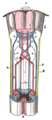
| Anterior corticospinal tract | |
|---|---|
 Anterior corticospinal tract seen in red at bottom center in figure (text tag found at upper-left). | |
 Decussation of pyramids. Scheme showing passage of various fasciculi from medulla spinalis to medulla oblongata. a. Pons. b. Medulla oblongata. c. Decussation of the pyramids. d. Section of cervical part of medulla spinalis. 1. Anterior cerebrospinal fasciculus (in red). 2. Lateral cerebrospinal fasciculus (in red). 3. Dorsal column tracts (gracile fasciculus and cuneate fasciculus) (in blue). 3’. Gracile and cuneate nuclei. 4. Anterolateral corticospinal tract (in dotted line). 5. Pyramid. 6. Lemniscus. 7. Medial longitudinal fasciculus. 8. Ventral spinocerebellar fasciculus (in blue). 9. Dorsal spinocerebellar fasciculus (in yellow). | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | tractus corticospinalis anterior, fasciculus cerebrospinalis anterior |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1618 |
| TA98 | A14.1.02.205 |
| TA2 | 6112 |
| FMA | 72636 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The anterior corticospinal tract (also called the ventral corticospinal tract, "Bundle of Turck", medial corticospinal tract, direct pyramidal tract, or anterior cerebrospinal fasciculus) is a small bundle of descending fibers that connect the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord. Descending tracts are pathways by which motor signals are sent from upper motor neurons in the brain to lower motor neurons which then directly innervate muscle to produce movement. The anterior corticospinal tract is usually small, varying inversely in size with the lateral corticospinal tract, which is the main part of the corticospinal tract.
It lies close to the anterior median fissure, and is present only in the upper part of the spinal cord; gradually diminishing in size as it descends, it ends about the middle of the thoracic region.
It consists of descending fibers that arise from cells in the motor area of the ipsilateral cerebral hemisphere. The impulse travels from these upper motor neurons (located in the pre-central gyrus of the brain) through the anterior column. In contrast to the fibers for the lateral corticospinal tract, the fibers for the anterior corticospinal tract do not decussate at the level of the medulla oblongata, although they do cross over in the spinal level they innervate.[1] They then synapse at the anterior horn with the lower motor neuron which then synapses with the target muscle at the motor end plate. In contrast to the lateral corticospinal tract which controls the movement of the limbs, the anterior corticospinal tract controls the movements of axial muscles (of the trunk).
A few of its fibers pass to the lateral column of the same side and to the gray matter at the base of the posterior grey column.[citation needed]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/5Views:252 37411 4333 712402 403259 221
-
Neuroanatomy - The Corticospinal Tract in 3D
-
Neuroanatomy - Corticospinal Tract (USMLE)
-
Descending pathways - corticospinal tract
-
Neurology - Motor Pathways
-
Spinal Pathways/Tracts - Part 1 - Introduction - Anatomy Tutorial
Transcription
Additional images
-
Decussation of pyramids.
-
The motor tract.
References
- ^ Berthold, Daniel Goude, C.-H. "Pyramidbanans främre okorsade del - Tractus cortico-spinalis anterior - Människans nervsystem: Uppslagsverk". nervsystemet.se.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Saladin, Kenneth S. "The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Somatic Reflexes." Anatomy & Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function. 6th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2012. N. pag. Print.
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 759 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 759 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- hier-799 at NeuroNames
- Overview at thebrain.mcgill.ca
- http://teachmeanatomy.info/neuro/pathways/descending-tracts-motor/