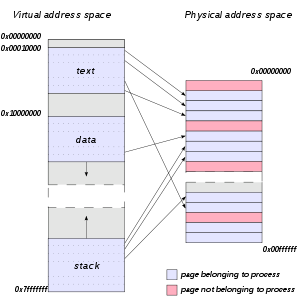
In computing, a virtual address space (VAS) or address space is the set of ranges of virtual addresses that an operating system makes available to a process.[1] The range of virtual addresses usually starts at a low address and can extend to the highest address allowed by the computer's instruction set architecture and supported by the operating system's pointer size implementation, which can be 4 bytes for 32-bit or 8 bytes for 64-bit OS versions. This provides several benefits, one of which is security through process isolation assuming each process is given a separate address space.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/5Views:2 30518 6121 1314032 744
-
An Introduction to Address Spaces
-
Address Space
-
VIRTUAL ADDRESS SPACE IN OPERATING SYSTEM
-
AZ 104 — Address Spaces
-
Virtual Memory | Address Space & Memory Space || Computer Organization and Architecture
Transcription
Example
- In the following description, the terminology used will be particular to the Windows NT operating system, but the concepts are applicable to other virtual memory operating systems.
When a new application on a 32-bit OS is executed, the process has a 4 GiB VAS: each one of the memory addresses (from 0 to 232 − 1) in that space can have a single byte as a value. Initially, none of them have values ('-' represents no value). Using or setting values in such a VAS would cause a memory exception.
0 4 GiB VAS |----------------------------------------------|
Then the application's executable file is mapped into the VAS. Addresses in the process VAS are mapped to bytes in the exe file. The OS manages the mapping:
0 4 GiB VAS |---vvv----------------------------------------| mapping ||| file bytes app
The v's are values from bytes in the mapped file. Then, required DLL files are mapped (this includes custom libraries as well as system ones such as kernel32.dll and user32.dll):
0 4 GiB VAS |---vvv--------vvvvvv---vvvv-------------------| mapping ||| |||||| |||| file bytes app kernel user
The process then starts executing bytes in the EXE file. However, the only way the process can use or set '-' values in its VAS is to ask the OS to map them to bytes from a file. A common way to use VAS memory in this way is to map it to the page file. The page file is a single file, but multiple distinct sets of contiguous bytes can be mapped into a VAS:
0 4 GiB VAS |---vvv--------vvvvvv---vvvv----vv---v----vvv--| mapping ||| |||||| |||| || | ||| file bytes app kernel user system_page_file
And different parts of the page file can map into the VAS of different processes:
0 4 GiB VAS 1 |---vvvv-------vvvvvv---vvvv----vv---v----vvv--| mapping |||| |||||| |||| || | ||| file bytes app1 app2 kernel user system_page_file mapping |||| |||||| |||| || | VAS 2 |--------vvvv--vvvvvv---vvvv-------vv---v------|
On Microsoft Windows 32-bit, by default, only 2 GiB are made available to processes for their own use.[2] The other 2 GiB are used by the operating system. On later 32-bit editions of Microsoft Windows, it is possible to extend the user-mode virtual address space to 3 GiB while only 1 GiB is left for kernel-mode virtual address space by marking the programs as IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE and enabling the /3GB switch in the boot.ini file.[3][4]
On Microsoft Windows 64-bit, in a process running an executable that was linked with /LARGEADDRESSAWARE:NO, the operating system artificially limits the user mode portion of the process's virtual address space to 2 GiB. This applies to both 32- and 64-bit executables.[5][6] Processes running executables that were linked with the /LARGEADDRESSAWARE:YES option, which is the default for 64-bit Visual Studio 2010 and later,[7] have access to more than 2 GiB of virtual address space: up to 4 GiB for 32-bit executables, up to 8 TiB for 64-bit executables in Windows through Windows 8, and up to 128 TiB for 64-bit executables in Windows 8.1 and later.[4][8]
Allocating memory via C's malloc establishes the page file as the backing store for any new virtual address space. However, a process can also explicitly map file bytes.
Linux
For x86 CPUs, Linux 32-bit allows splitting the user and kernel address ranges in different ways: 3G/1G user/kernel (default), 1G/3G user/kernel or 2G/2G user/kernel.[9]
See also
Notes
- ^ IBM Corporation. "What is an address space?". Retrieved August 24, 2013.
- ^ "Virtual Address Space". MSDN. Microsoft.
- ^ "LOADED_IMAGE structure". MSDN. Microsoft.
- ^ a b "4-Gigabyte Tuning: BCDEdit and Boot.ini". MSDN. Microsoft.
- ^ "/LARGEADDRESSAWARE (Handle Large Addresses)". MSDN. Microsoft.
- ^ "Virtual Address Space". MSDN. Microsoft.
- ^ "/LARGEADDRESSAWARE (Handle Large Addresses)". MSDN. Microsoft.
- ^ "/LARGEADDRESSAWARE (Handle Large Addresses)". MSDN. Microsoft.
- ^ "Linux kernel - x86: Memory split".
References
- "Advanced Windows" by Jeffrey Richter, Microsoft Press
