| Prunasina | ||
|---|---|---|
 | ||
| Nombre IUPAC | ||
| (2R)-2-phenyl-2-[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-9(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxyacetonitrile | ||
| General | ||
| Otros nombres |
(R)-Prunasin D-Prunasin D-Mandelonitrile-beta-D-glucoside | |
| Fórmula estructural |
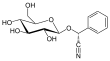 | |
| Fórmula molecular | C14H17NO6 | |
| Identificadores | ||
| Número CAS | 99-18-3[1] | |
| ChEBI | 17396 | |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1778417 | |
| ChemSpider | 106360 | |
| PubChem | 119033 | |
| UNII | 14W4BPM5FB | |
| KEGG | C00844 | |
|
C1=CC=C(C=C1)[C@H](C#N)O[C@H]2[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O2)CO)O)O)O
| ||
| Propiedades físicas | ||
| Masa molar | 295,29 g/mol | |
| Valores en el SI y en condiciones estándar (25 ℃ y 1 atm), salvo que se indique lo contrario. | ||
La prunasina es un glucósido cianogénico. Químicamente, es el glucósido del mandelonitrilo.
Es un compuesto quiral. Su enantiómero (R)-prunasina se encuentra en las partes verdes y el endocarpio del fruto de las plantas del género Prunus;[2] en estos, la prunasina es un intermediario en la biosíntesis de la amigdalina.[3] También la contienen las partes verdes de varias especies del género Olinia y Acacia.[4]
También se encuentra en un sucedáneo del café preparado con las raíces tostadas del diente de león.[5]
Metabolismo
Prunasina beta-glucosidasa es una enzima que utiliza (R)-prunasin y H2O para producir D-glucose y mandelonitrile.
Amygdalin beta-glucosidase es una enzima que utiliza (R)-amigdalina y H2O para producir (R)-prunasina y D-glucosa.
Referencias
- ↑ Número CAS
- ↑ Sanchez-Perez, R.; Belmonte, F. S.; Borch, J.; Dicenta, F.; Møller, B. L.; Jørgensen, K. (2012). «Prunasin Hydrolases during Fruit Development in Sweet and Bitter Almonds». Plant Physiology 158 (4): 1916-32. PMC 3320195. PMID 22353576. doi:10.1104/pp.111.192021.
- ↑ Keeler, Richard F.; Tu, Anthony T. (30 de noviembre de 1983). Handbook of Natural Toxins (en inglés). CRC Press. p. 127. ISBN 978-0-8247-1893-0. Consultado el 11 de octubre de 2020.
- ↑ Nahrstedt, Adolf; Rockenbach, Jürgen (1993). «Occurrence of the cyanogenic glucoside prunasin and II corresponding mandelic acid amide glucoside in Olinia species (oliniaceae)». Phytochemistry 34 (2): 433. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(93)80024-M.
- ↑ «Human Metabolome Database: Showing metabocard for Prunasin (HMDB0034934)». hmdb.ca. Consultado el 11 de octubre de 2020.
Enlaces externos
- Esta obra contiene una traducción derivada de «Prunasin» de Wikipedia en inglés, publicada por sus editores bajo la Licencia de documentación libre de GNU y la Licencia Creative Commons Atribución-CompartirIgual 4.0 Internacional.
 Wikimedia Commons alberga una categoría multimedia sobre Prunasina.
Wikimedia Commons alberga una categoría multimedia sobre Prunasina.
