| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Americium(III) chloride
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Americium(3+) chloride | |
| Other names
Americium chloride
Americium trichloride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| AmCl3 | |
| Molar mass | 349 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Light red, opaque crystals |
| Density | 5.87 g cm−3[1] |
| Melting point | 715 °C (1,319 °F; 988 K)[2] |
| Boiling point | 850 °C (1,560 °F; 1,120 K)[1] |
| Structure | |
| hexagonal (UCl3 type), hP8 | |
| P63/m, No. 176 | |
| Tricapped trigonal prismatic (nine-coordinate) | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Americium(III) fluoride Americium(III) bromide Americium(III) iodide |
Other cations
|
Plutonium(III) chloride Curium(III) chloride Europium(III) chloride |
| Americium(II) chloride | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
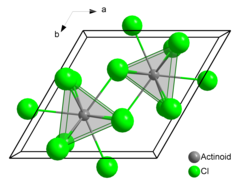
Americium(III) chloride or americium trichloride is the chemical compound composed of americium and chlorine with the formula AmCl3. This salt forms pink hexagonal crystals. In the solid state each americium atom has nine chlorine atoms as near neighbours, at approximately the same distance, in a tricapped trigonal prismatic configuration.[3][4]
The hexahydrate has a monocline crystal structure with: a = 970.2 pm, b = 656.7 pm and c = 800.9 pm; β = 93° 37'; space group: P2/n.[5]
Reactions
An americium(III) chloride electrorefining method has been investigated to separate mixtures of actinides, since the standard Gibbs free energy of formation of americium(III) chloride is much different than the rest of the actinide chlorides.[6] This can be used to remove americium from plutonium by melting the crude mixture together with salts such as sodium chloride.[7]
References
- ^ a b "Chemistry: Periodic Table: americium: compound data (americium (III) chloride)". WebElements. Retrieved 2008-06-24.
- ^ Perry, Dale L.; Phillips, Sidney L. (1995), Handbook of Inorganic Compounds, CRC Press, p. 15, ISBN 0-8493-8671-3, retrieved 2008-06-25
- ^ L. B. Asprey, T. K. Keenan, F. H. Kruse: "Crystal Structures of the Trifluorides, Trichlorides, Tribromides, and Triiodides of Americium and Curium", Inorg. Chem. 1965, 4 (7), 985–986; doi:10.1021/ic50029a013.
- ^ A. F. Wells: Structural Inorganic Chemistry 5th edition (1984) Oxford Science Publications, ISBN 0-19-855370-6.
- ^ John H. Burns, Joseph Richard Peterson: "The Crystal Structures of Americium Trichloride Hexahydrate and Berkelium Trichloride Hexahydrate", Inorg. Chem. 1971, 10 (1), 147–151; doi:10.1021/ic50095a029.
- ^ Nuclear Energy Agency (2001), Proceedings of the Workshop on Pyrochemical Separations, Avignon, France: OECD Publishing, pp. 276–277, ISBN 92-64-18443-0, retrieved 2008-06-24
- ^ Plutonium Processing In The Nuclear Weapons Complex, Diane Publishing, 1992, p. 21, ISBN 1-56806-568-X, retrieved 2008-06-24
