 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H23NO5 |
| Molar mass | 381.428 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
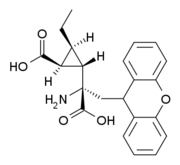
CECXG (3'-ethyl-LY-341,495) is a research drug which acts as a potent and selective antagonist for the group II metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR2/3), with reasonable selectivity for mGluR3. While it is some five times less potent than LY-341,495 at mGluR3, it has 38x higher affinity for mGluR3 over mGluR2,[1] making it one of the few ligands available that is able to distinguish between these two closely related receptor subtypes.[2][3][4]
References
- ^ Collado I, Ezquerra J, Mazón A, Pedregal C, Yruretagoyena B, Kingston AE, et al. (October 1998). "2,3'-disubstituted-2-(2'-carboxycyclopropyl)glycines as potent and selective antagonists of metabotropic glutamate receptors". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 8 (20): 2849–2854. doi:10.1016/S0960-894X(98)00510-1. PMID 9873635.
- ^ Schoepp DD, Jane DE, Monn JA (2002). "Pharmacology of metabotropic glutamate receptors". In Egebjerg J, Krogsgaard-Larsen P, Schousboe A (eds.). Glutamate and GABA receptors and transporters: structure, function and pharmacology. Taylor & Francis. pp. 171–173. ISBN 0-7484-0881-9.
- ^ Sørensen US, Bleisch TJ, Kingston AE, Wright RA, Johnson BG, Schoepp DD, Ornstein PL (January 2003). "Synthesis and structure-activity relationship studies of novel 2-diarylethyl substituted (2-carboxycycloprop-1-yl)glycines as high-affinity group II metabotropic glutamate receptor ligands". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 11 (2): 197–205. doi:10.1016/S0968-0896(02)00387-5. PMID 12470714.
- ^ Ure J, Baudry M, Perassolo M (August 2006). "Metabotropic glutamate receptors and epilepsy". Journal of the Neurological Sciences. 247 (1): 1–9. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2006.03.018. PMID 16697014. S2CID 22777207.
