| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
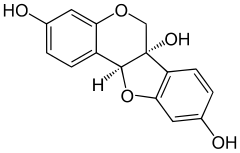
(6aS,11aS)-6H-[1]Benzofuro[3,2-c][1]benzopyran-3,6a,9(11aH)-triol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H12O5 | |
| Molar mass | 272.25 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Glycinol is a pterocarpan, a type of natural phenol. It is a phytoalexin found in the soybean (Glycine max). It is formed by the cyclisation of daidzein.[citation needed]
More recent literature supports that glycinol has potent phytoestrogenic activity.[1][2]
The so-called osteogenesis that is causes is postulated to be a preventative factor for osteoporosis.[citation needed]
It can be synthethised chemically and possesses two chiral centers.[3]
Glycinol is the direct precursor of glyceollins through the action of a prenyltransferase.[citation needed]
Experiments show that the 6a oxygen of glycinol is derived from molecular oxygen.[4]
References
- ^ Boué, Stephen M.; Tilghman, Syreeta L.; Elliott, Steven; Zimmerman, M. Carla; Williams, K. Y.; Payton-Stewart, Florastina; Miraflor, Allen P.; Howell, Melanie H.; Shih, Betty Y.; Carter-Wientjes, Carol H.; Segar, Chris; Beckman, Barbara S.; Wiese, Thomas E.; Cleveland, Thomas E.; McLachlan, John A.; Burow, Matthew E. (2009). "Identification of the Potent Phytoestrogen Glycinol in Elicited Soybean (Glycine max)". Endocrinology. 150 (5): 2446–2453. doi:10.1210/en.2008-1235. ISSN 0013-7227. PMC 2671905. PMID 19116342.
- ^ Strong, Amy L; Jones, Robert B; Glowacki, Julie; Boue, Stephen M; Burow, Matthew E; Bunnell, Bruce A (2017). "Glycinol enhances osteogenic differentiation and attenuates the effects of age on mesenchymal stem cells". Regenerative Medicine. 12 (5): 513–524. doi:10.2217/rme-2016-0148. ISSN 1746-0751. PMID 28718749.
- ^ Luniwal Amarjit; Khupse Rahul S; Reese Michael; Lei Fang; Erhardt Paul W (2009). "Total Syntheses of Racemic and Natural Glycinol". Journal of Natural Products. 72 (11): 2072–2075. doi:10.1021/np900509f. PMID 19943626.
- ^ Matthews, David E.; Plattner, Ronald D.; Vanetten, Hans D. (1989). "The 6a oxygen of the pterocarpan glycinol is derived from molecular oxygen". Phytochemistry. 28 (1): 113–115. Bibcode:1989PChem..28..113M. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(89)85020-4.
