| External globus pallidus | |
|---|---|
 External globus pallidus (GPe) seen in 2nd image from the left | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Globus pallidus |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | globus pallidus externus, globus pallidus lateralis |
| Acronym(s) | GPe |
| NeuroNames | 232 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1610 |
| TA98 | A14.1.09.509 |
| TA2 | 5570 |
| FMA | 61839 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The external globus pallidus (GPe or lateral globus pallidus) combines with the internal globus pallidus (GPi) to form the globus pallidus, an anatomical subset of the basal ganglia. Globus pallidus means "pale globe" in Latin, indicating its appearance. The external globus pallidus is the segment of the globus pallidus that is relatively further (lateral) from the midline of the brain.
The GPe GABAergic neurons, allow for its inhibitory function and projects axons to the subthalamic nucleus (in the diencephalon), the striatum, internal globus pallidus (GPi) and substantia nigra pars reticulata.[1]
The GPe is particular in comparison to the other elements of the set by the fact that it does not work as an output base of the basal ganglia (not sending axons to the thalamus) but as the main regulator of the basal ganglia system. It is sometimes used as a target for deep brain stimulation as a treatment for Parkinson's disease.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/5Views:2 827113 40244 821291 141442 769
-
Globus pallidus
-
Basal Ganglia Indirect Pathway
-
Memorize Basal Ganglia In 3 minutes
-
Neurology | Basal Ganglia Anatomy & Function | Direct & Indirect Pathways
-
The basal ganglia - The direct pathway | Nervous system diseases | NCLEX-RN | Khan Academy
Transcription
Function
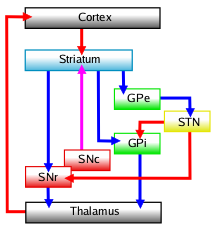
Indirect pathway
The basal ganglia functions to tonically inhibit movement, mainly in the absence of motor cortex command, via GABAergic inhibition of the ventral lateral nucleus and ventral anterior nucleus of the thalamus, as well as the superior colliculus and mesopontine tegmentum of the brain stem. When movement is required, the cerebral cortex sends commands to the striatum, which directly inhibits the medial globus pallidus and substantia nigra pars reticulata, decreasing thalamus and brainstem inhibition.[1] As the pathway from the striatum to the medial globus pallidus is monosynaptic (containing one synapse), it is called the direct pathway.
The indirect pathway, which contains the GPe and the subthalamic nucleus, functions to modulate the effects of the direct pathway. The GPe acts as an inhibitory "control device", adjusting subthalamic nucleus neuronal activity via GABAergic output.[2]
When movement adjustment is required, striatal inhibitory GABAergic axons are sent to the GPe, decreasing inhibition of the subthalamic nucleus. The subthalamic nucleus' glutamatergic neurons then stimulate the GPi and substantia nigra pars reticulata.
This multisynaptic indirect striatopallidal pathway allows for regulated excitatory input from the subthalamic nucleus to the GPi and substantia nigra pars reticulata. This combines with direct pathway inhibition in the GPi, allowing for fine tuned basal ganglia output, and more controlled movement.
Related pathology
Lateral globus pallidus dysfunction has been observed in the following conditions:
References
- ^ a b Parent, André; Hazrati, Lili-Naz (1995-01-01). "Functional anatomy of the basal ganglia. I. The cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical loop". Brain Research Reviews. 20 (1): 91–127. doi:10.1016/0165-0173(94)00007-C. PMID 7711769. S2CID 28252990.
- ^ Parent, André; Hazrati, Lili-Naz (1995-01-01). "Functional anatomy of the basal ganglia. II. The place of subthalamic nucleus and external pallidium in basal ganglia circuitry". Brain Research Reviews. 20 (1): 128–154. doi:10.1016/0165-0173(94)00008-D. PMID 7711765. S2CID 20808851.
- ^ Hegeman, Daniel J.; Hong, Ellie S.; Hernández, Vivian M.; Chan, C. Savio (2016-05-01). "The external globus pallidus: progress and perspectives". European Journal of Neuroscience. 43 (10): 1239–1265. doi:10.1111/ejn.13196. ISSN 1460-9568. PMC 4874844. PMID 26841063.
