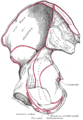
| Sphincter urethrae membranaceae muscle | |
|---|---|
 The male urethra laid open on its anterior (upper) surface. (Region visible, but muscle not labeled.) | |
 Coronal section of anterior part of pelvis, through the pubic arch. Seen from in front. (Region visible, but muscle not labeled.) | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Junction of the inferior rami of the pubis and ischium to the extent of 1.25 to 2 cm. |
| Insertion | Ischiopubic rami |
| Nerve | Somatic fibers from S2-S4 through pudendal nerve |
| Actions | Constricts urethra, maintains urinary continence |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus sphincter urethrae externus urethrae masculinae, musculus sphincter urethrae membranaceae |
| TA98 | A09.4.02.016M |
| TA2 | 2421 |
| FMA | 19733 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The external sphincter muscle of male urethra, also sphincter urethrae membranaceae, sphincter urethrae externus, surrounds the whole length of the membranous urethra, and is enclosed in the fascia of the urogenital diaphragm.
Its external fibers arise from the junction of the inferior pubic ramus and ischium to the extent of 1.25 to 2 cm., and from the neighboring fascia.
They arch across the front of the urethra and bulbourethral glands, pass around the urethra, and behind it unite with the muscle of the opposite side, by means of a tendinous raphe.
Its innermost fibers form a continuous circular investment for the membranous urethra.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:83 681108 61189 845
-
Micturition Reflex - Neural Control of Urination Animation Video.
-
Urinary Incontinence in Men, Animation
-
Male pelvis and perineum - plastic model
Transcription
Neural control of urination - micturition reflex. When the bladder is full, stretch receptors in the wall of the bladder send nerve impulses to the sacral region of the spinal cord. By way of a parasympathetic response, signals return to the bladder and stimulate contraction of the muscle of the bladder and relaxation of the internal urethral sphincter. This part of the reflex is involuntary and is predominant in infants and young children. As the central nervous system matures, it acquires voluntary control over the external urethral sphincter. Urination is controlled mainly by the micturition center in the pons. This center receives sensory signals from the bladder and communicates with the cortex about the appropriateness of urinating at the moment. At times when it's not convenient to urinate, the center sends back an inhibitory signal to keep the sphincters closed and prevent voiding. When you wish to urinate, this inhibition is removed; the spinal cord instructs the muscle of the bladder to contract and the sphincters to open to let the urine out.
Function
The muscle helps maintain continence of urine along with the internal urethral sphincter which is under control of the autonomic nervous system. The external sphincter muscle prevents urine leakage as the muscle is tonically contracted via somatic fibers that originate in Onuf's nucleus and pass through sacral spinal nerves S2-S4 then the pudendal nerve to synapse on the muscle.[1][2]
Voiding urine begins with voluntary relaxation of the external urethral sphincter. This is facilitated by inhibition of the somatic neurons in Onuf's nucleus via signals arising in the pontine micturition center and traveling through the descending reticulospinal tracts. During ejaculation, the external sphincter opens and the internal sphincter closes.[3]
Additional images
-
Right hip bone. Internal surface.
See also
- Levator ani
- External sphincter muscle of female urethra
- Internal urethral sphincter
- Prostatic urethra
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 429 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 429 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Jung J, Ahn HK, and Huh Y (September 2012). "Clinical and Functional Anatomy of the Urethral Sphincter". Int Neurourol J. 16 (3): 102–106. doi:10.5213/inj.2012.16.3.102. PMC 3469827. PMID 23094214.
- ^ Shah AP, Mevcha A, Wilby D, Alatsatianos A, Hardman JC, Jacques S, Wilton JC (November 2014). "Continence and micturition: An anatomical basis" (PDF). Clin. Anat. 27 (8): 1275–1283. doi:10.1002/ca.22388. PMID 24615792. S2CID 21875132.
- ^ J. B. Macalpine (November 1934). "The Musculature of the Bladder-neck of the Male in Health and Disease". Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine. 28 (1): 39–56. doi:10.1177/003591573402800112. PMC 2205523. PMID 19990023.
External links
- Anatomy figure: 41:06-04 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Muscles of the female urogenital diaphragm (deep perineal pouch) and structures located inferior to it."