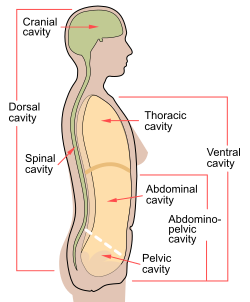
In anatomy, the abdominal wall represents the boundaries of the abdominal cavity. The abdominal wall is split into the anterolateral and posterior walls.[1]
There is a common set of layers covering and forming all the walls: the deepest being the visceral peritoneum, which covers many of the abdominal organs (most of the large and small intestines, for example), and the parietal peritoneum—which covers the visceral peritoneum below it, the extraperitoneal fat, the transversalis fascia, the internal and external oblique and transversus abdominis aponeurosis, and a layer of fascia, which has different names according to what it covers (e.g., transversalis, psoas fascia).[2]
In medical vernacular, the term 'abdominal wall' most commonly refers to the layers composing the anterior abdominal wall which, in addition to the layers mentioned above, includes the three layers of muscle: the transversus abdominis (transverse abdominal muscle), the internal (obliquus internus) and the external oblique (obliquus externus).[1][2][3]
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/3Views:244 597369 71028 703
-
Layers of the Abdominal Wall
-
Muscles of the Anterior Abdominal Wall - 3D Anatomy Tutorial
-
Layers of the Abdominal Wall – Anatomy | Medical Education Videos
Transcription
Structure
The contour of abdominal wall is roughly hexagonal. Its superior border is bounded by the coastal margins, lateral borders by mid-axillary lines, and inferior borders bounded by the anterior half of the iliac crest, inguinal ligaments, pubic crest, and pubic symphysis.[4]
Layers
In human anatomy, the layers of the anterolateral abdominal wall are (from superficial to deep):[1][2]
- Skin
- Subcutaneous tissue
- Fascia
- Camper's fascia - fatty superficial layer.
- Scarpa's fascia - deep fibrous layer.
- Superficial abdominal fascia
- Muscle
- Transversalis fascia
- Extraperitoneal fat
- Peritoneum
Inner surface
The surface contains several ligaments separated by fossae:[5]
| Ligament/fold | Remnant of | Lateral fossa | Hernia |
| median umbilical ligament | urachus | supravesical fossa | supravesical hernia (rare) |
| medial umbilical ligament | umbilical artery | medial inguinal fossa | direct inguinal hernia |
| lateral umbilical fold | inferior epigastric vessels | lateral inguinal fossa | indirect inguinal hernia |
See also
References
- ^ a b c Moore, Keith L.; Dalley, Arthur F.; Agur, Anne M.R. (2014). Clinically Oriented Anatomy. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 180–186. ISBN 978-1-4511-1945-9.
- ^ a b c Drake, Richard L.; Vogl, A. Wayne; Mitchell, Adam W. M. (2015). Gray's Anatomy For Students. Philadelphia, PA: Churchill Livingstone. pp. 259–260. ISBN 978-0-7020-5131-9.
- ^ "Duke Anatomy - Lab 5: Anterior Abdominal Body Wall & Abdominal Viscera". web.duke.edu. Retrieved 2019-09-02.
- ^ Mahadevan, Vishy (June 2009). "Anatomy of the anterior abdominal wall and groin". Surgery (Oxford). 27 (6): 251–254. doi:10.1016/j.mpsur.2009.03.002.
- ^ "Morphologic Variations of the Umbilical Ring, Umbilical Ligaments and Ligamentum Teres Hepatis". ResearchGate. Retrieved 2019-09-02.
External links
- skel&wallsabd at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) - "Skeleton of the Abdomen", Wesley Norman, PhD, DSc
- Abdominal+Wall at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Anterolateral Abdominal Wall Archived 2004-06-11 at the Wayback Machine - University of Edinburgh Faculty of Medicine
- Muscles of the Anterior Abdominal Wall Archived 2011-07-09 at the Wayback Machine - University of Arkansas
- YouTube video of abdominal wall form Colorectal Disease Journal