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2006.09.022. ISSN 0378-8741. PMID 17055201.
- ^ New cytotoxic prenylated isoflavonoids from Bituminaria morisiana. Cottiglia Filippo, Casu Laura, Bonsignore Leonardo, Casu Mariano, Floris Costantino, Leonti Marco, Gertsch Juerg and Heilmann Jörg, Planta medica 71 (3) (2005), pp. 254–260
- ^ Zimmermann, M. Carla; Tilghman, Syreeta L.; Boué, Stephen M.; Salvo, Virgilio A.; Elliott, Steven; et al. (1 October 2009). "Glyceollin I, a Novel Antiestrogenic Phytoalexin Isolated from Activated Soy". Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. American Society for Pharmacology & Experimental Therapeutics (ASPET). 332 (1): 35–45. doi:10.1124/jpet.109.160382. ISSN 0022-3565. PMC 2802480. PMID 19797619.
- ^ Cotrim, Gustavo dos Santos; Silva, Deivid Metzker da; Graça, José Perez da; Oliveira Junior, Adilson de; Castro, Cesar de; Zocolo, Guilherme Julião; Lannes, Lucíola Santos; Hoffmann-Campo, Clara Beatriz (2023). "Glycine max (L.) Merr. (Soybean) metabolome responses to potassium availability". Phytochemistry. 205: 113472. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2022.113472. ISSN 0031-9422. PMID 36270412. S2CID 253027906.
- ^ Matsuura, Nobuyasu; Nakai, Rie; Iinuma, Munekazu; Tanaka, Toshiyuki; Inoue, Kenichro (1994). "A prenylated flavanone from roots of Maackia amurensis subsp. Buergeri". Phytochemistry. Elsevier BV. 36 (1): 255–256. doi:10.1016/s0031-9422(00)97051-1. ISSN 0031-9422.
- ^ Leonti, Marco; Casu, Laura; Gertsch, Jürg; Bonsignore, Leonardo; Floris, Costantino; Casu, Mariano; Cottiglia, Filippo (18 March 2010). "A pterocarpan from the seeds of Bituminaria morisiana". Journal of Natural Medicines. Springer Science and Business Media LLC. 64 (3): 354–357. doi:10.1007/s11418-010-0408-7. ISSN 1340-3443. PMID 20238177. S2CID 19190934.
- ^ Tanaka, Hitoshi; Tanaka, Toshihiro; Etoh, Hideo (1997). "A pterocarpan from Erythrina orientalis". Phytochemistry. Elsevier BV. 45 (1): 205–207. doi:10.1016/s0031-9422(96)00841-2. ISSN 0031-9422.
- ^ Blagrove, R. J.; Colman, P. M.; Lilley, G. G.; Van Donkelaar, A.; Suzuki, E. (1983). "Physicochemical and structural studies of phaseolin from French bean seed". Plant Foods for Human Nutrition. Springer Science and Business Media LLC. 33 (2–3): 227–229. doi:10.1007/bf01091313. ISSN 0921-9668.
- ^ PERRIN, DAWN R.; BOTTOMLEY, W. (1961). "Pisatin: an Antifungal Substance from Pisum sativum L.". Nature. Springer Science and Business Media LLC. 191 (4783): 76–77. doi:10.1038/191076a0. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 13734533. S2CID 433477.
- ^ Manjary, Frédéric; Petitjean, Alain; Conan, Jean-Yves; Thérèse Martin, Marie; Frappier, François; Rasoanaivo, Philippe; Ratsimamanga-Urverg, Suzanne (1993). "A prenylated pterocarpan from Mundulea striata". Phytochemistry. Elsevier BV. 33 (2): 515–517. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(93)85554-5. ISSN 0031-9422.
External links
- Superpathway of pterocarpan biosynthesis (via formononetin) on metacyc.org
- Pterocarpans on the Comparative Toxicogenomics Database
