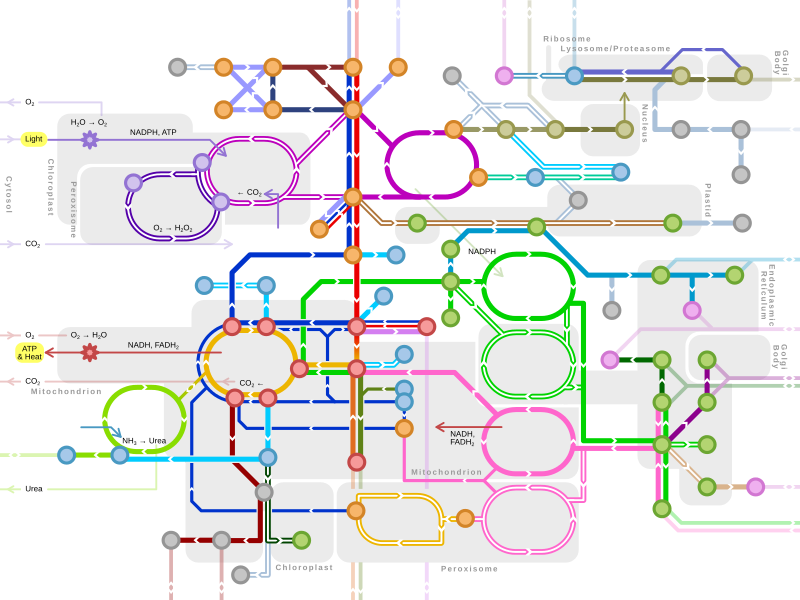
A metabolic network is the complete set of metabolic and physical processes that determine the physiological and biochemical properties of a cell. As such, these networks comprise the chemical reactions of metabolism, the metabolic pathways, as well as the regulatory interactions that guide these reactions.
With the sequencing of complete genomes, it is now possible to reconstruct the network of biochemical reactions in many organisms, from bacteria to human. Several of these networks are available online: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG),[1] EcoCyc,[2] BioCyc[3] and metaTIGER.[4] Metabolic networks are powerful tools for studying and modelling metabolism.
Single lines: pathways common to most lifeforms. Double lines: pathways not in humans (occurs in e.g. plants, fungi, prokaryotes). |
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/5Views:1 264 6061 271 044782 9385 35792 629
-
Urinary System, part 1: Crash Course A&P #38
-
Atomic Hook-Ups - Types of Chemical Bonds: Crash Course Chemistry #22
-
Respiratory System, part 2: Crash Course A&P #32
-
17. Logic Modeling of Cell Signaling Networks
-
Universal Mathematics: All Life on Earth Is Bound by One Spooky Algorithm | Geoffrey West
Transcription
Uses
Metabolic networks can be used to detect comorbidity patterns in diseased patients.[5] Certain diseases, such as obesity and diabetes, can be present in the same individual concurrently, sometimes one disease being a significant risk factor for the other disease.[6] The disease phenotypes themselves are normally the consequence of the cell's inability to breakdown or produce an essential substrate. However, an enzyme defect at one reaction may affect the fluxes of other subsequent reactions. These cascading effects couple the metabolic diseases associated with subsequent reactions resulting in comorbidity effects. Thus, metabolic disease networks can be used to determine if two disorders are connected due to their correlated reactions.[5]
See also
References
- ^ "GenomeNet". www.genome.ad.jp. Archived from the original on 2009-02-24. Retrieved 2020-04-01.
- ^ "EcoCyc: Encyclopedia of E. coli Genes and Metabolic Pathways". www.ecocyc.org.
- ^ "BioCyc Pathway/Genome Database Collection". biocyc.org.
- ^ "metaTIGER - Home". www.bioinformatics.leeds.ac.uk. Archived from the original on 2012-03-04. Retrieved 2010-06-09.
- ^ a b Lee, D.- S.; Park, J.; Kay, K. A.; Christakis, N. A.; Oltvai, Z. N.; Barabasi, A.- L. (2008). "The implications of human metabolic network topology for disease comorbidity". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 105 (29): 9880–9885. doi:10.1073/pnas.0802208105. PMC 2481357. PMID 18599447.
- ^ Ross, R.; Dagnone, D.; Jones, P. J.; Smith, H.; Paddags, A.; Hudson, R.; Janssen, I. (2000). "Reduction in obesity and related comorbid conditions after diet-induced weight loss or exercise-induced weight loss in men. A randomized, controlled trial". Annals of Internal Medicine. 133 (2): 92–103. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-133-2-200007180-00008. PMID 10896648. S2CID 13415272.