Τύρας | |
 Remains of Roman Tyras, near the medieval Genoese walls of the Maurocastro. | |
| Location | Bilhorod-Dnistrovskyi, Odesa Oblast, Ukraine |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 46°12′3″N 30°21′6″E / 46.20083°N 30.35167°E |
| Type | Settlement |
| History | |
| Builder | Settlers from Miletus |
| Founded | Approximately 600 BC |
| Abandoned | Late 4th century AD |
| Periods | Archaic Greek to Roman Imperial |
| Cultures | Greek, Roman |
| Site notes | |
| Condition | Ruined |
| Ownership | Public |
| Public access | Yes |
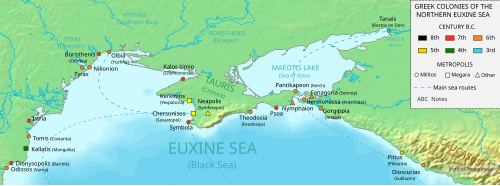
Tyras (Ancient Greek: Τύρας) was an ancient Greek city on the northern coast of the Black Sea. It was founded by colonists from Miletus, probably about 600 BC. The city was situated some 10 km from the mouth of the Tyras River, which is now called the Dniester. The surrounding native tribe was called the Tyragetae. The ruins of Tyras are now located in the modern city of Bilhorod-Dnistrovskyi in the Odesa Oblast of Ukraine.
YouTube Encyclopedic
-
1/1Views:408 281
-
Tyra's Hot Legs
Transcription
History
Of great importance in early times, in the 2nd century BC Tyras fell under the dominion of native kings whose names appear on its coins, and it was destroyed by the Getae about 50 BC.[1]
In 56 AD, it seems to have been restored by the Romans under Nero and henceforth formed part of the province of Lower Moesia. There exists a series of its coins with heads of emperors from Domitian to Alexander Severus.[1]
Indeed, the autonomous minting of coins in the city lasted from the time of the emperor Domitian (81 AD) up to the end of the reign of the emperor Alexander Severus (235 AD) with few breaks. The coins of Tyras of this period were of copper with the portraits of the members of the Imperial house for the province of the Roman Empire.
In Tyras was stationed a small unit of the Roman fleet, Classis Flavia Moesica.
Soon after the time of Alexander Severus, it was partially destroyed by the Goths, but archaeological findings show that Romans remained there until the end of the 4th century under Theodosius I. Later the Byzantines renamed the city, destroyed by barbarian invasions, with the new name Maurokastron, "black fort".
Its government was in the hands of five archons, a senate, a popular assembly and a registrar. The images on its coins suggest a trade in wheat, wine and fish. The few inscriptions are also mostly concerned with trade.[1]
Remains of the city are scant, as its site has been covered by the great medieval fortress called by the Genoese Maurocastro (and later Akkerman/Cetatea Albă).[1]
See also
References
- ^ a b c d Minns 1911.
- This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Minns, Ellis Hovell (1911). "Tyras". In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 27 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 548. This work in turn cites:
- E. H. Minns. Scythians and Greeks (Cambridge, 1909)
- V. V. Latyshev, Inscriptiones Orae Septentrionalis Ponti Euxini, Volume I.
Further reading
- Kleiman, I. B. (2001). "Defensive Structures on the Territory of Tyras". In Tsetskhladze, Gocha R. (ed.). North Pontic Archaeology: Recent Discoveries and Studies. Colloquia Pontica. Vol. 6. Leiden: Brill. pp. 53–66. ISBN 9789004120419.
- Karyshkovskij, Petr O.; Kleiman, Isaac B. (1994). The City of Tyras: A Historical and Archaeological Essay. Odesa: Polis Press. ISBN 9785770745313.


